Temporary anchorage devices enable controlled tooth movements such as anterior retraction, molar intrusion/distalization, nonsurgical open‑bite correction, and cant correction with simple placement, immediate loading, and minimal morbidity compared with plates or implants.
🔑 GENERAL PRINCIPLES
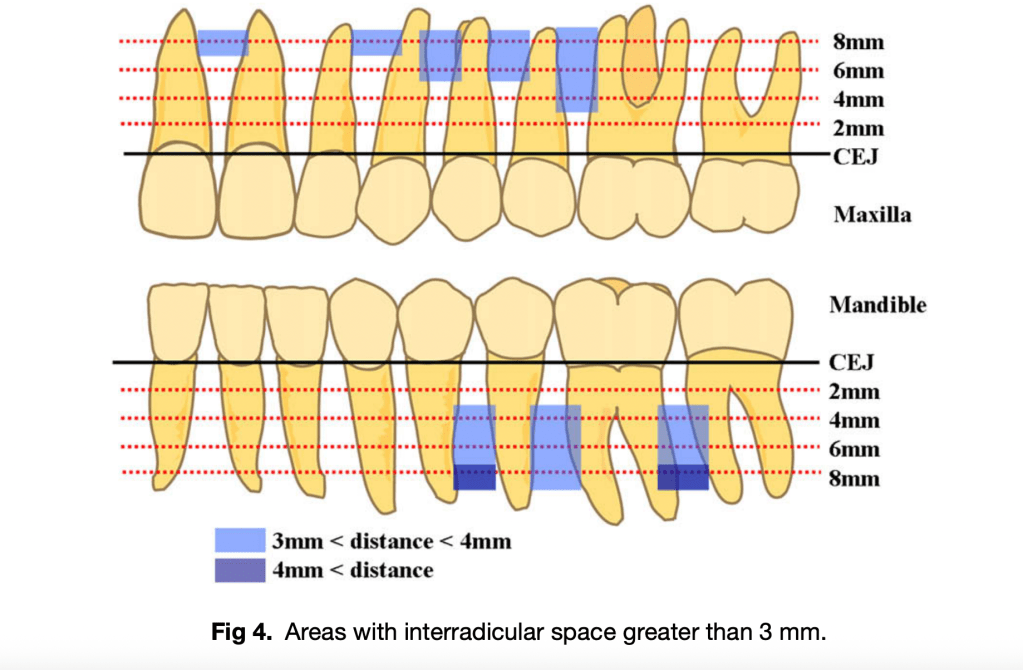
- Safe mesiodistal space: ≥ 3 mm between roots
- Safety depth (bone overlying narrowest interradicular area): ≥ 4 mm (ideally matching miniscrew length, 5–7 mm)
- Preferred vertical level: 4 mm from CEJ (attached gingiva zone)
- Anterior regions: Require subapical placement (≥ 6–8 mm from CEJ)
- Posterior regions: Often safe at 4 mm; angulation increases clearance and cortical support
- Placement angulation:
- Straight/perpendicular in premolar and subapical anterior regions
- Oblique/angulated in intermolar regions for safety
✅ COLOR LEGEND
- 🟢 SAFE: Adequate mesiodistal space (≥3 mm) & safety depth
- 🟡 CAUTION: Limited space; angulation or subapical placement needed
- 🔴 AVOID: Insufficient space, high root risk
📍 MAXILLA
| Region (Teeth) | Level from CEJ | Safety | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Central incisors | 8 mm | 🟡 | Subapical/equiapical only |
| Lateral incisor – Canine | 8 mm | 🟡 | Narrow at CEJ; safer apically |
| Canine – 1st premolar | 6 mm | 🟢 | Reliable site |
| 1st – 2nd premolars | 4 mm | 🟢 | Consistently safe |
| 2nd premolar – 1st molar | 4 mm | 🟢 | Best interdental space |
| 1st – 2nd molars | 4–6 mm | 🟡 | Angulated placement advised |
📍 MANDIBLE
| Region (Teeth) | Level from CEJ | Safety | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Anterior incisors | Any | 🔴 | Avoid interradicular; only true subapical |
| Lateral incisor – Canine | 4–6 mm | 🔴 | Space ❤ mm |
| 1st – 2nd premolars | 4 mm | 🟢 | Most reliable site |
| 2nd premolar – 1st molar | 4 mm | 🟢 | Consistently safe |
| 1st – 2nd molars | 4–6 mm | 🟢/🟡 | Safe; angulation may help for group distalization |

Reference:
Lee KJ, et al. Computed tomographic analysis of tooth-bearing alveolar bone for orthodontic miniscrew placement.AJODO. 2009;135:486–94.
🦷 CLINICAL MCQs – Miniscrew Placement (Based on Lee et al., AJODO 2009)
Section A – Clinical MCQs (Single Best Answer)
- A 25-year-old patient requires intrusion of maxillary central incisors. Based on CT evidence, the safest site for miniscrew placement is:
a) Between central incisors at 2 mm from CEJ
b) Between central incisors at 8 mm from CEJ
c) Between canine and 1st premolar at 2 mm from CEJ
d) Between 1st and 2nd molars at 2 mm from CEJ
Answer: b) Between central incisors at 8 mm from CEJ - In the maxilla, the largest interdental space was observed:
a) Between 1st and 2nd premolars at 4 mm
b) Between 2nd premolar and 1st molar at 8 mm
c) Between canine and 1st premolar at 2 mm
d) Between 1st and 2nd molars at 2 mm
Answer: b) Between 2nd premolar and 1st molar at 8 mm - Which mandibular region is considered most reliable for miniscrew placement at 4 mm from CEJ?
a) Between central incisors
b) Between 1st and 2nd premolars
c) Between lateral incisor and canine
d) Between canine and 1st premolar
Answer: b) Between 1st and 2nd premolars - Miniscrew placement in the mandibular anterior region is best achieved by:
a) 2–4 mm from CEJ in interradicular space
b) Subapical placement only
c) Angulated placement between central incisors
d) Placement between lateral incisor and canine at 6 mm
Answer: b) Subapical placement only
Section B – True / False
- Interradicular space greater than 3 mm is mandatory for safe miniscrew placement.
True - In the maxillary intermolar region, angulated miniscrew placement is recommended due to large safety depth but limited interroot space.
True - In the mandibular incisor region, sufficient interradicular space (>3 mm) is available at 4 mm from CEJ.
False - Buccal bone thickness is generally greater in posterior regions compared to anterior regions.
True - Panoramic radiographs are equally reliable as CT for identifying miniscrew safe zones.
False
Section C – Match the Following
| A (Region) | B (Safe placement level / guideline) |
|---|---|
| 1. Maxillary central incisors | a. 8 mm from CEJ (subapical/equiapical) |
| 2. Maxillary 1st–2nd premolars | b. 4 mm from CEJ |
| 3. Mandibular anterior incisors | c. Avoid interradicular; only subapical |
| 4. Mandibular 1st–2nd premolars | d. 4 mm from CEJ (safe site) |
| 5. Maxillary 1st–2nd molars | e. Angulated placement due to large safety depth |
Answer Key:
1–a, 2–b, 3–c, 4–d, 5–e
