source – don’t remember, had written it a lot time ago
Tag: Pathology
MULTIPLE MYELOMA
🔹Most common primary neoplasm of skeletal system.
- A disease of bone marrow
- A malignancy of plasma cells
- Monoclonal malignancies
🔹Clinical Features:
- Age: 60 – 65 years
- Sex: M>F
- Site: Vertebra, Ribs, Skull, Pelvis, Femur bone.
- Symptom: Bone pain (due to compression fractures)
- Signs:
- Lytic bone lesions
- Anemia
- Azotemia
- Hypercalcaemia
- Recurrent infection
🔹Oral Manifestations:
- Jaw: Mandible>Maxilla
- Site: Ramus & Angle of mandible at Molar area
- Signs:
- Intraosseous –
- Pain
- Swelling
- Numbness
- Mobility of teeth
- Extraosseous one’s resemble epulis/gingival enlargement.
🔹Radiographic features: Punched out areas
🔹 Lab. findings:
- Hyperglobulinemia
- Bence Jones protein in urine – Also seen in leukemia, polycythemia
- ⬆️ ESR
- ⬆️ Alkaline phosphatase
- Hyperuricemia
🔹Histological Features:
1. Cells are closely packed in large sheets..👇🏻
- Round/Ovoid
- Nuclei – eccentric placed
- Chromatin clumping in a cart wheel/checkerboard pattern
- Perinuclear halo (Golgi complexes)
2. Russell bodies: Russell bodies are multiple round cytoplasmic hyaline inclusions that are frequently seen in bone marrow aspirates in myeloma. They are composed of immunoglobulin molecules within vesicular structures derived from rough endoplasmic reticulum. Plasma cells containing them are sometimes referred to as Mott cells.
🔹Treatment:
- Bisphosphonate therapy
- Chemotherapy
References: Shafer’sTextbook Of Oral Pathology
Dr. Mehnaz Memon🖊
ORAL SUBMUCOUS FIBROSIS
DIFFERENCE BETWEEN INFECTED AND AFFECTED DENTIN
source – don’t remember, had written it a lot time ago
ADENOMATOID ODONTOGENIC TUMOR
source – don’t remember, had written it long back. , textbook – Shafers
APTHOUS ULCER
source – don’t remember, had written it long back. , textbook – Shafers
PEMPHIGUS
source – don’t remember, had written it long back. , textbook – Shafers
VERRUCOUS CARCINOMA
source – don’t remember, had written it long back. , textbook – Shafers
DENTIGEROUS CYST
source – don’t remember, had written it long back. , textbook – Shafers
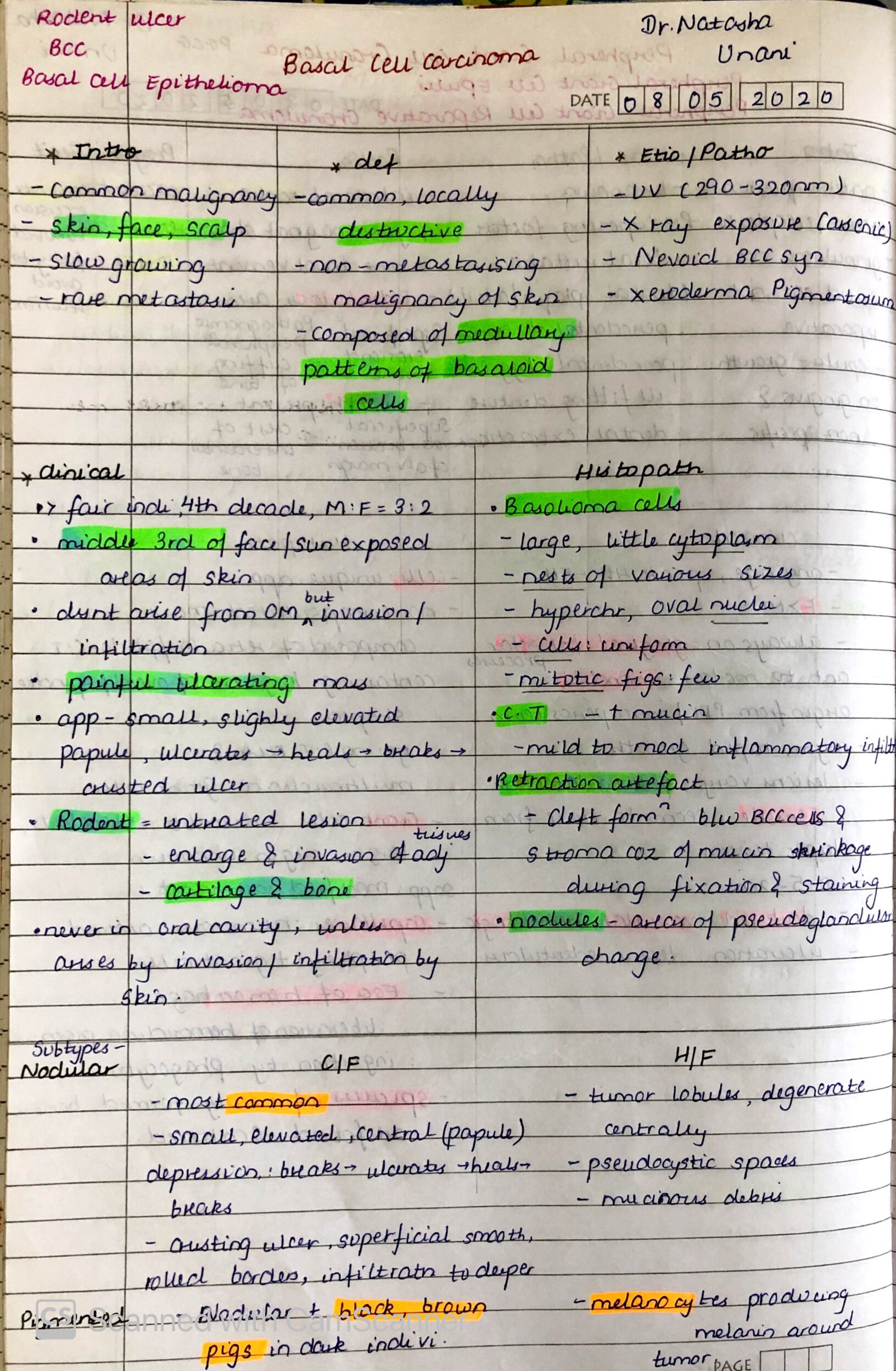
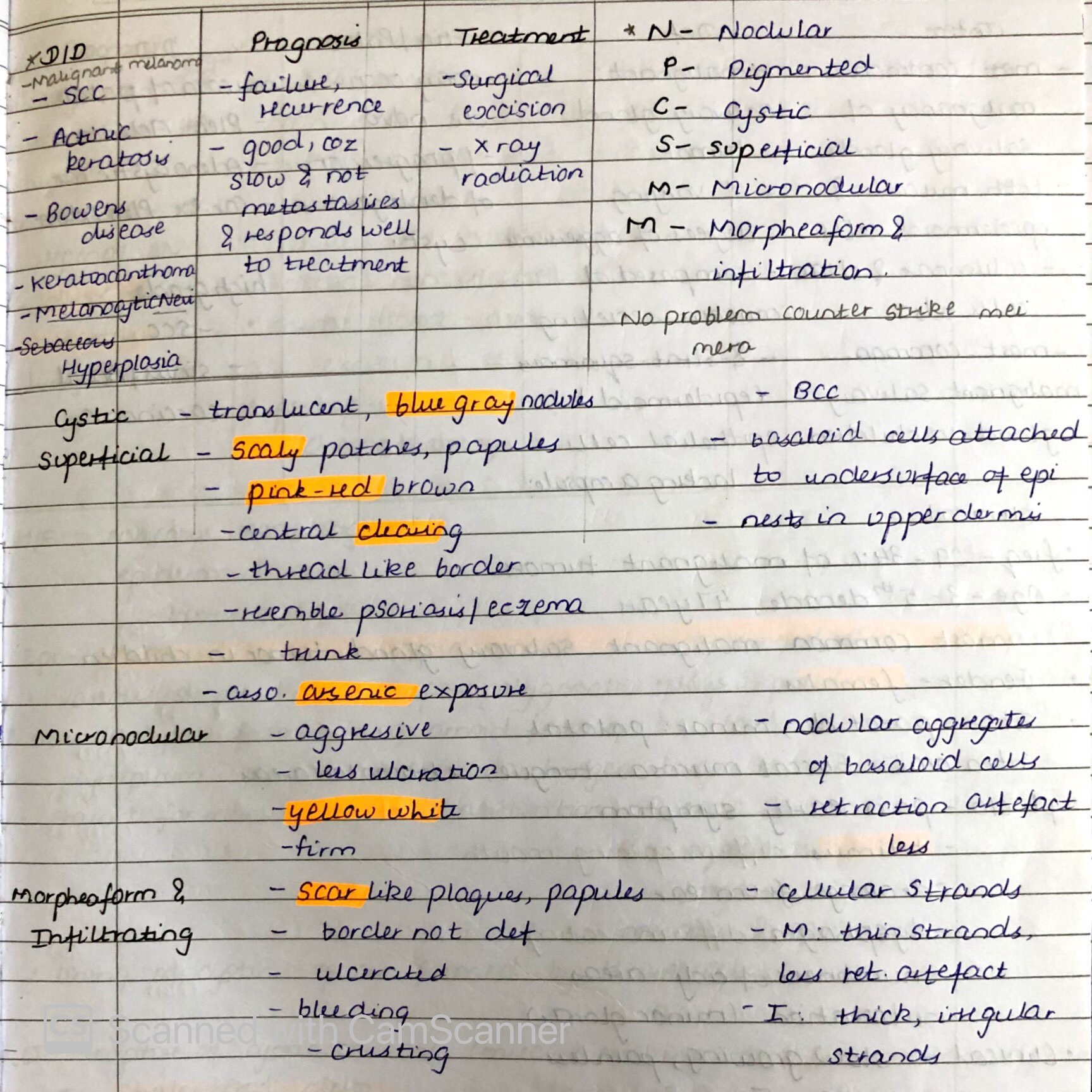
BASAL CELL CARCINOMA
source – don’t remember, had written it long back. , textbook – Shafers