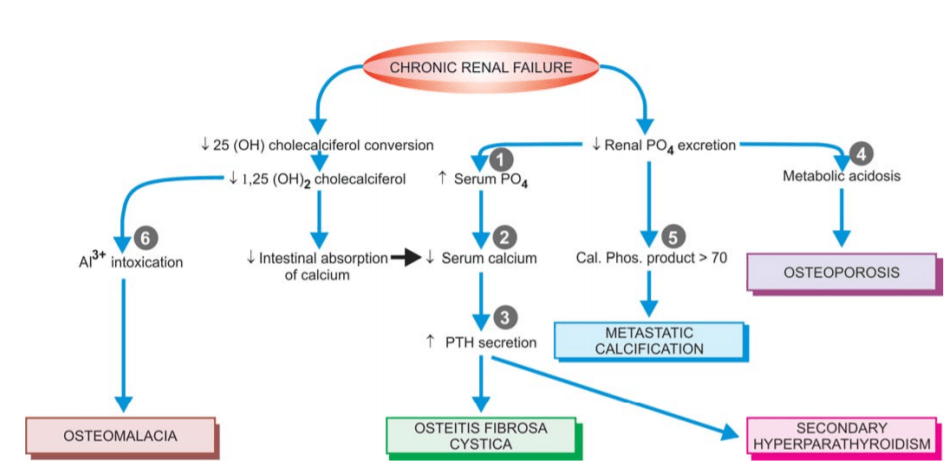
So what is renal osteodystrophy?




MORPHOLOGIC FEATURES.
The following skeletal lesions can be identified in renal osteodystrophy:
- Mixed osteomalacia-osteitis fibrosa is the most common manifestation of renal osteodystrophy resulting from
disordered vitamin D metabolism and secondary hyperparathyroidism. - Pure osteitis fibrosa results from metabolic complications of secondary hyperparathyroidism.
- Pure osteomalacia of renal osteodystrophy is
attributed to aluminium toxicity. - Renal rickets resembling the changes seen in children
with nutritional rickets with widened osteoid seams
may occur . - Osteosclerosis is characterised by enhanced bone
density in the upper and lower margins of vertebrae. - Metastatic calcification is seen at extraosseous sites
such as in medium-sized blood vessels, periarticular
tissues, myocardium, eyes, lungs and gastric mucosa.

source -textbook of pathology for dental students c p baveja and image source- Google