Also called as Tongue Tie


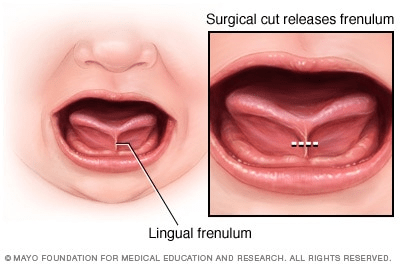
Source- textbook of oral pathology Shafers and Google images
Also called as Tongue Tie



Source- textbook of oral pathology Shafers and Google images
Also called as Tongue Hypertrophy, Prolapsus of the tongue, Enlarged Tongue and Pseudomacroglossia


Source- textbook of oral pathology Shafers and Google images


Source- textbook of oral pathology Shafers and Google images
Also called as Octocephaly, Holoproscencephaly Agnathia


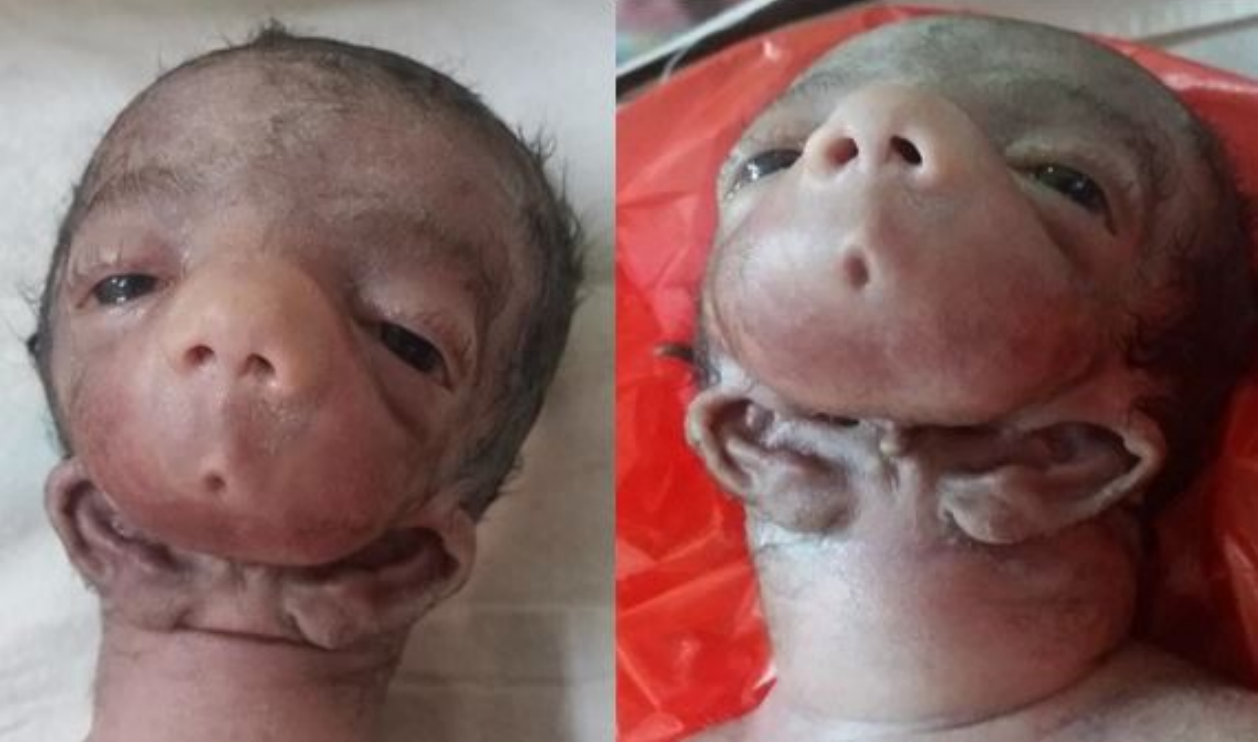
Source – textbook of oral pathology Shafers and Google images


General factors which would influence and tend to favour mandibular prognathism are as follows:
• Increased height of the ramus
• Increased mandibular body length
• Increased gonial angle
• Anterior positioning of the glenoid fossa
•Decreased maxillary length
• Posterior positioning of the maxilla in relation to the cranium
• Prominent chin button
•Varying soft-tissue contours
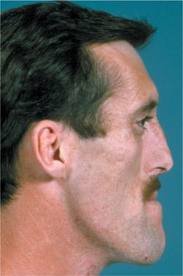
Source- textbook of oral pathology Shafers and Google images



Source- textbook of oral pathology Shafers and Google images
What is malaria ?
•Malaria is a life-threatening disease.
• It’s typically transmitted through the bite of an infected Anopheles mosquito.

•Infected mosquitoes carry the Plasmodium parasite.
•When this mosquito bites you, the parasite is released into your bloodstream.
•Once the parasites are inside your body, they travel to the liver, where they mature. After several days, the mature parasites enter the bloodstream and begin to infect red blood cells.
•Within 48 to 72 hours, the parasites inside the red blood cells multiply, causing the infected cells to burst open.
•The parasites continue to infect red blood cells, resulting in symptoms that occur in cycles that last two to three days at a time.
AREAS WHERE MALARIA IS FOUND –
Malaria is typically found in tropical and subtropical climates where the parasites can live.

Drugs used in malaria

Source – 1.textbook of pharmacology for dental students tara shanbhag
2. Healthline
3 pinterest and Google images





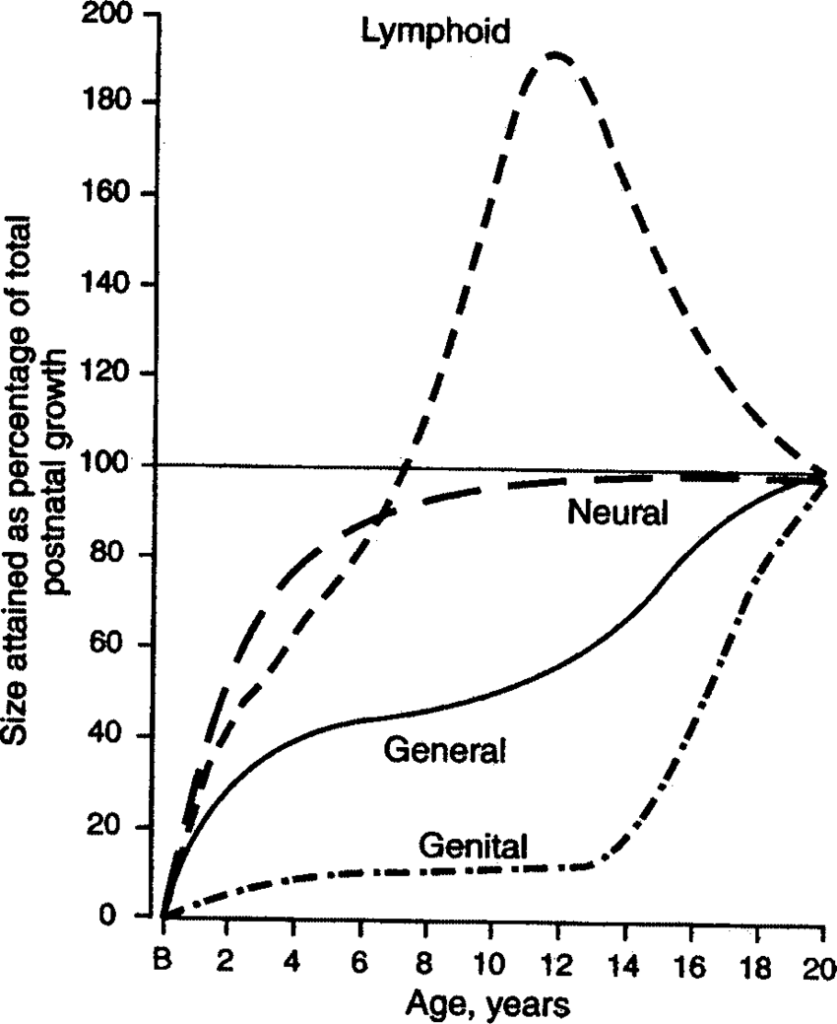







Source – Bhalajhi and Google images





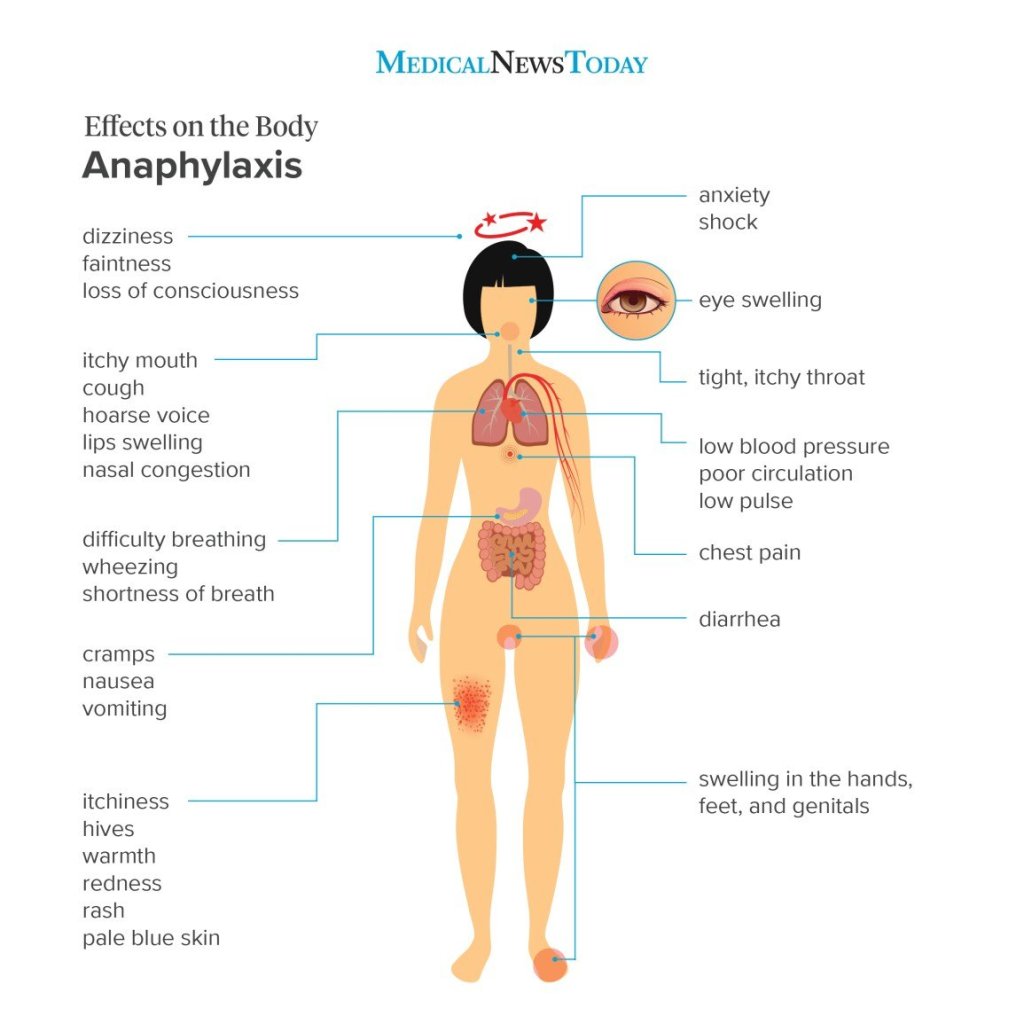




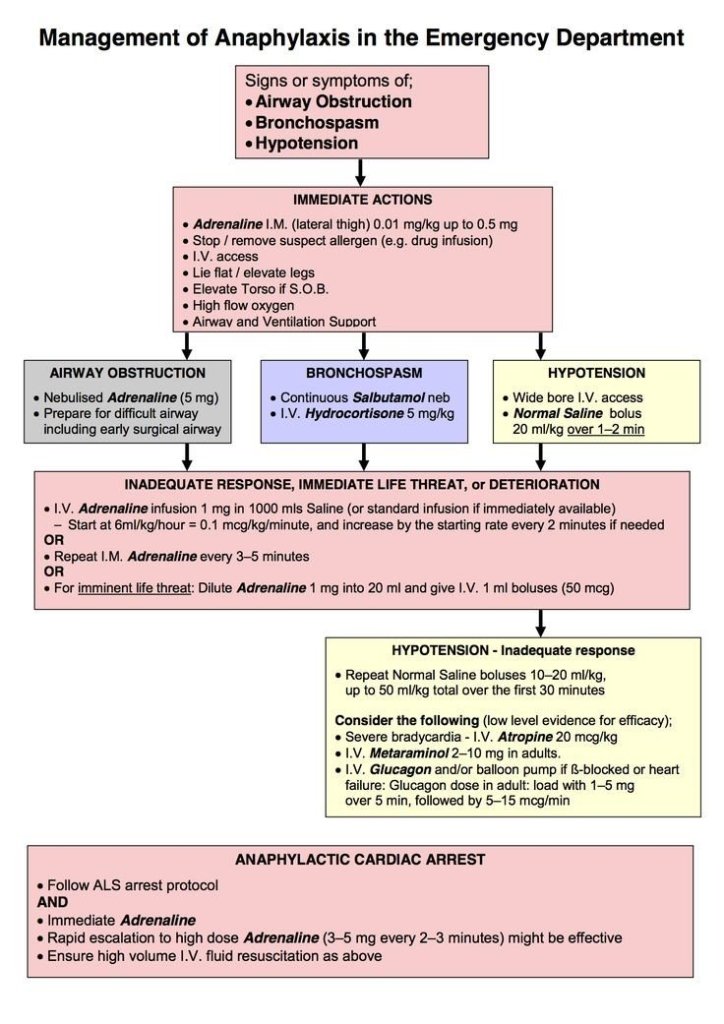
Source – Davidson’s clinical medicine and S. N Chugh and images – Google and pinterest
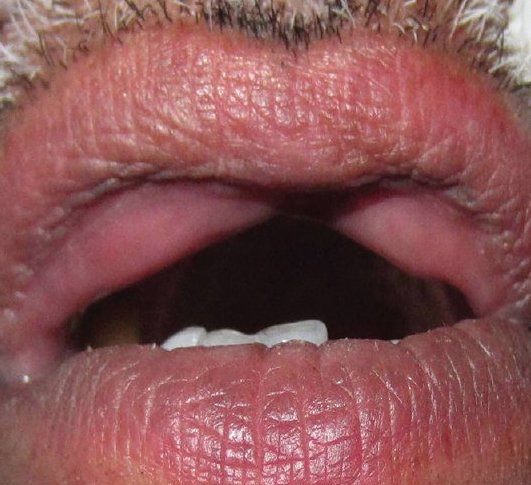
Double lip

Ascher syndrome


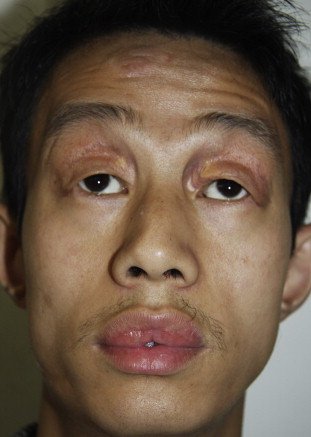
Source – textbook of oral pathology Shafers and Google images