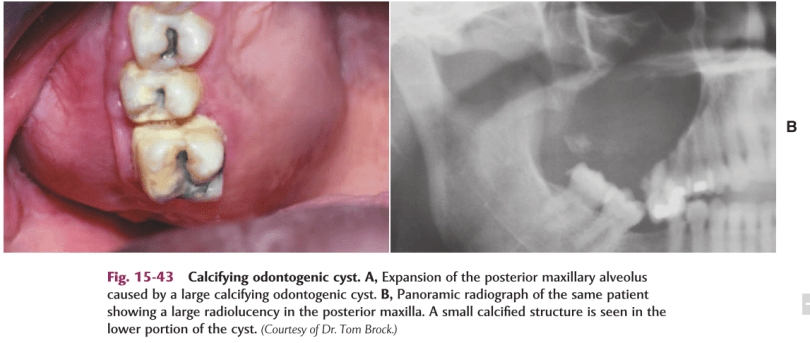
DEF:-Calcifying odontogenic cyst (COC), previously known as Gorlin cyst, is a rare, well-circumscribed, solid or cystic lesion derived from odontogenic epithelium that resembles follicular ameloblastoma but contains ‘ghost cells’ and spherical calcifications.
Other Names:-
1.Keratinizing and/or Calcifying Epithelial Odontogenic Cyst,
2.Gorlin Cyst
3.Cystic Keratinizing Tumour
4.Dentinogenic Ghost Cell Tumour
5.Odontogenic ghost cell cyst
- It Has many features of odontogenic tumor, therefore it is placed in the category of tumors in the latest WHO classification of odontogenic cysts and tumors.
- In the latest WHO publication on odontogenic tumours (Prætorius and Ledesma-Montes, 2005) it was classified as a benign odontogenic tumour and was renamed calcifying cystic odontogenic tumour (CCOT).
- CLINICAL FEATURES:-
- Age : Wide range, peak in 2nd decade.
- Sex : Equal.
- Site : Anterior segment of both jaws
- Calcifying odontogenic cysts that are associated with odontomas tend to occur in younger patients, with a mean age of 17 years.
- PATHOGENESIS:-
- COC is a unicystic process and develops from the reduced dental epithelium or remnants of dental lamina.
- The cyst lining has the potential to induce formation of dentinoid or even odontoma in adjacent CT wall.
- CLASSIFICATION OF THE ODONTOGENIC GHOST CELL LESIONS:-
- Group 1 : ‘Simple’ cysts Calcifying odontogenic cyst (COC)
- Group 2 : Cysts associated with odontogenic hamartomas or benign neoplasms: calcifying cystic odontogenic tumours (CCOT).
- Group 3 : Solid benign odontogenic neoplasms with similar cell morphology to that in the COC, and with dentinoid Formation
- .Group 4 : Malignant odontogenic neoplasms with features similar to those of the dentinogenic ghost cell tumour Ghost cell odontogenic carcinoma.
- SIGNS & SYMPTOMS:-
- Swelling is the commonest complaint, seldom associated with pain.
- Intraosseous lesions can cause hard bony expansion and resulting facial asymmetry.
- Displacement of teeth can also occur.
- RADIOLOGICAL FEATURES:-
- Intraosseous lesions produce well defined lucency which is usually unilocular.
- Irregular calcified masses of varying sizes may be seen within the lucency.
- Displacement of root/roots with or without root resorption and expansion of cortical plates also seen.

*Radiograph of a calcifying odontogenic cyst with well-demarcated margins extending from the right to the left premolar regions of the mandible. Numerous calcifications are present, some suggestive of small denticles.
- HISTOLOGICAL FEATURES:-
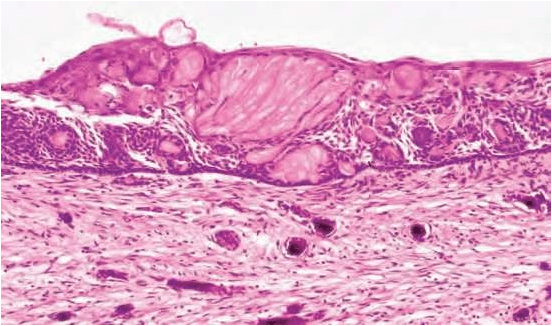
- Lining is usually thin about 6 – 8 cell thick, may be thickened in other areas.
- Lining shows characteristic odontogenic features with reversely polarized basal cell layer.
- TYPICALLY – GHOST CELLS may be seen in thicker areas of lining.
- Ghost cells are enlarged, ballooned, ovoid, eosinophilic cells with well
defined cell boundaries.
5.Some times many cells may fuse.
6.They represent abnormal keratinization and frequently calcify.
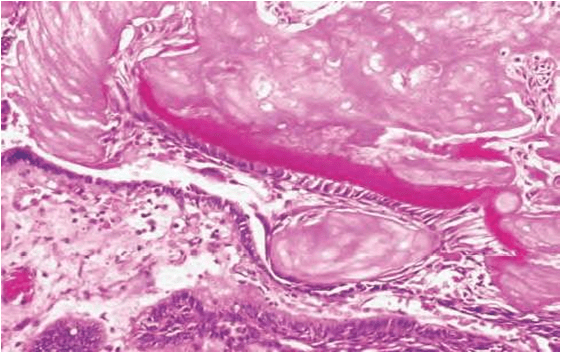
7.Tubular dentinoid and even complex odontome may be found in connective tissue wall close to epithelial lining.
- DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS:-
Based on radiographic appearance, following lesions must be included in the provisional diagnosis –
- Ameloblastoma
- CEOT
- AOT
- Ameloblastic fibro odontoma
References :-
1.Shafers- 8e
2.Neville -3e
3.Google-Slideshare