
Nancy 13th edition

Nancy 13th edition


https://www.instagram.com/s/aGlnaGxpZ2h0OjE4MTA3MTAwODIzMTUzMzU2?igshid=xo73gjk8yp0w
To access realistic looking recordings library which will help improve your ECG skills, head on to the next page!




source: AK Tripathi- Essentials of Medicine for Dental Students, 2nd edition



source: AK Tripathi- Essentials of Medicine for Dental Students, 2nd edition
General Medicine is indeed a highly important and high weightage subject in NEET MDS Exam. It is one of the subjects which are common to both Medical and Dental Courses. Given below is the list of standard books to refer & most important topics covered under General Medicine which helps in your Preparation Planning.
Given below are the list of Questions MERITERS experts will answer that are essential for an effective and efficient preparation:
5-11/240 Questions (4%)


Author : J. Larry Jameson , Anthony S. Fauci, Dennis L. Kasper, Stephen L. Hauser, Dan L. Longo, Joseph Loscalzo
INR 8,637 Buy on Amazon

Author : Walker
INR 1,876 Buy on Amazon
| UNIT | MOST IMPORTANT TOPICS |
|---|---|
| Infections | Bacterial infection Viral infection AIDS HIVHSVMiscellaneous |
| Central Nervous System | EpilepsyParkinsonismFacial nerve palsyMiscellaneous |
| GIT, Liver And Kidney | Acid Base BalanceHepatitis Nephrotic syndromeConn’s syndromeHelicobacter pylori Urinary Tract infectionDubin Johnson syndromeRenal calculiAppendicitisMiscellaneous Renal Failure |
| Hematology And Endocrinology | HaemophiliaAnaemiaLeukemiaThalassemiaDICMiscellaneous blood diseaseDiabetes mallitusHyperthyroidism and HypothyroidismHyperparathyroidism(ALSO RICKETS)Vitamin D diseaseTumor lysis syndromePheochromocytoma |
| Respiratory system | Obstructive and Restrictive respiratory diseaseAsthmaCOPD Pneumonia TuberculosisRespiratory failure |
| Cardiovascular system | Heart failureMyocardial infectionValvular diseaseEndocarditis CPRMiscellaneous |
1. Single best answer
2. Image based questions
3. True or false type questions
We hope this blog will assist you in preparing this subject meticulously for MDS entrance exams.
Prepare judiciously..
SOURCE: MERITERS!!
Cyclosporine therapy may cause gingival hyperplasia
Gingival growth occurs in patients taking phenytoin.
Patients with cardiac disease should receive dental treatment in minimal stressful environment. Anxiety,exertion and pain should be minimized.
Irregular pulse, engorged jugular veins and tachypnea may indicate the presence of cardiac disease.A history of hypertension, ischemic heart disease or any other cardiac problem particularly congenital heart disease and drug intake (anticoagulant, aspirin) should be sought.Angina may present as pain in the mandible, teeth and other oral Tissues Epinephrine in the local anesthesia may raise the blood pressure and precipitate dysarrhythmias.In patients with IHD, facilities for medical help, oxygen and nitroglycerine should be Available General anesthesia should be avoided for at least three months in patients with recent onset angina
Patient’s with Cushing’s syndrome more prone to get infections.(candidiasis)
Elective dental surgery should be deferred for 6 months following acute MI.Prophylaxis for infective endocarditis is mandatory in cases where there is a risk.Cardiac patients on anticoagulant drugs or aspirin are at increased risk of bleeding following dental procedures.Hence, these drugs should preferably be stopped a week before the procedure.Calcium channel blockers may cause gingival swelling and lichenoid lesions in the oral cavity. ACE inhibitorscan cause loss of taste, burning sensation in oral cavity,and angioedema. Dry mouth can result due toantihypertensive drugs such as d
Rifampicin can cause red saliva.
Elective dental care is avoided in patients with acuterenal failure
Elective dental procedures are better tolerated on non-dialysis days
Blood pressure measurement is advised at every visit.
Brown to black macular pigmentation in oral mucosa can be suspected for Addison disease.
Gonorrhea may present uncommonly with oral manifestations like tonsillitis, lymphadenitis, and painful oral and pharyngeal ulcers.
Oral manifestations in peptic ulcer disease are rare.However erosive dental lesions could be appreciated on lingual surface of lower incisors or palatal surface of upper maxillary teeth.
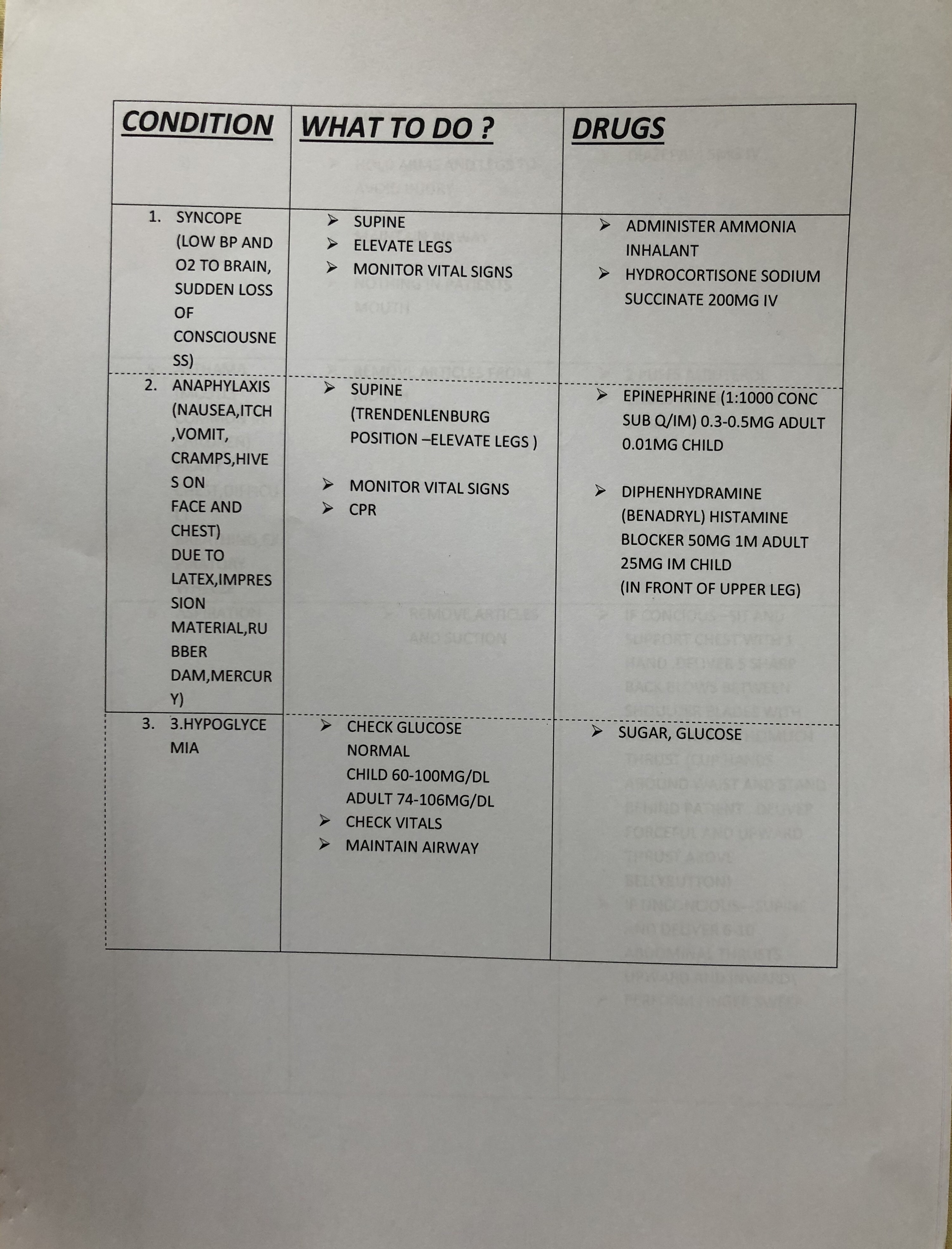

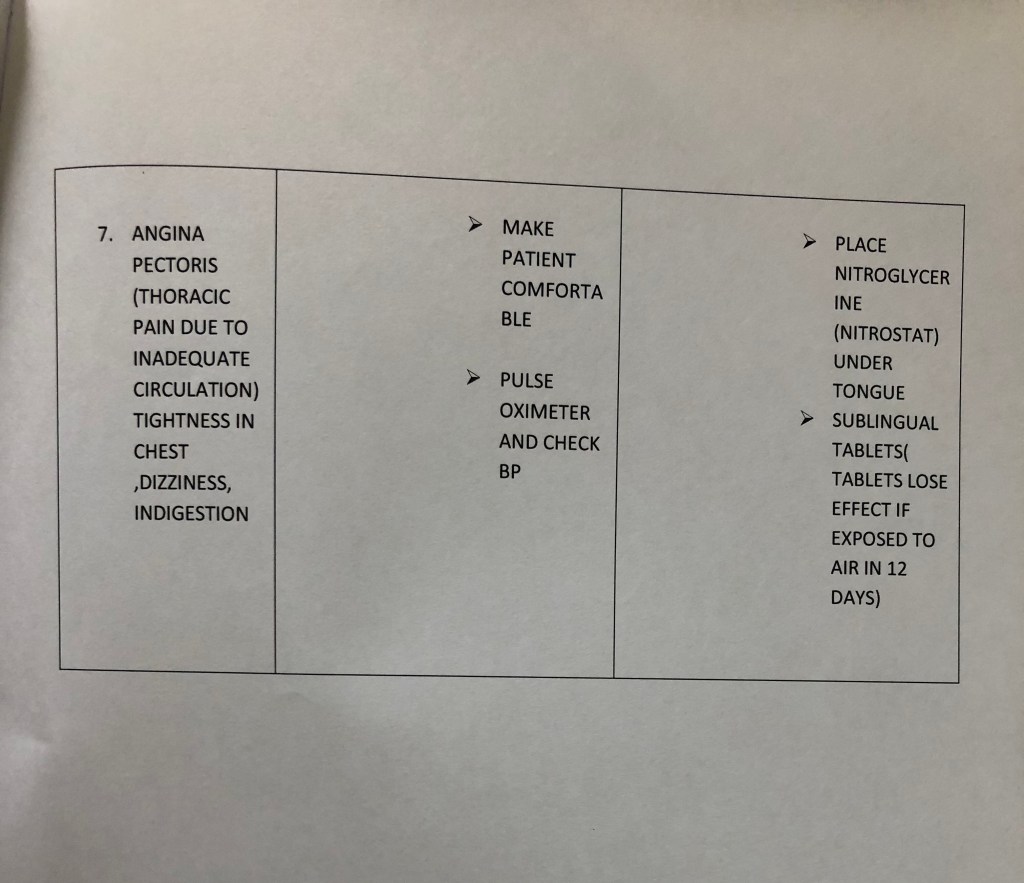
source – Nancy 13th edition

source – Nancy 13th edition


source – Nancy 13th edition

source – Nancy 13th edition