

REFERENCES: GROSSMAN TEXTBOOK


REFERENCES: GROSSMAN TEXTBOOK


References: GROSSMAN TEXTBOOK
ASEPSIS : By rubber dam placement or isolation or by sterilization of instruments.
2. STERILIZATION :
a) DEBRIDEMENT OF ROOT CANAL :
b)DRAINAGE :
c) IMMOBILIZATION :
d)ATRAUMATIC PROCEDURES :
e)TERPHINATION:
f)CHEMO PROPHYLAXIS:
References: GROSSMANS TEXBOOK
So what is the pulp – in simple words it’s a tissue that forms the inner tooth structure along with the blood vessels and contains nerves .
Pulp capping is the process of placing a specialized agent in contact with or in a close proximity to the pulp with the intention to encourage formation of new dentin ( secondary dentin) and also promote healing of the pulp.
Even before the discovery pulp capping agents, exposure lead to pulpitis or pulpal infection and ultimately pulp necrosis.
Examples of a very common pulp capping agent used – calcium hydroxide cement.
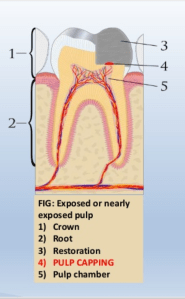
Placement of an agent directly on the exposed pulp is direct pulp capping.
It is done in the following situations-
Note- direct pulp capping is considered oy for immature permanent teeth or for future permanent teeth

Source – Google
Procedure where gross caries are removed from the lesions and cavity is sealed for a time with a biocompatible material.
And secondary dentin formation is induced even when pulp is not exposed but is near exposure.
This induces new dentin formation.
It is done in the following situations-
Note – it promotes formation of reparative dentin, promotes dental sclerosis and remineralizing the carious dentin.
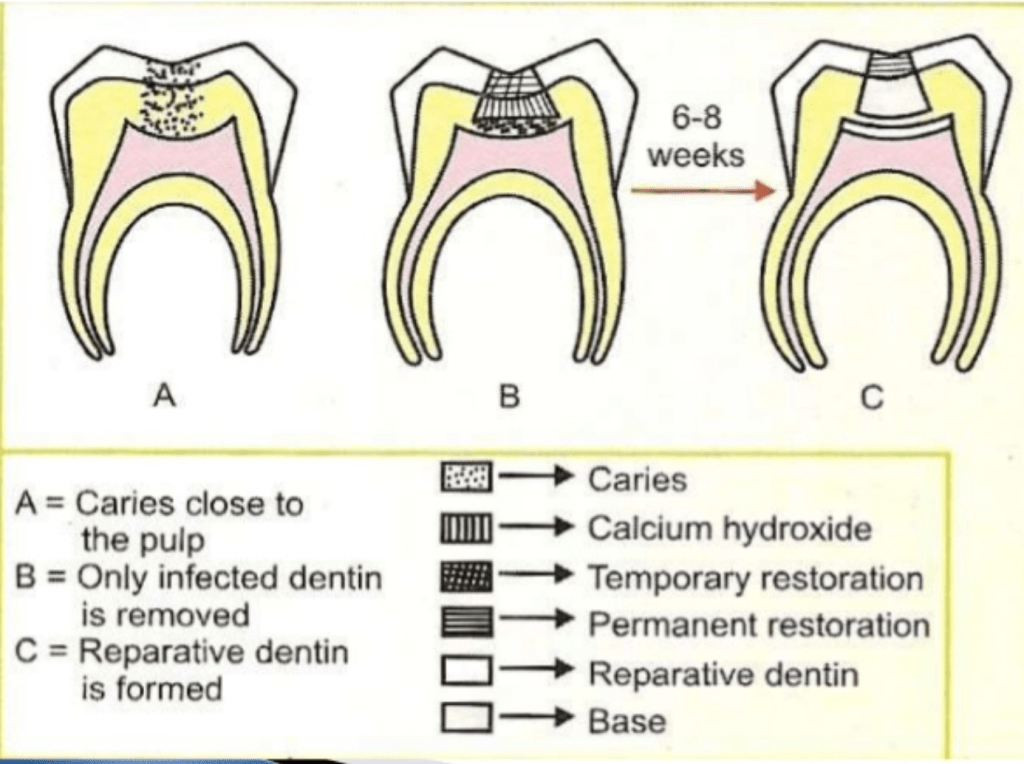
Source-google
•Stimulate reparative dentin formation.
•Preserve pulp vitality
•Release fluoride to prevent secondary caries .
•Bactericidal or bacteriostatic
• Adhere to dentin and restorative material
•Resist forces during mastication .
•Provide bacterial seal.
•Calcium hydroxide
•Zinc-Oxide – Eugenol
• GIC and adhesive resins
• MTA
• Biodentine
•Tricalcium phosphate ceramic
•Polycarboxylate cements
Source – Sturdevant’s art and science of operative dentistry ,slide share and manappallil
Image source – Google and slide share


References: GROSSMANS TEXTBOOK



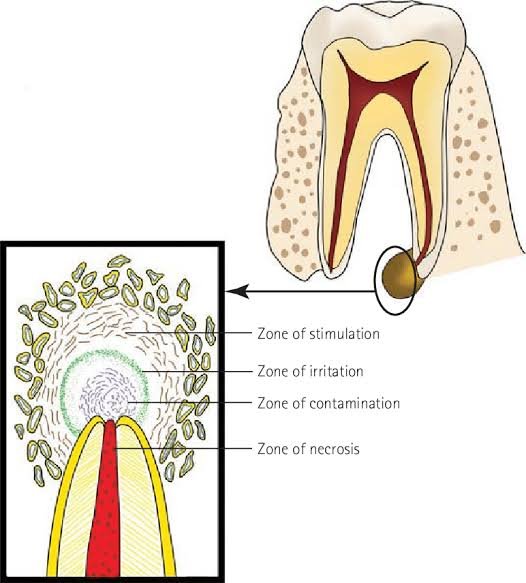
References: Grossman textbook .
Written by – Dr.Urusa I Inamdar
In 1864, S.C. Barnum, introduced the rubber dam into dentistry. It is used to define the operating field by isolating one or more teeth from the oral environment. The dam eliminates saliva from the operating site and retracts the soft tissue.
Time consumption and patient objection are the most frequently quoted disadvantages of the rubber dam.
Certain oral conditions may preclude the use of the rubber dam , these include :
In addition, patients suffering from asthma may not tolerate the rubber dam if breathing through the nose is difficult. Latex allergy.
However, latex free rubber dam material is currently available.
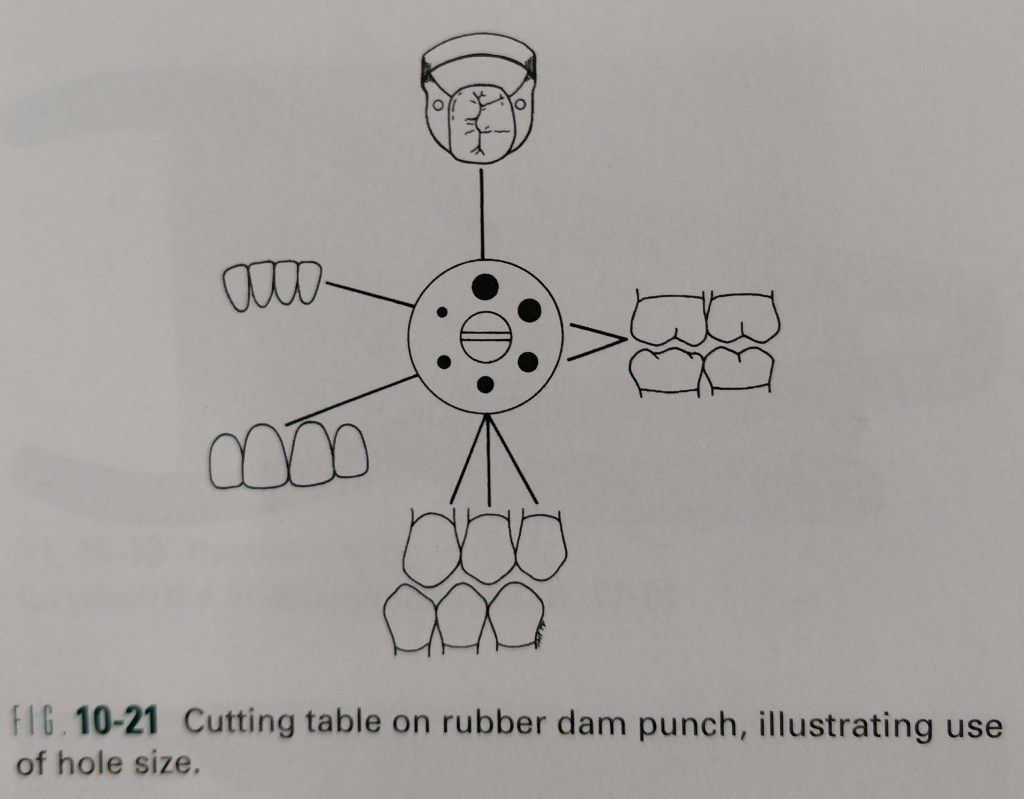
The procedure just detailed describes the method of sequentially placing the retainer and rubber dam on the anchor tooth.
Reference:
Sturdevant’s – Art and science of Operative Dentistry (4th edition)



References: STURDEVANTS 7th edition


References:Sturdevants 7th edition




References: Sturdevants 7th edition