

REFERENCE:
Pharmacology 4th Ed: Tara V Shanbhag, Smita Shenoy


REFERENCE:
Pharmacology 4th Ed: Tara V Shanbhag, Smita Shenoy


REFERENCE:
Pharmacology 4th Ed: Tara V Shanbhag, Smita Shenoy


Pharmacology 4th Ed: Tara V Shanbhag, Smita Shenoy

ADVERSE EFFECTS:
Less effective & less tolerated than PPI’s
Cimetidine:- Short duration of action; Enzyme inhibiror, increases plasma concentration of co-administrated drugs; Crosses BBB & produce CNS effects (confusion, headache, hallucinations); Increases plasma prolactin level, cause menstrual irregularities & galactorrhoea in women, gynaecomastia, oligospermia & impotence in men.
Other adverse effects:
Constipation, diarrhea, dry skin, tinnitus, nausea, vomiting etc.
REFERENCE:
Pharmacology 4th Ed: Tara V Shanbhag, Smita Shenoy
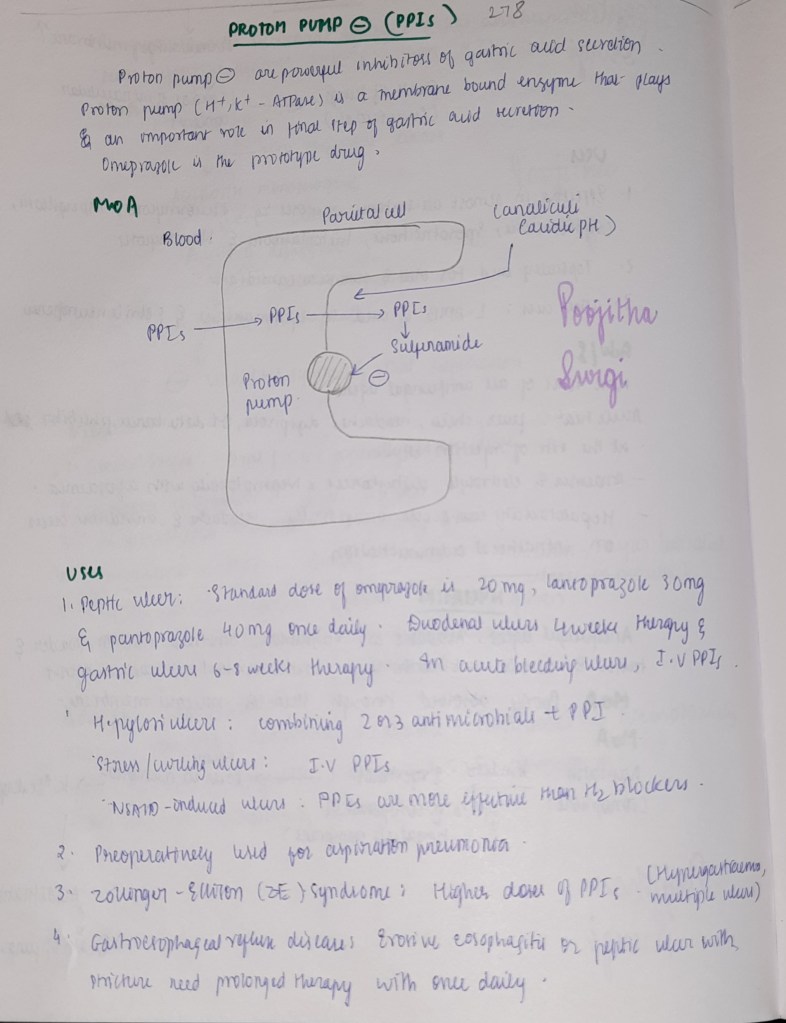

Pharmacology 4th Ed: Tara V Shanbhag, Smita Shenoy


Pharmacology 4th Ed: Tara V Shanbhag, Smita Shenoy

Pharmacology 4th Ed: Tara V Shanbhag, Smita Shenoy

Pharmacology 4th Ed: Tara V Shanbhag, Smita Shenoy
It is a sulphone, oldest and cheapest ; most widely used for leprosy
MECHANISM OF ACTION

ADVERSE EFFECTS
Dose related hemolytic anemia in G6PD deficiency,
OTHERS: Anorexia, Nausea, Vomiting, Fever, Headache, Allergic dermatitis, Itching, Peripheral neuropathy, Methaemoglobin
Exacerbation of lesions- ‘ sulphone syndrome‘:- fever, dermatitis, pruritis, lymphadenopathy, methaemoglobinaemia, anemia, hepatitis
PHARMACOKINETICS
🟡 Given orally
🟡 almost completely absorbed from gut
🟡 bound to plasma proteins
🟡 widely distributed in in body and concentrated in infected skin, muscle, liver, kidney
🟡 partly secreted in bile and undergoes enterohepatic cycling
🟡 metabolized by acetylation and metabolites are excreted in urine
Reference:
Pharmacology 4th Ed: Tara V Shanbhag, Smita Shenoy


REFERENCE:
Pharmacology 4th Ed: Tara V Shanbhag, Smita Shenoy