
P.falciparum infection
🤒Clinical Features:
This is the most dangerous of the malarias and patients are either ‘killed or cured’. The onset is often insidious, with malaise, headache and vomiting. Cough and mild diarrhoea are also common. The fever has no particular pattern.
🦗Neurological
- Coma
- Hypoglycaemia
- Seizures
- Cranial nerve palsies
- Opisthotonus (a type of abnormal posture where the back becomes extremely arched due to muscle spasms)

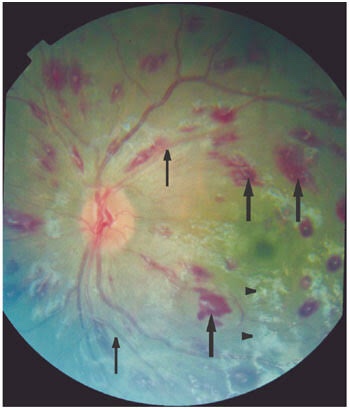
🦗Optic fundi
🦗Respiratory
- Pulmonary edema
- Secondary bacterial pneumonia
🦗Cardiovascular
- Shock
- Cardiac failure (‘algid malaria’)
- Dysrhythmias with Quinine
🦗Renal
- Acute renal failure
- Severe haemolysis results in haemoglobinuria (black water fever)
🦗Abdomen
- Hepatic dysfunction & haemolysis lead to Jaundice
- Tender liver edge with hepatitis
- Pain in left upper quadrant with splenomegaly
🦗Blood
- Parasitaemia
- Anaemia – Normocytic Normochromic
- Thrombocytopenia
- Coagulopathy

Dentowesome 2020
@dr.mehnaz🖊
References: Davidson’s Principles and Practice of Medicine Textbook; Image source: ResearchGate, Quizlet


