Classification of Bone pathology:-


Regards:-
Kriti Naja Jain 🙂
Reference :-
Neville oral and maxillofacial pathology 3rd e
Classification of Bone pathology:-


Regards:-
Kriti Naja Jain 🙂
Reference :-
Neville oral and maxillofacial pathology 3rd e
•Alcohol is one of the most common cause of chronic liver disease worldwide,the consumption continuing to increase in many countries.
•Chronic and excessive alcohol ingestion is a major cause of liver disease and is responsible for nearly 50% of the mortality from all cirrhosis.
•Patients with alcoholic liver disease (ALD) may also have risk factors for the other diseases (eg :- coexisting NAFLD or chronic viral hepatitis infection), and these may interact to increase disease severity.

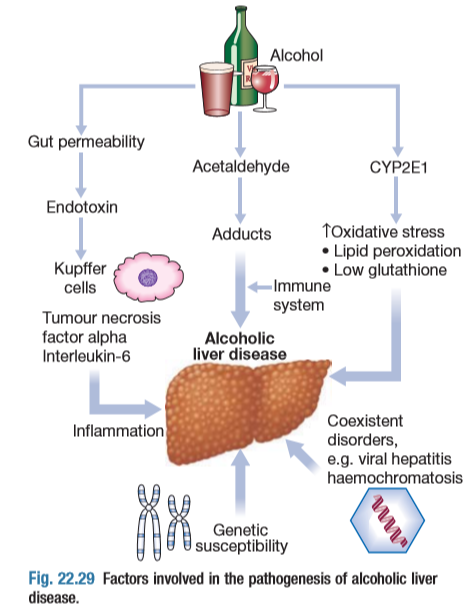
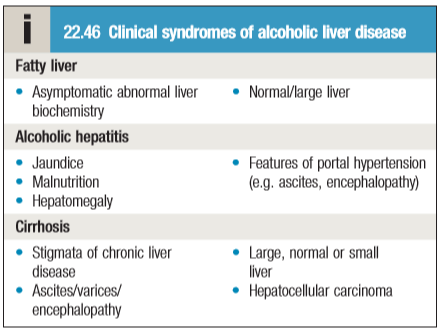
•Three types of ALD are recognised ,but these overlap considerably ,as do the pathological changes seen in the liver.





Thank you,
Kriti Naja Jain 🙂
Reference:-
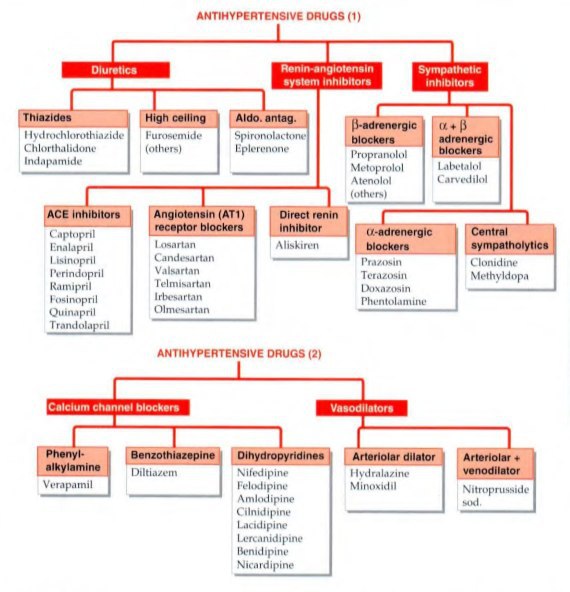
The objective of antihypertensive therapy is to reduce the incidence of adverse cardiovascular events, particularly CAD stroke and heart failures.
Here , we discuss some side effects of the Major drugs which is mainly prescribed for the treatment:-





The choice of antihypertensive therapy is initially indicated by the patient’s age and ethnic background.

Comorbid conditions also have an influence on initial drug selection,for example:-
•beta blocker might be the most appropriate treatment for a pateint with angina.
•Thiazides diuretics and dihydropyridines calcium channel blockers antagonists are the most suitable drugs for treatment in older people.
Thank you,
Regards,
KRITI Naja Jain 🙂
REference:-
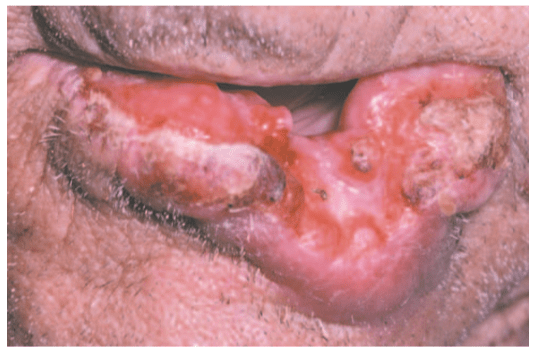

ETIOLOGY:-
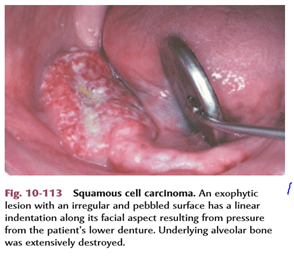

● Exophytic (mass forming; fungating, papillary, verruciform)
● Endophytic (invasive, burrowing, ulcerated)
● Leukoplakic (white patch)
● Erythroplakic (red patch)
● Erythroleukoplakic (combined red-and-white patch)

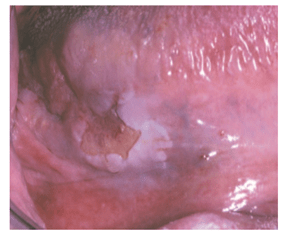
Tumor size and the extent of metastatic spread of oral squamous cell carcinoma are the best indicators of the patient’s prognosis. Quantifying these clinical parameters is called staging the disease.
The most popular staging protocol, the tumor-node-metastasis (TNM) system.
This staging protocol depends on three basic clinical features:
1. T—Size of the primary tumor, in centimeters
2. N—Involvement of local lymph nodes
3. M—Distant metastasis
The American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) designated staging by TNM Classification was used.
TNM clinical classification:-


Features are:-
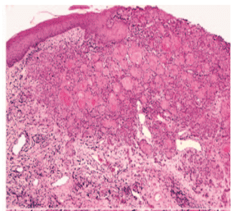
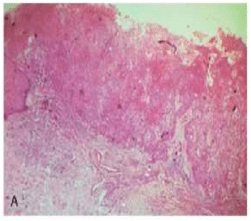
* a system of grading tumours in which a grade 1 lesion was highly differentiated (its cells were producing much keratin), while grade 4 was very poorly differentiated (the cells were highly anaplastic and showed no keratin formation).

I-WELL DIFFERENTIATED:
-consists of sheets and nests of cells
-cells are generally large
– intercellular bridges or tonofibrils are not demonstrated.
-The nuclei are large and demonstrate variability in the intensity of the staining reaction.
-Nuclei that stain heavily with hematoxylin are referred to as hyperchromatic.
-mitotic figures may be found(Many of these mitotic figures are atypical.)
-the most prominent features of the welldifferentiated epidermoid carcinoma is the presence of individual cell keratinization-the formation of numerous epithelial or keratin pearls of varying size.
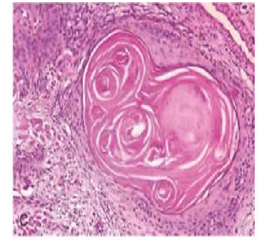
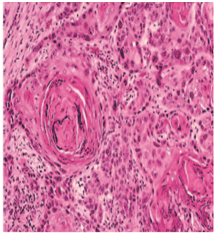
II– ModeratelyDifferentiated epidermoid carcinomas:
– lose certain features so that their resemblance to squamous epithelium is less pronounced
-The characteristic shape of the cells and their arrangement may be altered.
– The growth rate of individual cells is more rapid,
– the greater number of mitotic figures,
– even greater variation in sizes, shape and tinctorial reaction,the failure to carry out the function of a differentiated squa- mous cell, the formation of keratin.
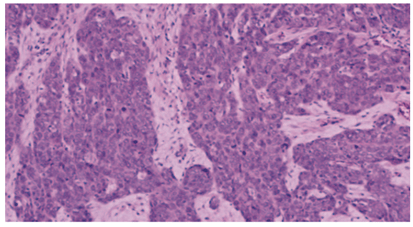
III-POORLY DIFFERENTIATED TYPE:
-bear little resemblance to their cell of origin
-will often present diagnostic difficulties because of the primitive and uncharacteristic histological appearance of malignant,
-rapidly dividing cells
– cells show an even greater lack of cohesiveness and are extremely vagarious.

2.JAKOBSS0N’s GRADING SYSTEM:-
-In 1973, Jakobsson et al developed a multifactorial
grading system which had the advantage of scoring tumour-host interactions and tumour characteristics, but eventually proved to be useful only when applied to tongue cancers.
-Parameters used in Jakobsson’s method are:-
i- KRE- keratinization
ii-NP- nuclear pleomorphism
iii-MIT-mitosis
iv-POI- pattern of invasion
v-LPR- lympho-plasmocyticrspon
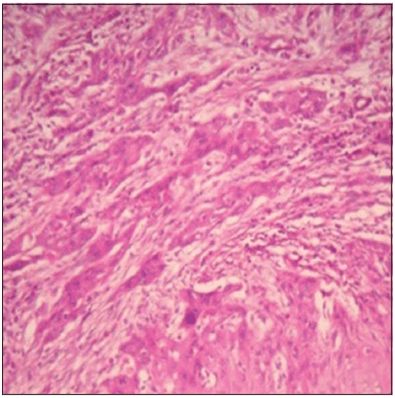
-Similar findings were observed in Anneroth and Hansen’s grading where the criteria were similar except that the parameter vascular invasion (VI) was omitted.
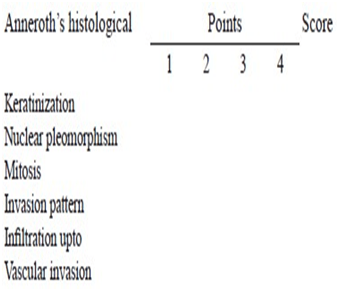
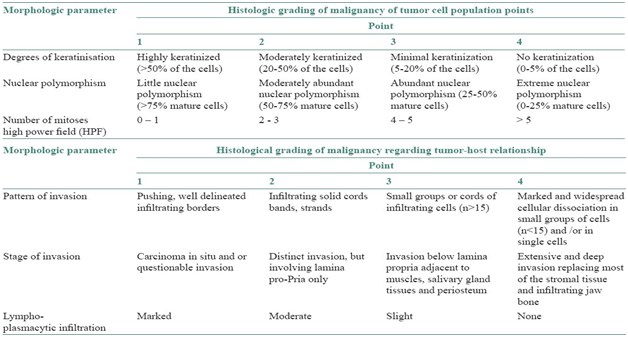
3-Anneroth’s classification:
Anneroth’s classification (multifactor grading system)
-According to the classification, three parameters reflecting tumor cell features including keratinization, polymorphism, and mitoses were evaluated in the whole thickness of the tumor and each was scored from 1 to 4. Mode of invasion and inflammatory infiltration representing tumor-host relationship were graded in the most invasive margins and scored from 1 to 4:
-Variables such as:-
i-pattern of invasion,
ii- tumor thickness,
iii-degree of keratinization,
iv-nuclear pleomorphism,
v-lymphocytic response,
vi-mitotic rate
4.BRYNE’S GRADING SYSTEM:-
-Bryne et al (1989) modified Anneroth’ s grading system and developed a malignancy grading focusing on the invasive front of the tumour.
– This method of grading appeared to be less time-consuming in the assessment of the neoplasm.
-Nevertheless, this system is not sufficiently homogeneous to allow grading parameters to be assessed individually
-This was performed at the invasive tumor front (ITF).
-The Bryne’s grading system is more predictive for LNM as compared with the multifactorial grading systems that is, Jakobsson’s and Anneroth and Hansen’s. Broder’s grading system is of no prognostic value.
-Parameters used are:-
i-Keratinisation
ii-nuclear polymorphism
iii-mitosis
iv-pattern of invasion
v-lympho-plasmocytic response
vi-lymph nodes
REFERENCES :
| 1.Comparative study of various grading systems in oral squamous cell carcinoma and their value in predicting lymph node metastasis |
| Saleha Jamadar1, TV Narayan1, Balasundari Shreedhar2, Leeky Mohanty1, Sadhana Shenoy1 1 Department of Oral Pathology and Microbiology, The Oxford Dental College, Hospital and Research Centre, Bommanahalli, Bengaluru, Karnataka, India 2 Department of Oral Pathology and Microbiology, Career Dental College, Lucknow,Uttar Pradesh, India |
2.A study on histological grading of oral squamous cell carcinoma and its co-relationship with regional metastasis
M Akhter, S Hossain, Quazi B Rahman, Motiur R Molla
Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Bangabandhu Sheikh Mujib Medical University, Dhaka, Bangladesh
3.Shafer’s Textbook of Oral Pathology,8e
4.NEVILLE -Oral & Maxillofacial Pathology,3e






Reference:-
2. Shafers 8th e
3. Neville 3rd e