

Sources: Sturdevants 7th edition


Sources: Sturdevants 7th edition
Several modifications have been proposed for in class II cavity design for amalgam restorations . These modifications are changes from the classic preparation design . They are indicated for those situations which are not ideal. Modifications are based on following factors:
MODIFICATIONS :
2. SLOT PREPARATION : It is similar to class V amalgam cavity preparation except that it is done on the proximal surface of the tooth. It is indicated in proximal root surface caries with gingival recession. The design is similar to that of the slot preparation except it is approached from the facial aspect without disturbing the contact area.
3. CONSERVATIVE DESIGNS : It is recommended in all posterior teeth where caries incidence is very low and all occlusal pits and fissures are not involved. The conservative design preserves all the remaining sound tooth structures such as transverse ridge or oblique ridge and thereby protects the cuspal strength .
4. MODIFICATIONS TO PRESERVE ESTHETICS : To preserve the esthetics in the critical area during a mesio-occlusal cavity preparation , the facial wall of the mesial box should be prepared straight , i.e parallel to the long axis of the tooth rather than gingivally divergent . Another modification is to avoid breaking the facial contact whenever caries is limited only to the mesio-lingual embrassure.
5. MODIFICATIONS OF ROTATED TEETH : Depending on the degree of rotation , the proximal box is displaced facially or lingually.
6. ADJOINING RESTORATIONS : The intersecting margins of the two restorations -should be at right angles . Care should be taken so as to prepare the outline of the new cavity without weakening the amalgam margin of the existing restoration .
7. MODIFICATIONS FOR ABUTMENT TOOTH: The facial and lingual walls of the proximal box must be extended more so that the entire rest seat can be prepared in the amalgam without encroaching on the occlusal margins.
The pulpal floor is deepend an extra 0.5 mm apical to the region of the rest seat so as to provide an adequate thickness of amalgam.
8. CUSP CAPPING : It is indicated where there are extensive caries underneath the cusps and facio-lingual extensions of the occlusal preparation is more than 2/3rd the distance between the facial and lingual cusp tips. For cusp capping 1.5 to 2 mm of cusp reduction is necessary . The reduced cusps must meet the adjacent unreduced cusp at 90 degree cavosurface angle to provide both adequate edge strength of amalgam.
References: STURDEVANTS 7TH EDITION
LASER: Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation .Laser dentistry is easier, more precise ,less traumatic for patients . Lasers provide a state-of-the-art approach for modern dentistry.
DISCOVERY : It was discovered by Shallow and Towns on 1958. First working laser was built by Maiman of Hughes research laboratory in 1960.
COMPONENTS OF LASER :
BASIC PRINCIPLES OF LASERS
LASER TISSUE INTERACTION :
TYPES OF LASERS :
1.BASED ON WAVELENGTH :
2. BASED ON TARGET TISSUE
LASER APPLICATION IN CONSERVATIVE DENTISTRY :
REFERENCES: STURDEVANTS 7TH EDITION
DENTIN HYPERSENSITIVITY :It is characterized by short , sharp pain arising from exposed dentin in response to stimuli typically thermal , chemical, osmotic, evaporative, tactile and which cannot be ascribed to any other form of dental defect or pathology.
ETIOLOGY :
ENAMEL LOSS :
CEMENTAL LOSS:
DEVELOPMENT OF DENTIN HYPERSENSITIVITY
There are two phases in the devlopment of dentin hypersensitivity .
Several theories have been put forward to explain the dentin hypersensitivity.
CLINICAL FEATURES:
DIAGNOSIS :
CASE HISTORY :
CLINICAL EXAMINATION :
PREVENTION :
MANAGEMENT :
DESENSITIZATION BY OCCLUDING DENTINAL TUBULES :
DESENSITIZATION BY BLOCKING PULPAL SENSORY NERVES
REFERENCE: STURDEVANTS 7TH EDITION
One of the basic goals of conservative dentistry is to preserve the health of the pulp as it is subjected to many insults such as caries, trauma, operative procedures, restorative materials.
Pulpal irritants can be classified as microbial, mechanical, chemical, thermal.
NEED FOR PULP PROTECTION
PULP PROTECTIVE AGENTS
CLASSIFICATION
CAVITY SEALERS: These are materials that provide a protective coating to the walls of the prepared cavity .They are applied to all the walls of the cavity and seal the interface between the restoration and the tooth . Eg: cavity varnish and resin bonding agents.
CAVITY VARNISH: A varnish is a natural gum or a synthetic resin dissolved in an organic solvent . Once it is applied to tooth surface the organic solvent evaporates leaving behind a protective film. Varnish is used beneath amalgam restoration to seal the amalgam tooth interface until corrosion product form to reduce the marginal gap. Thickness of varnish is 2-5 micrometer . They does not provide thermal protection and are contraindicated for GIC .
RESIN BONDING AGENTS: Currently the best method for the bonding composite resin to the tooth structure. Apart form adhesion it also provides cavity sealing. They are also employed for bonding amalgam restorations to reduce micro leakage .
CAVITY LINERS :They are used to provide a barrier against the passage of irritants from the cements or other restorative materials and to reduce the sensitivity of freshly cut dentin . They are usually suspension of calcium hydroxide in a volatile solvent . TYPES : TYPE III GIC , TYPE IV ZOE . Thickness is 0.5 mm
CAVITY BASES: A base is a layer of cement placed beneath the permanent restoration to encourage recovery of the injured pulp and to protect it against numerous types of insults. TYPES : high strength bases and low strength bases .
HIGH STRENGTH BASES provide thermal protection for pulp and mechanical support for the restoration . Eg : zinc phosphate , zinc polycarboxylate, RMGI, GIC
LOW STRENGTH BASES have minimum strength and rigidity . act as a barrier to irritation , chemicals and to provide therapeutic effect to pulp.Eg calcium hydroxide . ZnOE .
REFERENCE : STURDEVANT’S 7TH EDITION
ASHTINDER 🖊
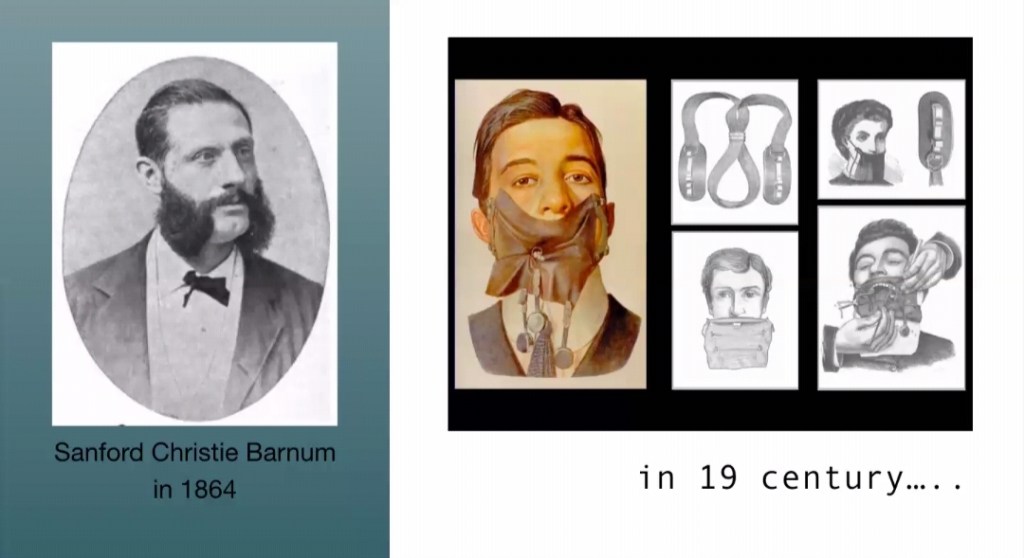
It’s hard to believe that a sheet of rubber can make you feel more comfortable during a dental treatment and allow dentists to do better, but a “RUBBER DAM” can . S.C. BARNUM
It is a direct method of isolation. It is a safeguard against the bacterial contamination from saliva and accidental swallowing of instruments.
HISTORY :

ADVANTAGES:
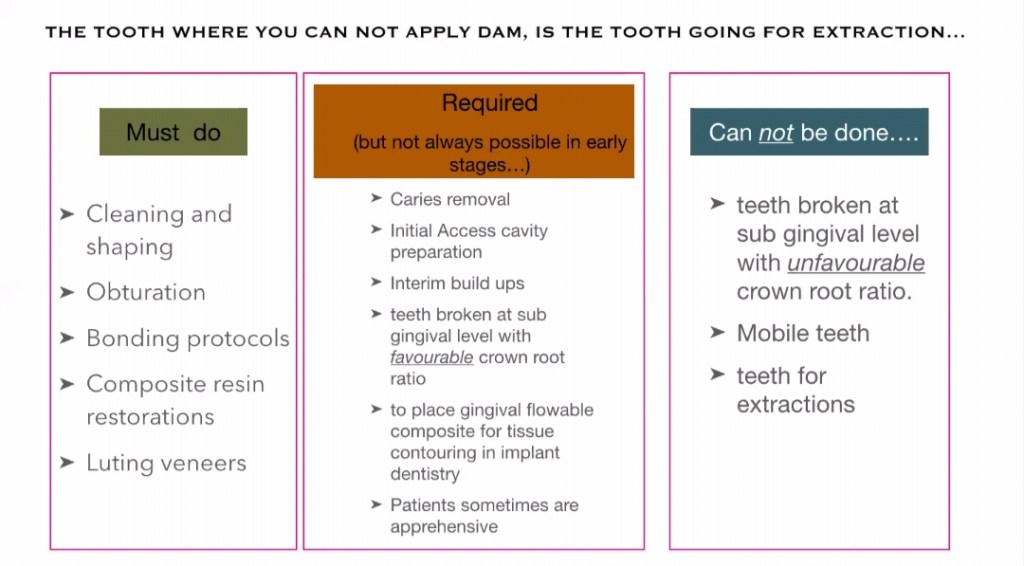
INDICATIONS:
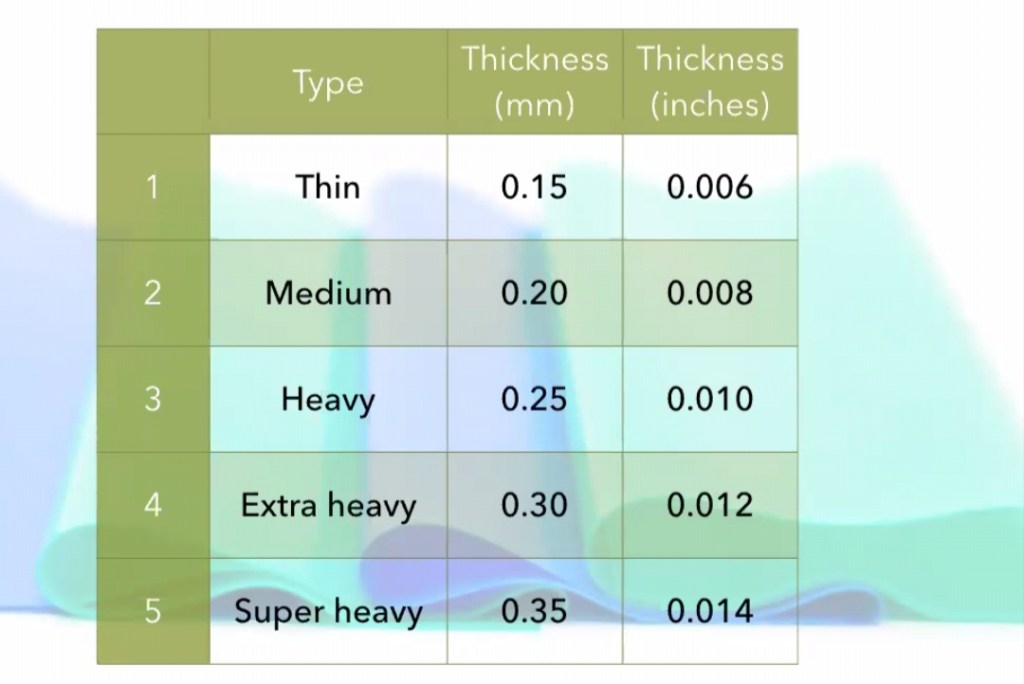
ARMAMENTARIUM:
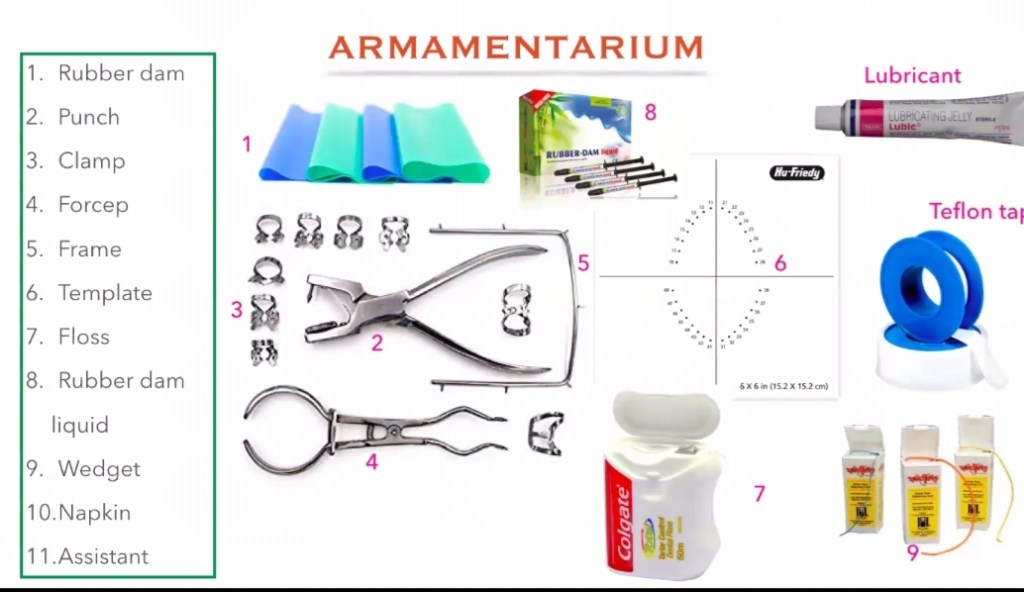
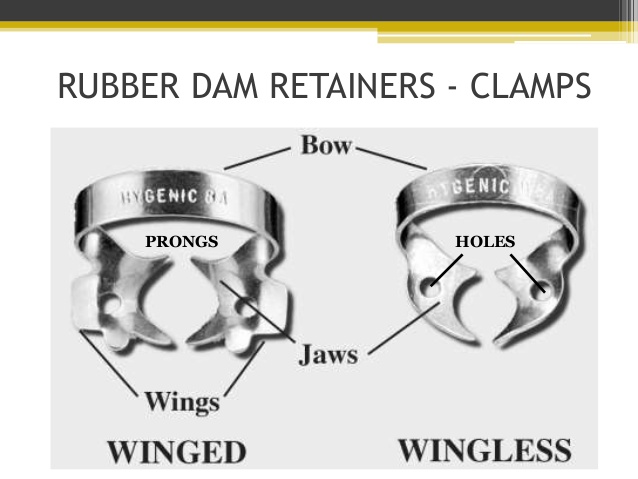
2, RUBBER DAM CLAMPS:
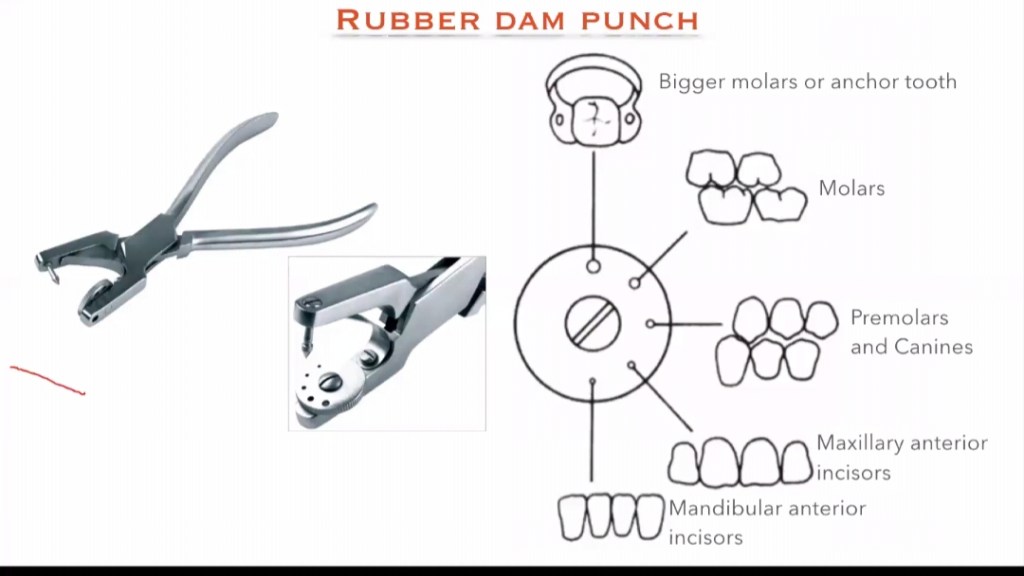
3. RUBBER DAM PUNCH :
It is an instrument which have a metal table and a tapered , sharp, pointed plunger to produce clear cuts holes on the rubber dam sheet so that the teeth can be isolated. It is of 2 types: Single hole punch and multi hole punch.
4. RUBBER DAM FRAME:
5. RUBBER DAM FORCEPS:
6. RUBBER DAM TEMPLATE:
7. RUBBER DAM NAPKIN :
8. WEDGET CORDS:
9. FLOSS:
REFERENCE: GROSS-MAN’S ENDODONTIC PRACTICE 13TH EDITION .
Silver diammine fluoride, (SDF) is a topical medicament used to treat and prevent dental caries and relieve dentinal hypersensitivity. It is a colorless or blue-tinted, odourless liquid composed of silver, ammonium and fluoride ions at a pH of 10.4 . Ammonia compounds reduce the oxidative potential of SDF, increase its stability and helps to maintain a constant concentration over a period of time, rendering it safe for use in the mouth.Silver and Flouride ions possess antimicrobial properties and are used in the remineralization of enamel and dentin on teeth for preventing and arresting dental caries.
BRANDS AVAILABLE IN INDIA:
38% SDF solution, e-SDF , 5 ml Bottle, Kids-e-dental Llp,
INDICATIONS:
CONTRAINDICATIONS:
POSTER PRESENTATION ON SDF


We are at the peak of pandemic and it is challenging in many unprecedented ways.
We are in this together and we will get through this together . Here is a small initiative on our part to spread awareness about covid -19.
“STOP THE SPREAD OF VIRUS “

“STAY HOME, STAY SAFE”