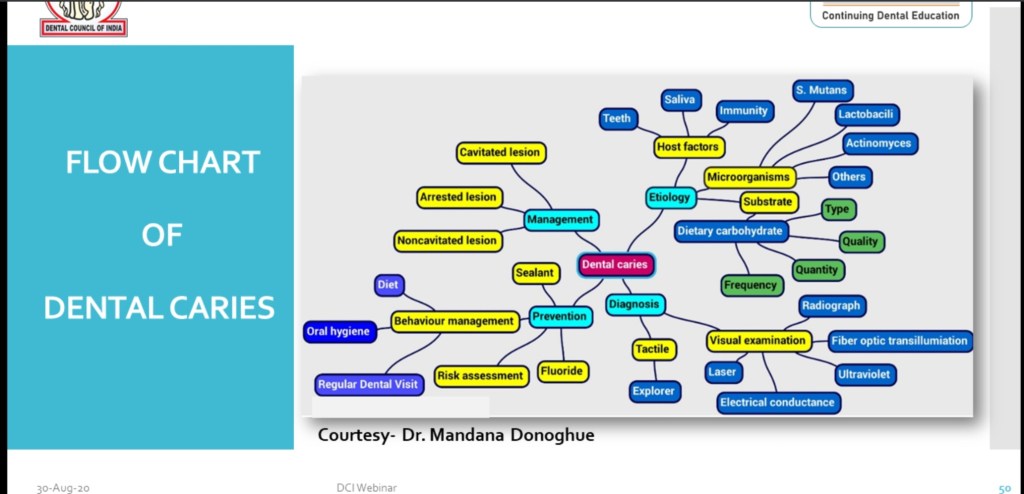
Flow Chart of Dental Caries includes:-
•Etiology
•Diagnosis
•Management
•Prevention
Source:- DCI WEBNEIR on Dental caries-30 Aug 2020.

Flow Chart of Dental Caries includes:-
•Etiology
•Diagnosis
•Management
•Prevention
Source:- DCI WEBNEIR on Dental caries-30 Aug 2020.
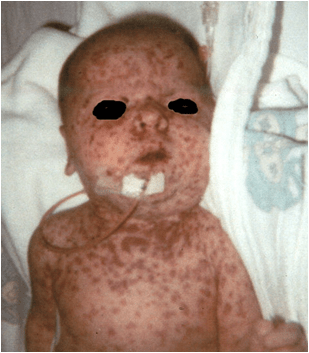
Clinical features:-
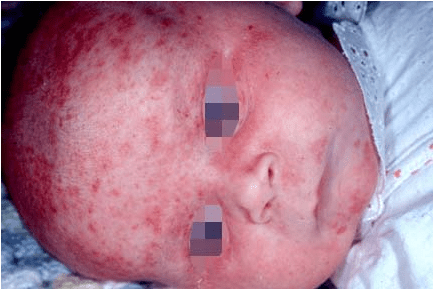
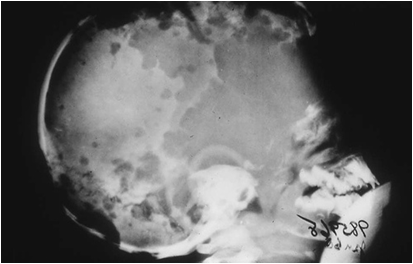
Oral manifestations:-
Histologic Features:-
1.Very similar to HSC; histiocytic proliferation with or without eosinophils.
2.These histiocytes do not contain significant amounts of cholesterol.
3.‘Foam cells’ not a feature.
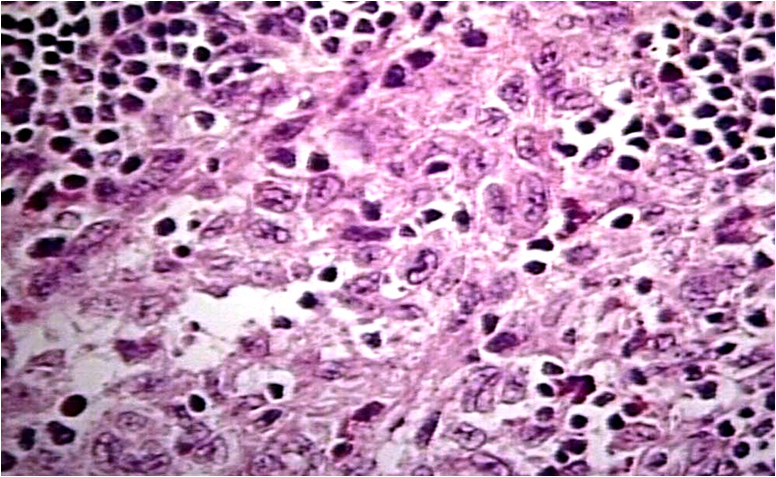
Treatment & Prognosis:-
References:-
Shafer’s 8th edition
Hematologic Diseases :-
• Hematologic diseases are disorders which
primarily affect the blood.
• Anemia is usually defined as a decrease
in the amount of red blood cells (RBCs) or
hemoglobin in the blood.
• Oral Manifestations:–
– folate and vit. B12 deficiency
– iron deficiency
– glossitis
• red colour
• athrophic papilae
• recurrent aphthae
– candidal infection
– angular stomatitis
– oral pain
• Leukemia is a group of cancers that
usually begins in the bone marrow and
results in high numbers of abnormal white
blood cells.
*Oral Manifestations:-
– gingival hypertrophy
– petechiae
– mucosal ulcers
– hemorrhage
Treatment of leukemia
– reactivation of herpes simplex virus – oral mucosistis.
References:-
1.Google- slideshare.
Careful examination of the oral cavity may
reveal findings indicative of an underlying
systemic condition, and allow for early diagnosis
and treatment. Examination should include
evaluation for mucosal changes, periodontal
inflammation and bleeding, and general
condition of the teeth.
I.GIT Diseases
• Gastrointestinal diseases refer to diseases involving
the gastrointestinal tract, namely the esophagus,
stomach, small intestine, large intestine and rectum,
and the accessory organs of digestions, the liver,
gallbladder, and pancreas.
• Crohn’s disease, also known as Crohn
syndrome and regional enteritis, is a type of
inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
• Ulcerative colitis is a form of inflammatory
bowel disease (IBD) that causes inflammation
and ulcers in the colon.
• Gastroesophageal reflux is a chronic symptom
of mucosal damage caused by stomach acid
coming up from the stomach into the
esophagus.
• Chronic liver disease in the clinical context is a
disease process of the liver that involves a
process of progressive destruction and
regeneration of the liver parenchyma leading to
fibrosis and cirrhosis.
1. Crohn disease:–
– diffuse labial, gingival or mucosal swelling
– „cobblestoning“ of buccal mucosa and
gingiva
– aphtous ulcers
– mucosal tags
– angular cheilitis
– oral granulomas
2.Ulcerative colitis:-
– oral signs are present in periods of
exacerbation of disease
– aphtous ulceration or superficial
hemorrhagic ulcers
– angular stomatitis
– pyostomatitis vegetans, pyostomatitis
gangrenosum.
3.Gastroesophageal reflux:-
– reduction of the pH of the oral cavity below
5,5
– enamel damage
– damage of the dentin – higher sensitivity (to
temperature..), caries
4. Chronic liver diseases:-
– jaundice
– petechiae or gingival bleeding (hemostasis
disorder)
RREFERENCES:-
1.Google -slideshare
2.Davidson-22nd edition


References: Shafer’sTextbook Of Oral Pathology