Fibrous dysplasia is a chronic problem in which scar-like tissue grows in place of normal bone. It often results in one or more, of the following: Bone deformity. Brittle bones.















Fibrous dysplasia is a chronic problem in which scar-like tissue grows in place of normal bone. It often results in one or more, of the following: Bone deformity. Brittle bones.

















It is also called as ‘African jaw lymphoma’. It is a lymphoreticular cell malignancy. In the African form jaw involvement is 75% and in cases of the American form, abdomen involvement is more common. It is a B-cell neoplasm.

Etiology
• Epstein-Barrvirus(EBV)which also causes nasopharyn- geal carcinoma and infectious mononucleosis is considered to be the etiological factor. There are higher EBV antibody levels in patients of Burkitt’s lymphoma.
Clinical Features
Oral Manifestations
Histology
Shows characteristic starry sky appearance.
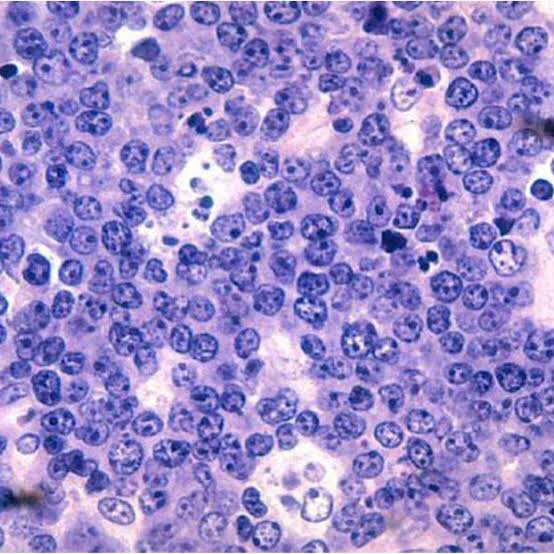

• Radiological diagnosis—moth eaten appearance is seen with loss of lamina dura around the teeth.
• Laboratorydiagnosis—monotonous sea of un differentiated monomorphic lymphoreticular cells, usually showing abundant mitotic activity. There is also hyperchro- matosis and loss of cohesiveness. Characteristic ‘starry sky’ appearance is seen.
Management
• Cytotoxicdrugs—cytotoxicdrugs like cyclophosphamide 40 mg/kg in single IV administration and repeated about 2 weeks later. Vincristine and methotrexate have been successful in some cases.
• Multiagent chemotherapy—combination of drugs such as cyclophosphamide, vincristine and methotrexate give better results than any single drug. Majority of patients show dramatic response to the therapy. The swelling regresses and the displaced teeth return to their normal position within 1 to 2 weeks.
REFERENCE- SHAFER’S TEXTBOOK OF ORAL PATHOLOGY AND ANIL GHOM TEXTBOOK OF ORAL MEDICINE
BY Dr. KRITI NAJA JAIN :-
1. FIBROUS DYSPLASIA :-
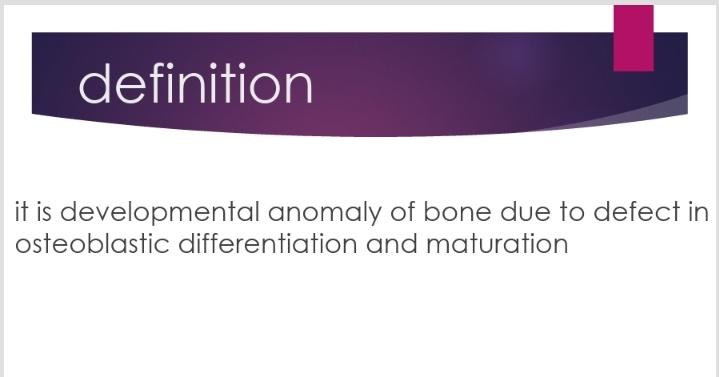
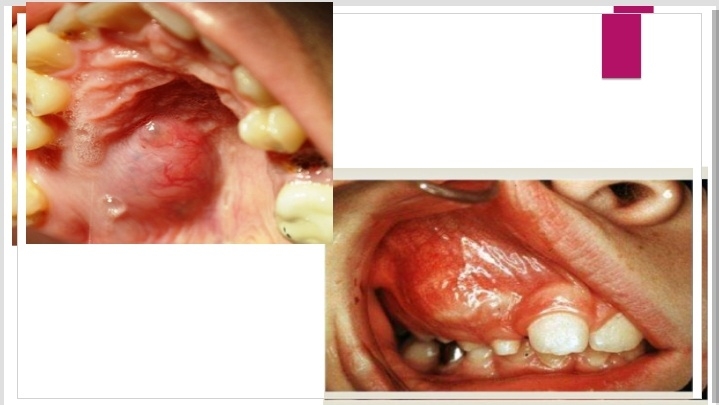
Def:- Fibrous dysplasia is an uncommon nonhereditary, developmental anomaly of the bone due to a defect in osteoblastic differentiation and maturation.
HISTOPATHOLOGY:


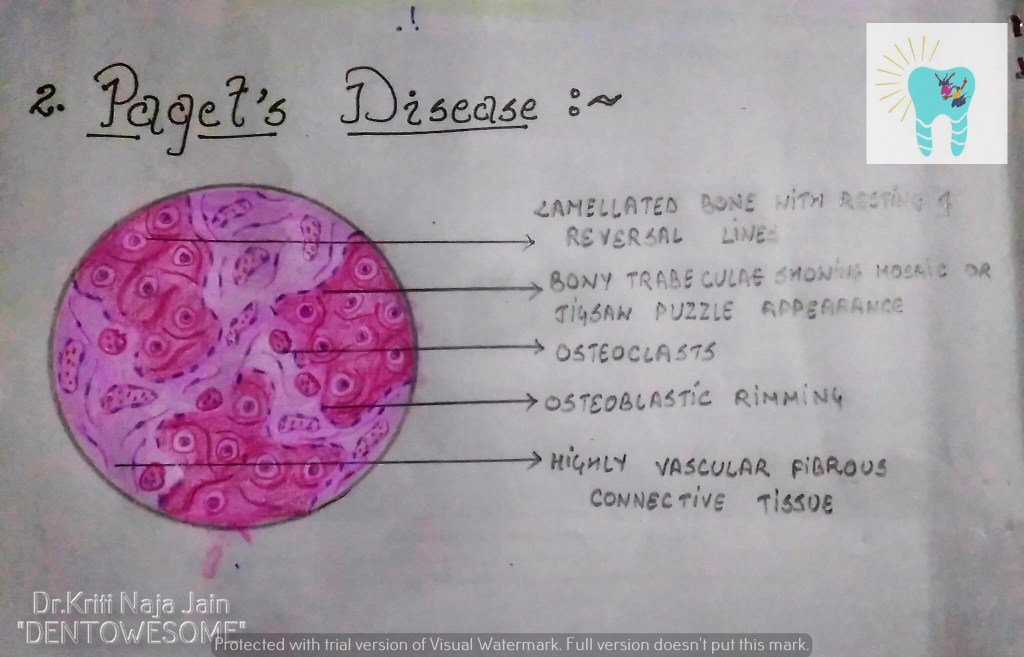
2. PAGET’S DISEASE (OSTEITIS DEFORMANS):-
Def:- Paget’s disease of bone is a condition characterized by abnormal and anarchic resorption and deposition of bone, resulting in distortion and weakening of the
affected bones.
HISTOPATHOLOGY:-

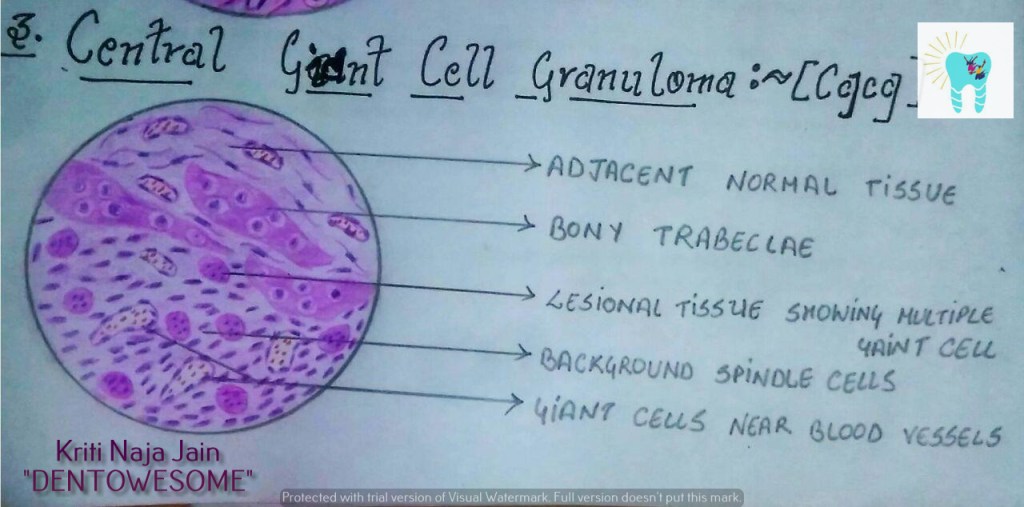
3. CENTRAL GAINT CELL GRANULOMA(GIANT CELL LESION; GIANT CELL TUMOR):-
Def :- Central giant cell granuloma (CGCG) is an uncommon, benign and proliferative lesion whose aetiology is not defined. Central giant cell granuloma is a relatively common benign intraosseous destructive giant cell lesion, which often affects the anterior part of the jawbone. By seeing clinical and radiographically , CGCG is divided into two types:-
1. Nonaggressive lesions make up most cases, exhibit few or no symptoms, demonstrate slow growth, and do not show cortical perforation or root resorption of teeth involved in the lesion.
2. Aggressive lesions are characterized by pain, rapid growth, cortical perforation, and root resorption. They show a marked tendency to recur after treatment, compared with the nonaggressive types.
HISTOPATHOLOGY:-

REFERENCE:-
1.Maji Jose 2nd edition
BY: Dr.Kriti Naja Jain :-
1.LICHEN PLANUS:-
*Lichen planus is a chronic mucocutaneous disorder manifested in a various forms in the oral cavity.
*The most characteristic pattern is” RETICULAR TYPE” with the interlacing white stripe called “WICKHAM’S STRIAE”.
*HISTOPATHOLOGY:-


2.PEMPHIGUS :-
Pmphigus is a tissue specific autoimmune disease affecting the skin and mucosa. Clinical manifestations is in the from of “vesiculobullous lesions” that rupture to form ulcer and erosions .
*Vesiculobullous lesions develop due to immune mediated acantholysis causing intraepithelial vesicle formation.
*HISTOPATHOLOGY :-


3.PEMPHIGOID :-
Pemphigoid is a vesiculobullous lesions that develop due to an autoimmune reaction directed against some components of basement membrane.
*This results in seperation of epithelium from the connective tissue with sub epithelial vesicles formation .
*Bullous pemphigoid and cicatricial pemphigoid are two different types of pemphigoid lesions.
*HISTOPATHOLOGY:-


REFERENCE:-





source – don’t remember, had written it a lot time ago
Comprises three layers
Details of cardiac muscle cells:
Long, muscular tube delivers food from the pharynx to the stomach.
Connects with the esophagus, superiorly and the duodenum, inferiorly.
Regions of the stomach: