Reference- carranza’s clinical periodontology 3rd south asian edition
Author: sakshibhude
Notes on Periodontal Examination
Reference- Carranza’s clinical periodontology 3rd south asian edition

HEALTHY GINGIVA VS GINGIVITIS


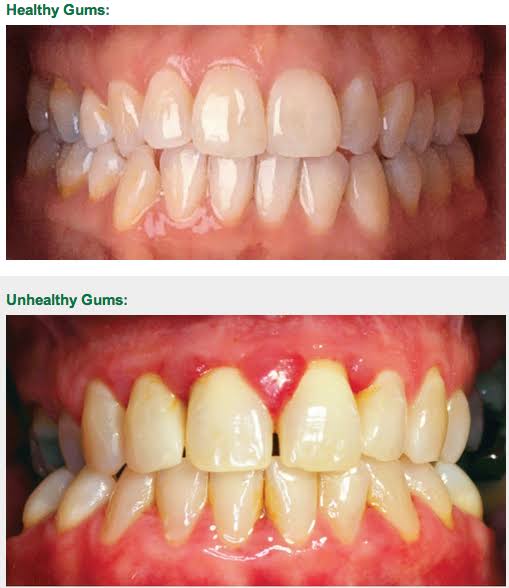
Reference – Carranza’s clinical periodontology(3rd south asian edition)
NOTES ON LOCAL ANAESTHESIA
Reference- Neelima Malik oral surgery
INFERIOR ALVEOLAR NERVE BLOCK




Reference- Handbook of local anaesthsia by Stanley F. Malamed
ANTERIOR ALVEOLAR NERVE BLOCK



Reference-
Handbook of local anaesthesia by Stanley F. Malamed
POSTERIOR SUPERIOR ALVEOLAR NERVE BLOCK



Reference-
Handbook of local anaesthesia by Stanley F. Malamed
CONGENITAL HEART DEFECTS
Defn and classification:-

Ventricular Septal Defect


Atrial Septal Defect

Patent Ductus Arteriosus

Teratology of Fallot (imp saq)

Reference- a.k. tripathi for general medicine

ADAMS CLASP
Clasps are the retentive components of the removable appliances.

Mode of action-
- Clasps act by engaging certain areas of teeth called the undercuts.
- Two types of undercuts are found in natural dentition
- Buccal and lingual cervical
- Mesial and distal proximal
- Adams clasp engages the mesial and distal proximal undercuts.
Adams clasp also called as universal clasp, liverpool clasp and modified arrowhead clasp.
Parts of adams clasp-
- Two arrowheads
- Bridge
- Two retentive arms
Advantages of adams clasp-
- Rigid and offers excellent retention
- Fabricated on deciduous and permanent dentition
- Can be fabricated on fully or partially erupted tooth
- Can be used on molars, premolars and incisors.
- Small and occupies minimum space
- Can be modified in many ways.
- Universal pliers can be used for fabricating.
Modifications of adams clasp-
- Adams with single arrowhead
- Adams with J hook
- Adams with incorporated helix
- Adams with additional arrowhead
- Adams on incisor and premolars
- Adams with distal extension
Reference- Bhalajhi 7th edition
STEPS IN FABRICATION OF ADAMS CLASP
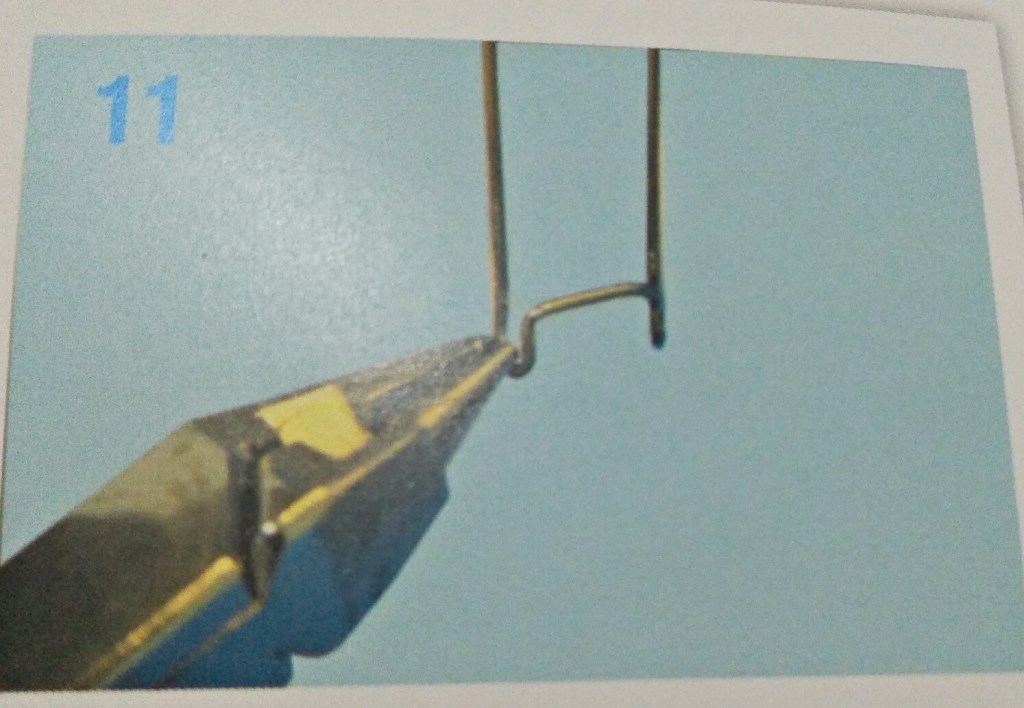
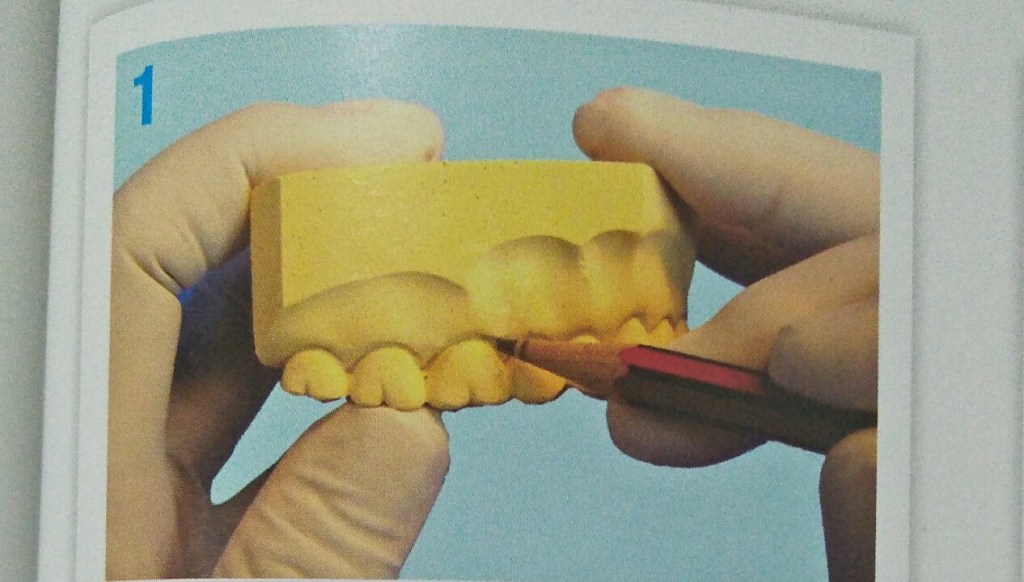
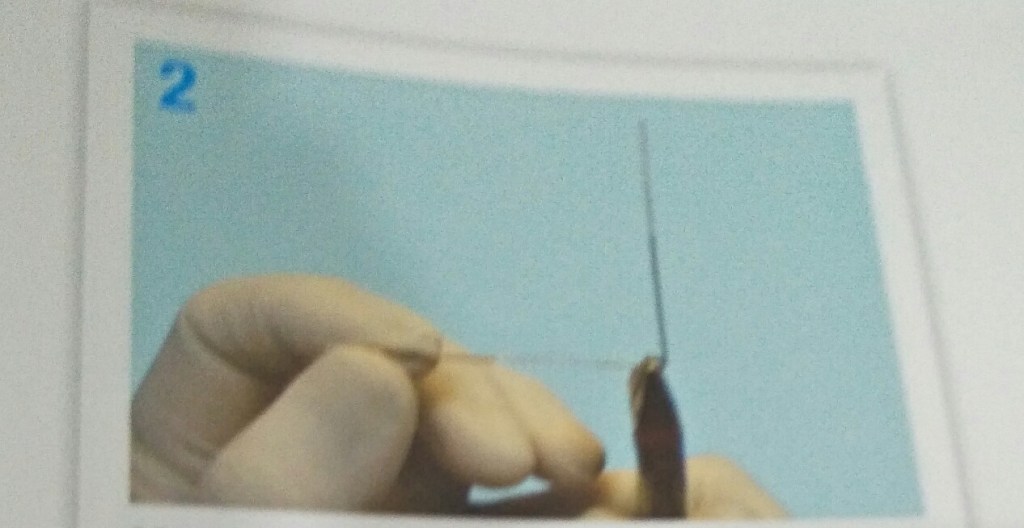

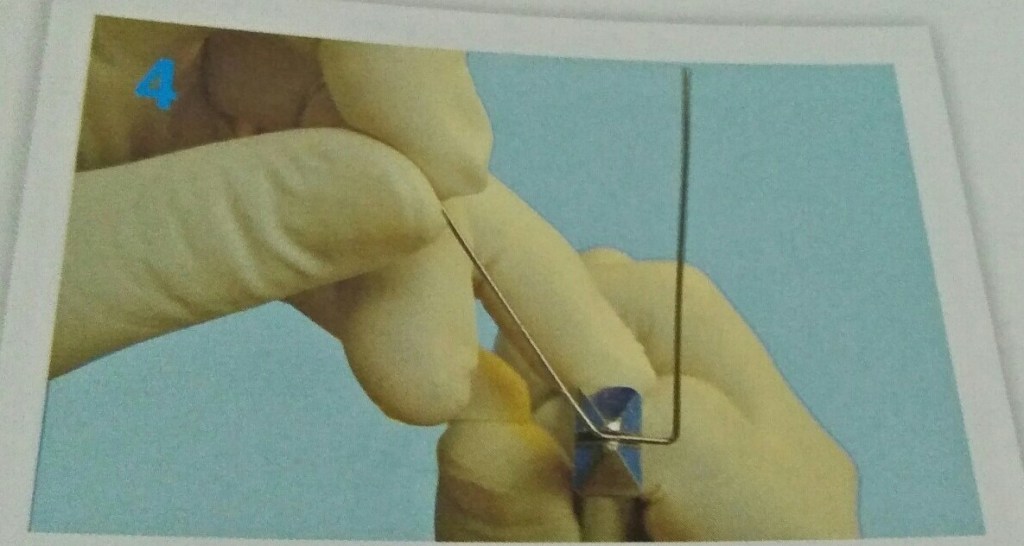





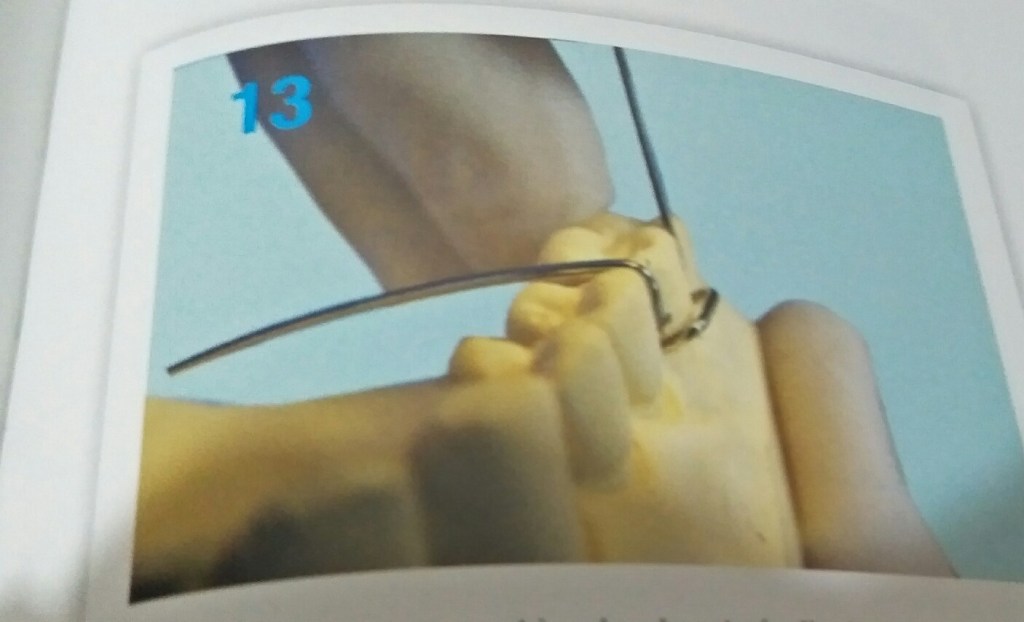

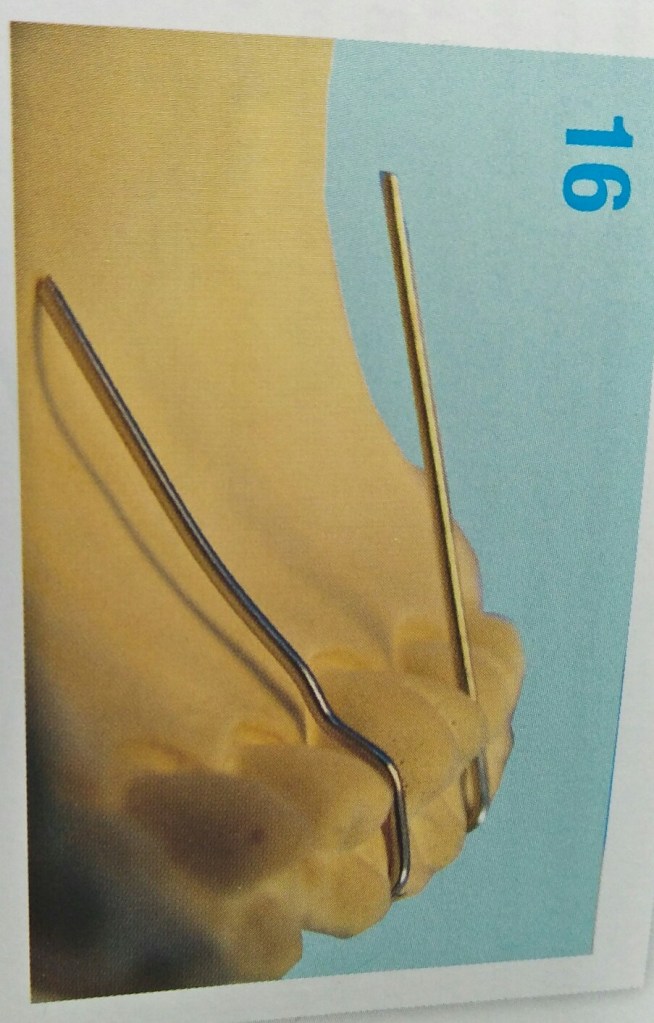
3 things to be noted after the clasp is placed on tooth:-
- When viewed from occlusal aspect bridge is parallel to buccal aspect.
- Bridge to be at 45 degree to long axis of tooth.
- When viewed from buccal aspect parallel to occlusal surface.
Reference- bhalajhi ortho