


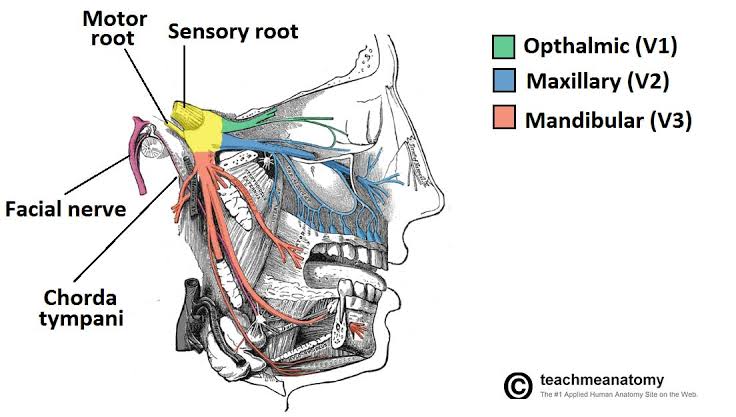

References- Shafers book of oral pathology 3rd edition
– a.k. tripathi for general medicine 3r





References- Shafers book of oral pathology 3rd edition
– a.k. tripathi for general medicine 3r




Reference- shafers book of oral pathology 3rd edition
It is the persistent inflammation and necrosis of liver for 6 mnths.

Reference- a.k. tripathi for medicine

Clinical Features:-
Treatment:-
Prophylaxis:-

Reference- a.k. tripathi for medicine
EPILEPSY Defn.– Any disorder characterized by recurrent seizures due to underlying chronic disease.
So broadly there are 2 types of epilepsy:-
Partial can be further divided into:-
Generalized can be divided into:-


Reference-
A.K.Tripathi for general medicine 3rd edition

Reference:-
A.K. Tripathi 3rd edition



Reference- Essential of oral pathology Purkait 3rd edition

Hypocalcemia and Hypercalcemia are the two important metabolic disorders of calcium.
Hypocalcemia- decrease in serum calcium level below 9.2 mg/dl
Hypercalcemia-increase in serum calcium level above 10.5mg/dl
So lets study them by comparing their features.


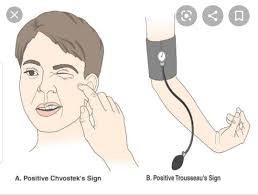
Chvostek’s sign-contraction of facial muscles on tapping over facial nerve branches.
Trousseau’s sign-Appearance of carpal spasm when sphygmomanometer cuff inflated above systolic blood pressure.
Both the signs are seen in hypocalcemia.
Reference- A.K.Tripathi oral medicine for dental students 3rd edition
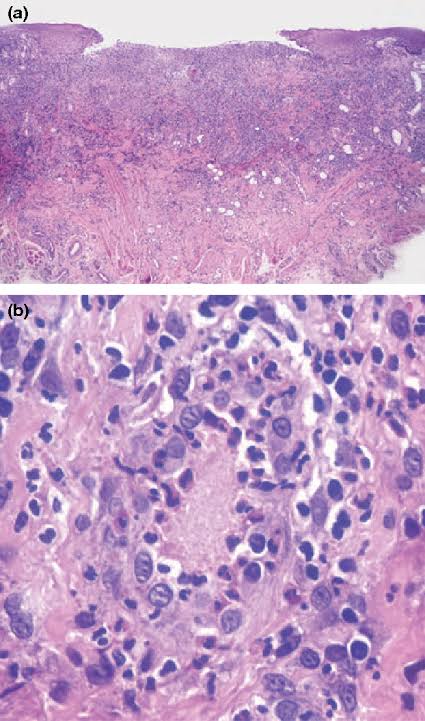
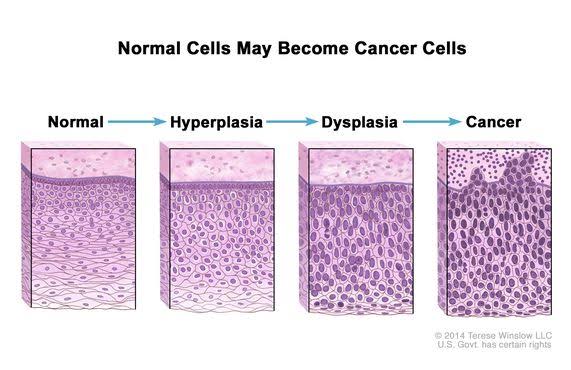
Dysplasia defn- Characterized by loss of uniformity of individual cells and loss of their architectural orientation.
At cellular level- known as atypia
At tissue level-dsyplasia


References- Shafers book of oral pathology 9th edition
Essentials of Oral pathology-Purkait 3rd edition



