A. Trigeminal Ganglion:
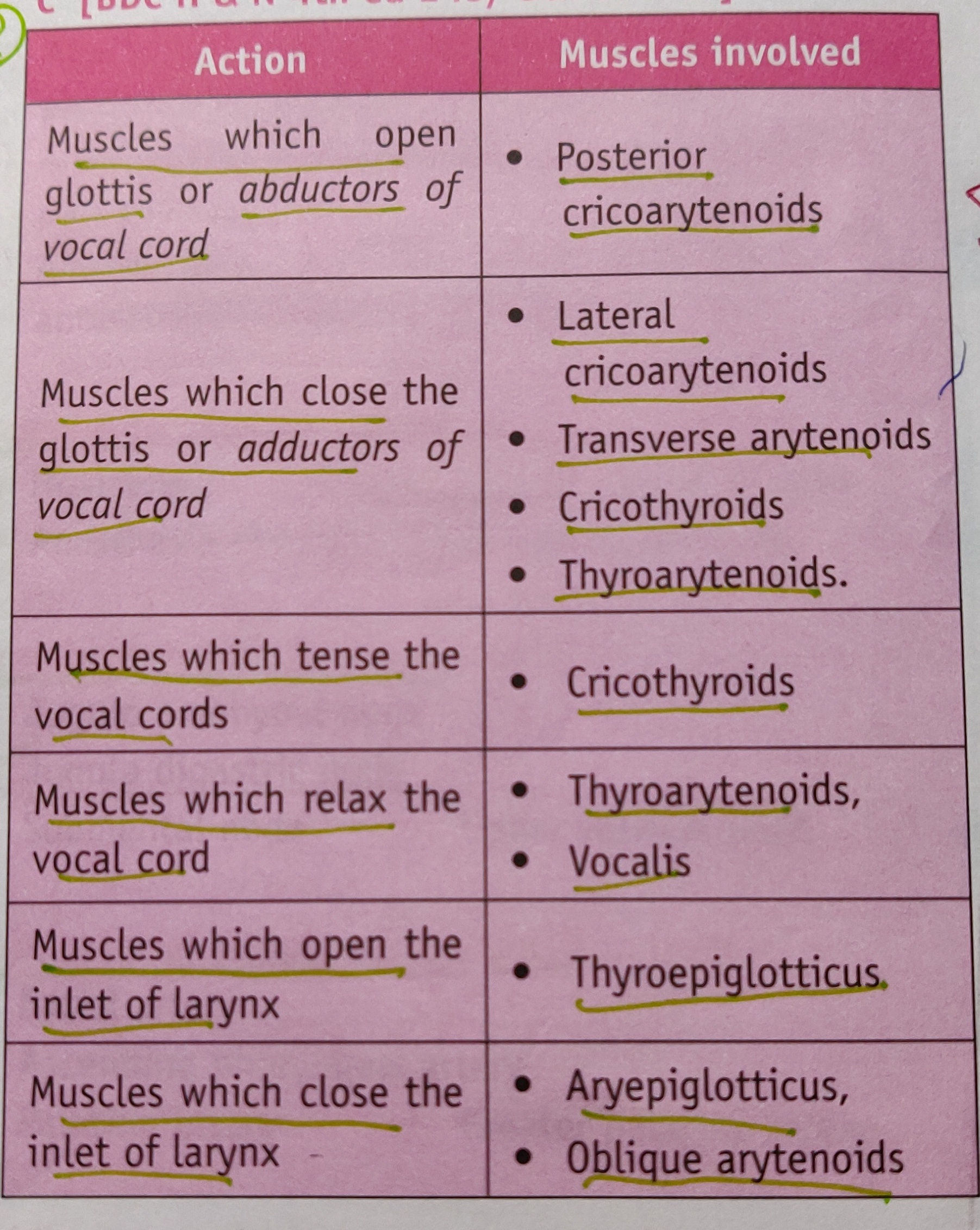
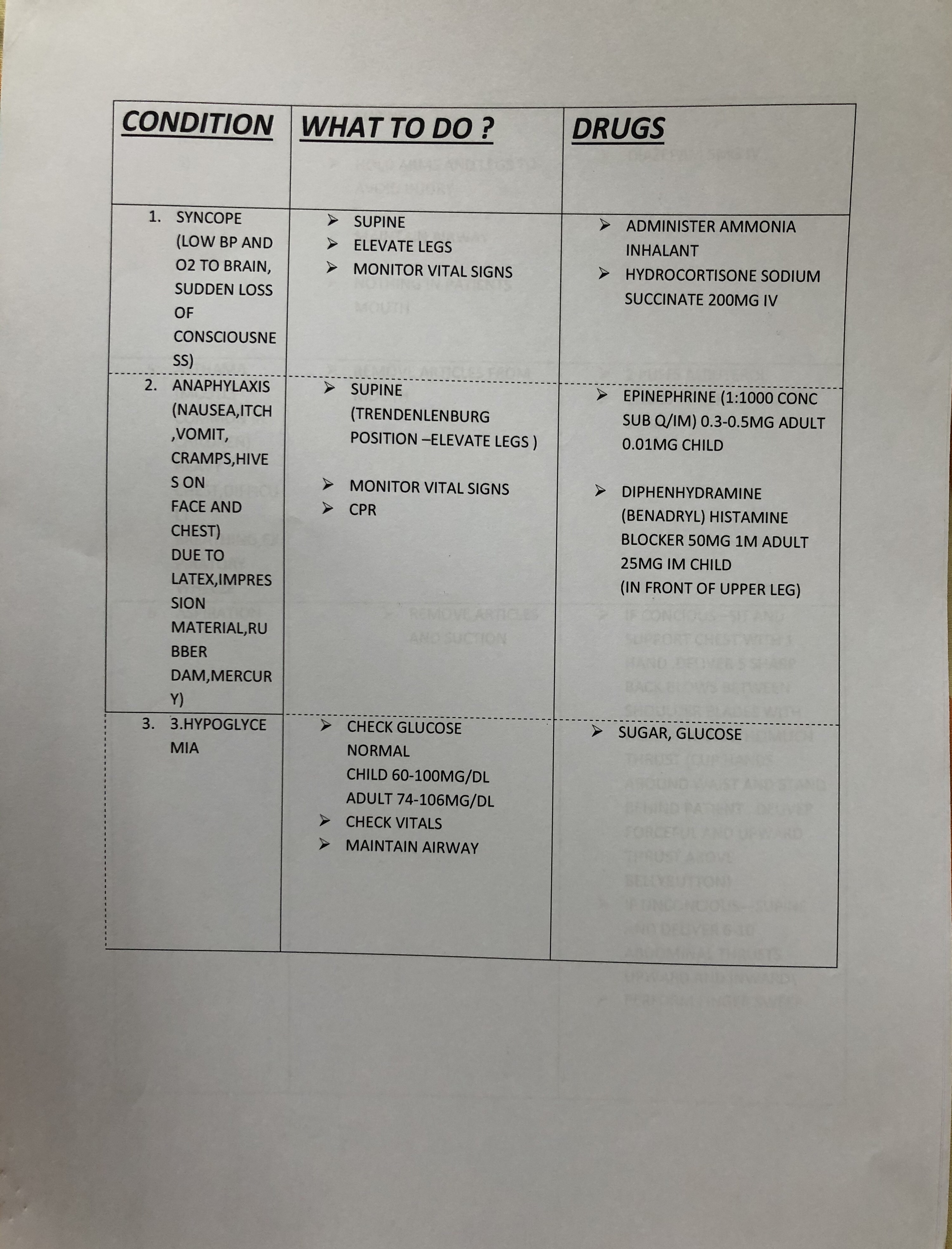
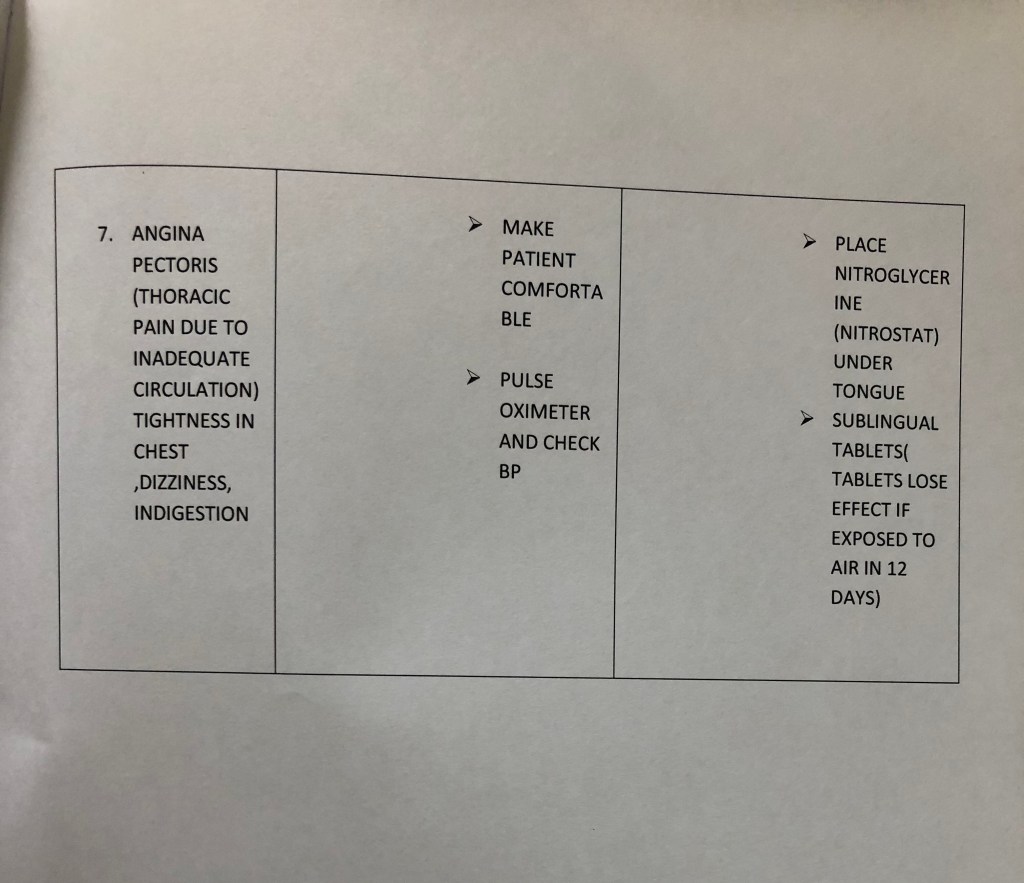
• Crescentric or seminlunar shaped sensory ganglion of 5th cranial nerve
• The ganglion lies on the trigeminal impression on the anterior surface of petrous part of temporal bone near it’s Apex and occupies a special place of duramater called the trigeminal or Meckel’s Cave.
• The central process of the ganglion cells form the large sensory root while the peripheral processes of the ganglion cells forms the three divisions of the trigeminal nerve.
B. Celiary Ganglion:
• Parasympathetic ganglion placed in course of the occulomotor nerve.
• It lies near apex of orbit between the optic nerve and tendon of the lateral rectus muscle.
• It has sensory , motor, and sympathetic roots.
i) The sensory root comes from nasociliary nerve. It contains sensory fibres from the eyeball.
ii) The motor root arises from occulomotor nerve. It carries preganglionic fibres from Edinger-Westphal nucleus to supply the sphincter pupillary and ciliaris muscle.
iii) The sympathetic roots carries postganglionic fibres of superior cervical ganglion to supply the blood vessels of eye ball and the dilator pupillary.
C. Pterygopalatine Ganglion (Spheno-palatine Ganglion):
• This is the largest parasympathetic peripheral ganglion.
• It lies in pterygopalatine fossa just below the maxillary nerve.
• Topographically it is related to MAXILLARY NERVE, but functionally it is connected to the FACIAL NERVE.
• The motor or the parasympathetic root is formed by the nerve of pterygoid canal. It carries preganglionic fibres of superior salibay nucleus through the nervus intermedius; facial nerve, and the nerve of pterygoid canal to reach the ganglion. The postganglionic fibres supply the lacrimal glands, mucous glands of nose, paranaska sinuses, the palate and the nasopharynx.
The sympathetic roots is also derived from nerve of pterygoid canal. It carries post ganglionic fibres of superior cervical sympathetic ganglion to supply the nose, the paranasal sinuses, the palate and the nasopharynx.
The sensory root comes from maxillary nerve and continues as branches of the nerve.
D. Submandibular Ganglion:
• Topographically it is related to LINGUAL NERVE but functionally it is connected to FACIAL NERVE.
• It is relay station for secretomotor fibres to the submandibular and sublingual glands.
• The parasympathetic preganglionic fibres that arise in the superior salivatory nucleus pass through the facial nerve, the chords tympani, and the lingual nerve to reach the ganglion.
• Post ganlionic fibres for the submandibular gland reach through branches of the ganglion. Post ganglionic fibres for the sublingual and anterior lingual gland are supplied through lingual nerve
• The sympathetic fibres carries the post ganglionic fibres of superior cervical ganglion to supply the submandibular and sublingual glands.
(Note: Sympathetic fibres pass through the submandibular ganglion without relay)
E. Otic Ganglion:
• Topographically it is related to MANDIBULAR NERVE, but functionally it is a part of the GLOSSOPHARYNGEAL NERVE.
• It is situated in the infratemporal fossa, just below the foramen ovale and surrounds the origin of nerve to medial pteygoid.
• The preganglionic Parasympathetic fibres from the inferior salivary nucleus are passed through the glossopharyngeal nerve, its tympanic branch, the tympanic plexus and the lesser petrosal nerve to reach the ganglion. The post ganlionic fibres reach the parotid gland through auriculotemporal nerve.
F. Geniculate Ganglion
• The geniculate ganglion is located on the first bend of the facial nerve. It is sensory ganglion.
• The taste fibres present in the nerve are peripheral processes of pseudounipolar neurons present in the geniculate ganglion.
(Note: The three ganglion associated with facial nerve are geniculate, submandibular and pterygopalatine)
SYMPHATHETIC GANGLION
G. Superior Cervical Ganglion
• It is spindle shaped and largest of all the three ganglia.
• It is formed by fusion of upper and cervical ganglia.
• Communications are with 9th, 10th, and 12th cranial nerves and with the external and recurrent laryngeal nerves.
H. Middle Cervical Ganglion
• Smallest cervical ganglion
• Formed by fusion of 5th and 6th cervical ganglia.
• Communications are through thyroid, tracheal, esophageal and middle cervical cardiac branches.
• It is connected with the inferior cervical ganglion directly and also through a loop that winds round the subclavian artery. This loop is Ansa Subclavia.
I. Inferior Cervical Ganglion
• It is often fused with the first thoracic ganglion and is known as cervicothoracic ganglion.
• It is also called the stellate ganglion because it is star shaped.
• It is formed by fusion of 7th and 8th cervical ganglia.
• Communications are through vertebral, subclavian and inferior cervical cardiac branches.
Source: Dental Pulse- MCQS for Dental PG Entrance Examinations. Volume 1 11th edition.