
Written by – Sanjana Agrawal
SOURCE – GHOMS TEXTBOOK

Written by – Sanjana Agrawal
SOURCE – GHOMS TEXTBOOK



Written by – Sanjana Agrawal
SOURCE – GHOMS TEXTBOOK

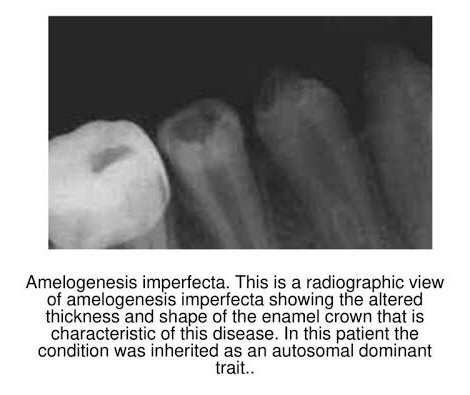
➡️ Represents a group of hereditary defects of enamel unassociated with any other generalized defects. It is entirely an ectodermal disturbance, since the mesodermal components of the teeth are basically normal.
➡️ Otherwise known as…


➡️ 3 stages:
Based on clinical, histological & genetic criteria:
🔹 TYPE I HYPOPLASTIC
🔹 TYPE II HYPOMATURATION
🔹 TYPE III HYPOCALCIFICATION
🔹 TYPE IV COMBINATION TYPE
1) Hypoplastic – Enamel not formed to full normal thickness.
2) Hypomaturation –
3) Hypocalcified –
References: Shafer’sTextbook Of Oral Pathology; Internet
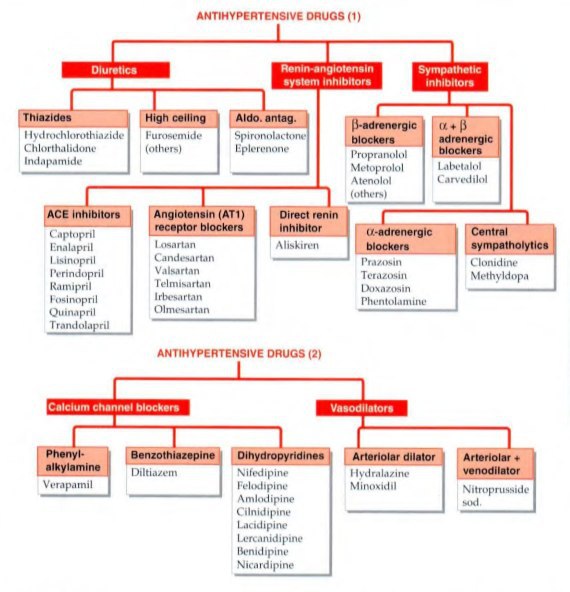
The objective of antihypertensive therapy is to reduce the incidence of adverse cardiovascular events, particularly CAD stroke and heart failures.
Here , we discuss some side effects of the Major drugs which is mainly prescribed for the treatment:-





The choice of antihypertensive therapy is initially indicated by the patient’s age and ethnic background.

Comorbid conditions also have an influence on initial drug selection,for example:-
•beta blocker might be the most appropriate treatment for a pateint with angina.
•Thiazides diuretics and dihydropyridines calcium channel blockers antagonists are the most suitable drugs for treatment in older people.
Thank you,
Regards,
KRITI Naja Jain 🙂
REference:-
Based on morphological alphabetical description of shape – 4 types:
Occlusal fissures: Deep invagination of enamel, described as broad/narrow funnels, constricted hour glasses, multiple invaginations with inverted Y-shaped divisions & irregularly shaped.
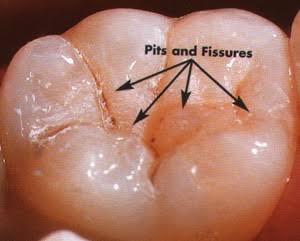
Deep and narrow Pit & Fissure
⬇️
Retention of food debris & microbes
⬇️
Fermentation of food by microbes
⬇️
Formation of Acid
⬇️
Caries
➡️ The lesions develops from attack on their walls.
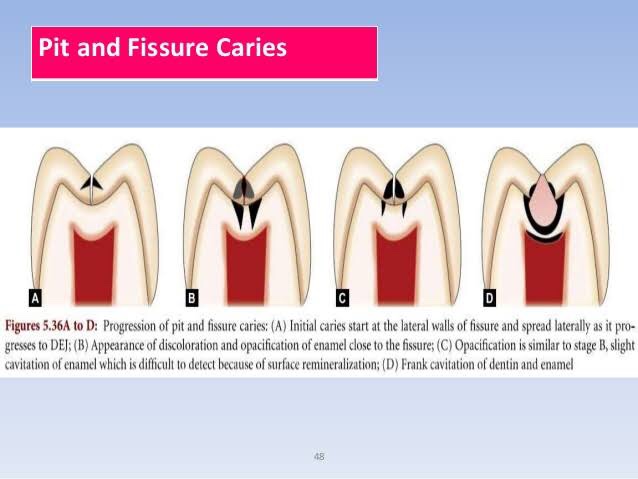
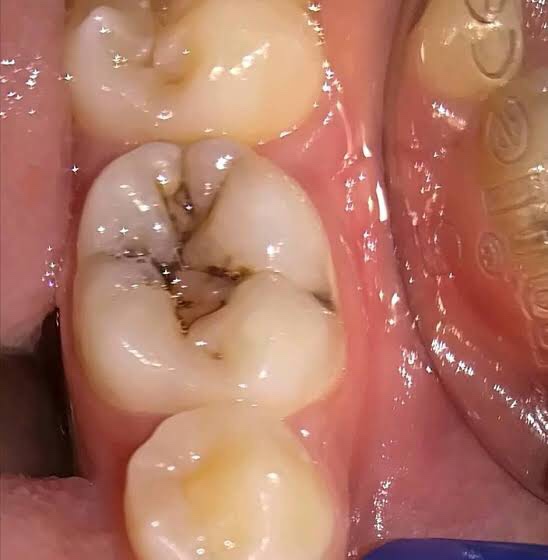
• Clinical View:
References: Wheeler’s Textbook, Google images

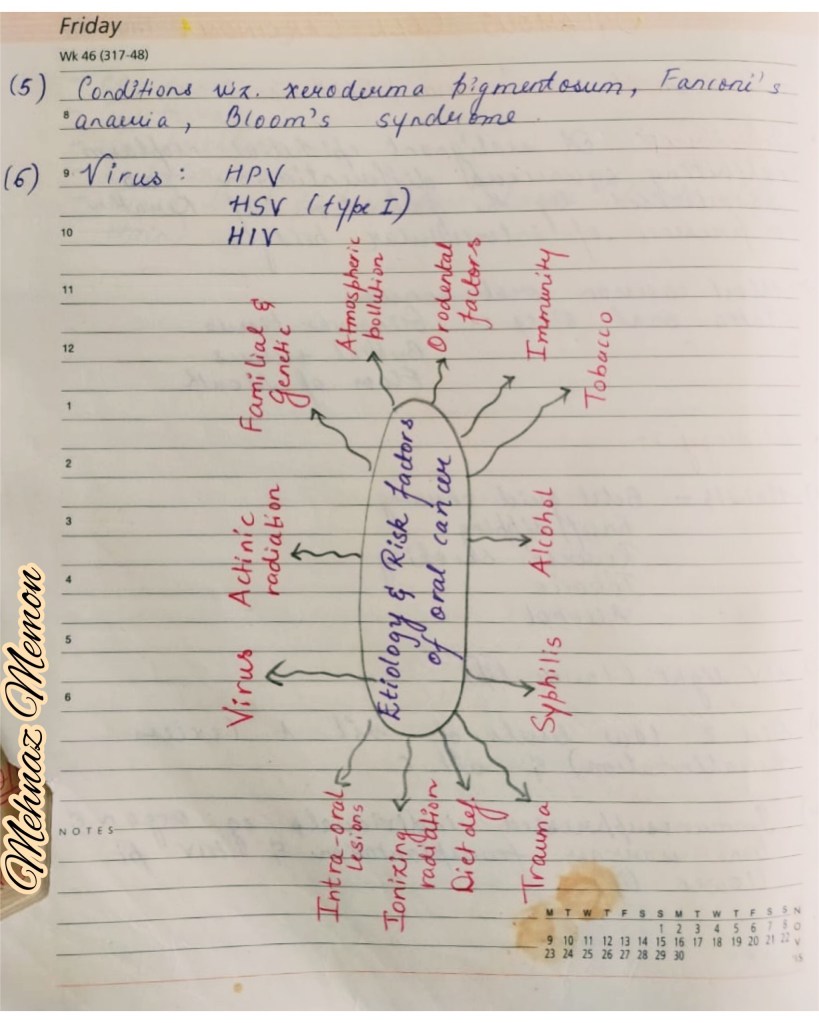
References: Textbook of Oral medicine by Ghoms