1) Vascular Uses:
(i) Hypotensive States: (Shock, Spinal Anaesthesia)
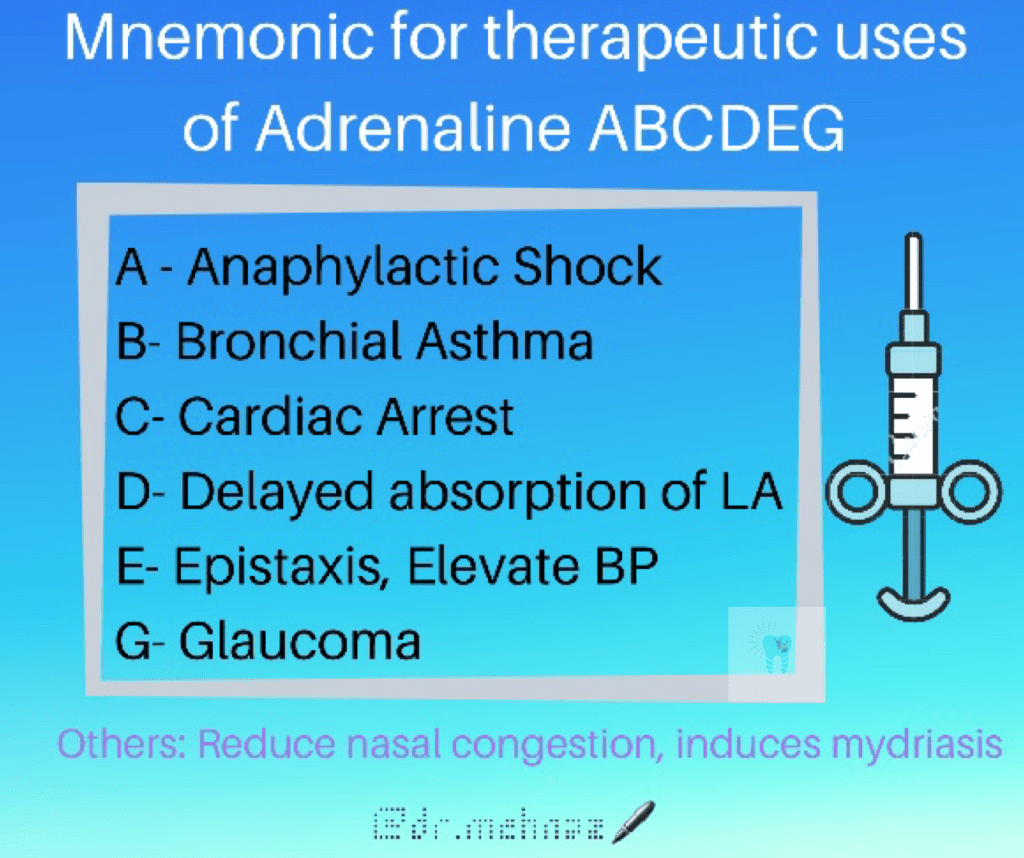
➡️ In case of anaphylactic shock or angioedema of Larynx or for bronchospasm attending drug hypersensitivity (Adrenaline + sub-class of gluco-corticoids) is recommended.
- Put the patient in reclining position, administer oxygen at high flow rate
- Inject adrenaline 0.5 mg (0.5 ml of 1 in 1000 solution for adult, 0.3 ml for child (6-12 years) & 0.15 ml for child (upto 6 years) i.m
- Repeat every 5-10 min. in case patient does not improve.
- This is the only life saving measure
(ii) Along with local anaesthetic:
➡️ Adrenaline 1 in 2,00,000 to 1 in 1,00,000 for infilteration, nerve block, spinal anaesthesia
🔅Effects:
- Duration of anaesthesia prolonged
- Systemic toxicity of LA ⬇️
- Local bleeding minimized
(iii) Control of local bleeding: (Skin, mucous membrane eg. Epistaxis)
➡️ Compresses of adrenaline 1 in 10,000 can control arteriolar & capillary bleeding
2) Cardiac Uses:
🔅Cardiac Arrest (Drowning, Stokes-Adam syndrome)
👉🏻 Adrenaline is used to stimulate the heart, i.v infusion with external cardiac massage
3) Allergic disorders:
- Adrenaline is a physiological antagonist of histamine which is an important mediator of many acute hypersensitivity reaction
- Affords quick relief in urticaria, angioedema
- Ineffective in delayed type allergy because histamine not involved.
4) Mydriatic:
👉🏻 The ester prodrug of adrenaline – Dipivefrine is an adjuvant drug for open angle glaucoma
5) Insulin hypoglycaemia:
👉🏻 Adrenaline can be used as an expedient measure but glucose should be given as soon as possible.
Dr. Mehnaz Memon🖊
References: Essentials of Medical pharmacology, KD Tripathi (7th Ed)