Muhad Noorman p, Team dentowesome, final year

Reference: DAVIDSON INTERNAL MEDICINE 20 TH ED
Muhad Noorman p, Team dentowesome, final year


Reference: DAVIDSON INTERNAL MEDICINE 20 TH ED
Muhad Noorman, Team dentowesome, final year


Reference, Textbook of surgery for Dental students , SRB, INTERNET
Muhad Noorman, Team dentowesome, Final year

Hyperthyroidism and Thyrotoxicosis




Reference, :- TEXTBOOK OF CLINICAL MEDICINE, SN CHUG
Davidson internal medicine
Muhad Noorman, Team dentowesome, Final year


Reference: Clinical Medicine for Dental students, SN CHUG
Muhad Noorman P, Team Dentowesome, Final year
Reference: Davidsons Internal medicine , Internet
Wilson’s disease, also known as hepatolenticular degeneration and progressive lenticular degeneration, is a rare genetic disorder that causes copper overload in the body.
Common cause of liver cirrohsis in children.
Etiology:- A mutation in the ATP7B gene, which codes for copper transportation, causes Wilson’s disease
Clinical Features:-
Liver related
Nausea, weakness, vomiting, jaundice, bloating, spider angiomas, muscle cramps etc..
Neurological
Memory, Speech impairments. Altered gait, personality changes, headache, insomnia etc…
Characteristic clinical signs:- SUNFLOWER CATARACT AND KAYSER-FLEISCHER RINGS. KF rings are golden brown ring like discoloration of eyes due to copper deposition.
Lab investigation:- Altered Liver enzymes
Elevated Serum copper level
Increased urinary copper excretion. Low Serum ceruloplasmin level. Liver biopsy will reveal copper deposition. Imaging like MRI/CT for lenticular imaging.
Treatment:-. Copper chelating agents like d-penicillamine, Trientine etc.. can be used. Oral Zinz tetrathiomolybdate can be given ti reduce dietary absorption of Copper.
Muhad Noorman P, Final year, Team dentowesome
Abnormal accumulation of Iron in Liver , Pancreas and heart causing widespread damage of organs resulting in cirrohsis and diabetes mellitus.
Also known as Celtic Curse or Bronze diabetes
Autosomal recessive transmission due to HEF gene mutation.
Clinical features:-
Male : Female ratio = 10:1. Weaknesses, lethargy, diabetes mellitus, liver cirrohsis , arthralgia, skin hyperpigmentation, impotence, hepatomegaly, hypogonadism.
Lab investigation:- Serum Iron
Transferrin saturation > 45%. Plasma ferritin > 200 ng/ml. Liver biopsy (gold standard) > 1000 MCG/L. DNA Mapping study for gene mutation.
Treatment:- Venesection for all people with Iron biochemical overload. Chelating agents like Desferoxamine can be also taken.
References: DAVIDSONS INTERNAL MEDICINE, INTERNET

It is purpulish discoloration of skin and mucous membrane due to sub-cutaneous and sub-mucous extravasation of blood.

Image :- Google
Writing :- notes made from mastering bds and Sanjay Kumar Purkait books
It is histological cannotation to premalignance marked by abbarent and uncoordinated cellular proliferation depicted at cellular level as atypia which is reflected as dysplasia.
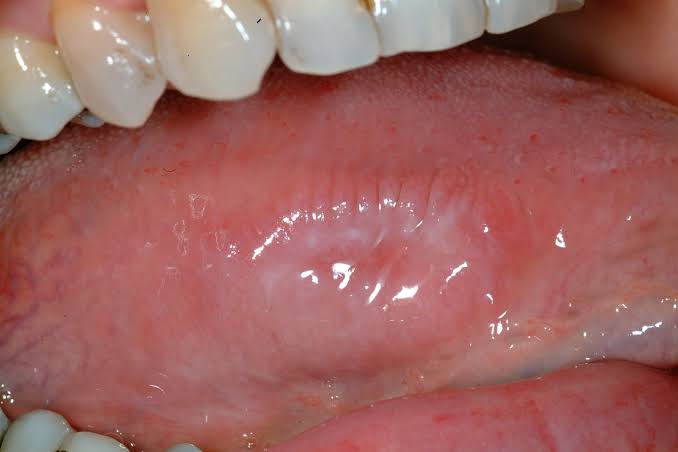
An oral precancerous lesion, also called dysplasia, is a growth that contains abnormal cells confined to the lining of the oral cavity, or mouth. This lining is called the mucosa. It covers the inside of the cheeks, the inside of the lips, the gums, the tongue, and the roof and floor of the mouth.
Dysplasia can be mild moderate and severe.

Image :- Google
Writing :- notes made from mastering bds and Sanjay Kumar Purkait books

TMJ has hinge like junction.
Luxation occurs when :-

Luxation is unilateral but bilateral Luxation also occurs.

Image :- Google
Writing :- notes made from mastering bds and Sanjay Kumar Purkait books

It is one of most incapacitating of all diseases involving this structure.
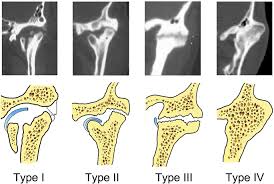
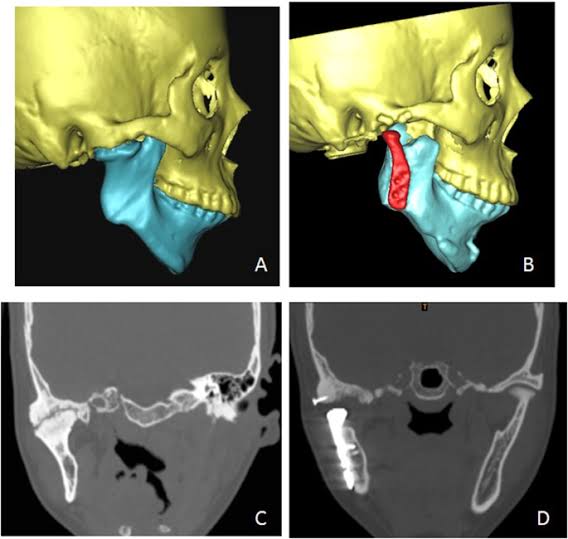
Image :- Google
Writing :- notes made from mastering bds and Sanjay Kumar Purkait books