- Also called as Bull’s teeth
- Increase in size of crown
- Decrease in size of root
- Abnormally large sized pulp chambers
- CLASSIFICATION = Ratio of crown body/ root
- Syndromes associated with
- Klinefelter syndrome
- Type 5 AI
- Down syndrome
- Ectodermal dysplasia
- Tricho Dento Osseous syndrome
- Tricho = Kinky coiled
- Dento = Enamel hypoplasia and Taurodontism
- Osseous = Sclerotic bone
Category: Oral Pathology
TALON’S CUSP #NEET
- Talon means extra claw = Extra cusp
- Seen in Labial or lingual side of incisor
- MC seen in Central Incisors
- TYPES
| True Talon | Major typeCovers more than > ½ of distance from CEJ |
| Semi Talon | Minor type Covers >¼ and <½ of distance from CEJ |
| Trace Talon | Prominent congulum <¼ from CEJ |
- Associated with
- Rubinstein Taybi syndrome
- Broad thumb
- Broad first toe
- Short Stature
- Sturge Weber Syndrome = seen in Benign and malignant tumors
- Mohr Syndrome = type of oral facial digital syndrome
- ORO = Cleft tongue or Multilobed Tongue
- FACIAL = Median Cleft lip
- DIGITAL = Multiple fingers
- Rubinstein Taybi syndrome
PEG LATERALS #NEET
- Seen in Microdontia
- Seen in Congenital syphilis = also called hutchinson incisors
ELEPHANTIASIS GINGIVA
- Seen in Hereditary fibromatosis gingivae
- Pseduoedentiliusm is present = overgrown gingiva covers the crowns of tooth making it look like edentulism
GHOST TEETH
- Large sized pulp chambers
- Thin enamel and dentin
- Also called, Regional Odontodysplasia
- Also called odontogenesis imperfecta
- Also called odontogenic dysplasia
- H/P
- UNMINERALIZED DENTIN quantity is more
- Wide predentin zone
- Large areas of interglobular dentin
- Presence of enameloid conglomerates
- Calcification seen in REE of unerupted teeth
- UNMINERALIZED DENTIN quantity is more
DENTIN DYSPLASIA TYPE 2
- Coronal type
- Abnormally large sized pulp chambers = THISTLE TUBE APPEARANCE of pulp chambers
DENTIN DYSPLASIA TYPE 1
- Extremely short roots
- Obliteration of Pulp chambers with osteodentin
- Osteodentin – histologically looks like
- Cascades of dentin = one layer of dentin forms, it stops and then new layer of dentin forms on top of it
- Lava flowing around boulders
- Cascades of dentin = one layer of dentin forms, it stops and then new layer of dentin forms on top of it
- Few pulpal remnants are left behind – crescent shaped pulpal remnants
DENTINOGENESIS IMPERFECTA
- Not associated with osteogenesis imperfecta
- Mutation in gene – DSPP – dentin sialo phospho protein
- DSPP located on chromosome number 4
- Revised shield classification
- Common traits seen in both types
- Flat DEJ line
- Gene = DSSP
- Common traits seen in both types
| Type 1 Opalescent dentin type | Type 2 Brandy white type |
Bulbous crowns are seen With cervical constriction Giving tulip shaped crownsWHY? Because of atypical dentin formation = obliteration of pulp chambers | Large sized pulp chambers Very thin dentin – hence, radiographically SHELL TEETH |
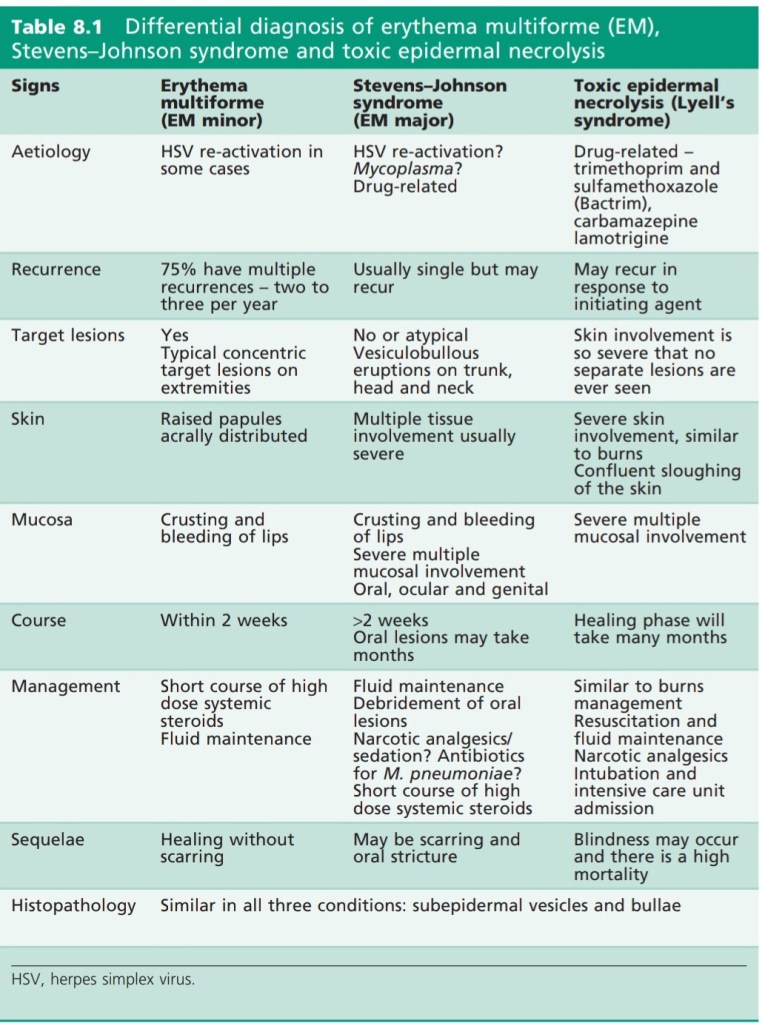
D/D of erythema multiforme, Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis
Further Reading/Reference: https://books-library.net/files/download-pdf-ebooks.org-1519330145Iz3C6.pdf
Dentigerous cyst




