

References: Ghom’s Textbook of Oral Medicine, Shafer’sTextbook Of Oral Pathology


References: Ghom’s Textbook of Oral Medicine, Shafer’sTextbook Of Oral Pathology




Dr. Mehnaz Memon🖊
References: Shafer’sTextbook Of Oral Pathology
By KRITI NAJA JAIN:-








REFERENCES:-

source – don’t remember, had written it a lot time ago
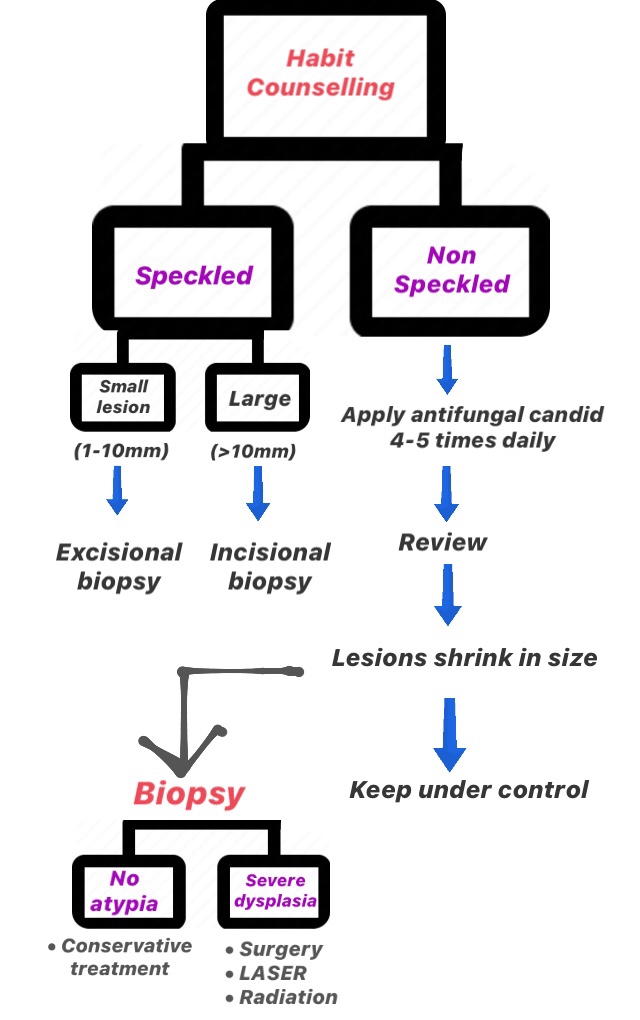
LEUKOPLAKIA

3) Surgical Approach
References: Ghoms, Textbook of Oral Medicine
Dr. Mehnaz Memon🖊













Reference:-
1.Shafers 8th e
2. Neville 3rd e
3.Purkit’s 3rd e

source – don’t remember, had written it a lot time ago

source – don’t remember, had written it a lot time ago
Classification of Bone pathology:-


Regards:-
Kriti Naja Jain 🙂
Reference :-
Neville oral and maxillofacial pathology 3rd e
➡️ The general term Radiation is applied in 2 different forms of energy-
➡️ Cellular defects occur due to-
⬇️
Restores within 60-120 days post-radiation therapy
4. Difficulty in eating –
Dr. Mehnaz Memon🖊
References: Shafers Textbook Of Oral Pathology 7Ed