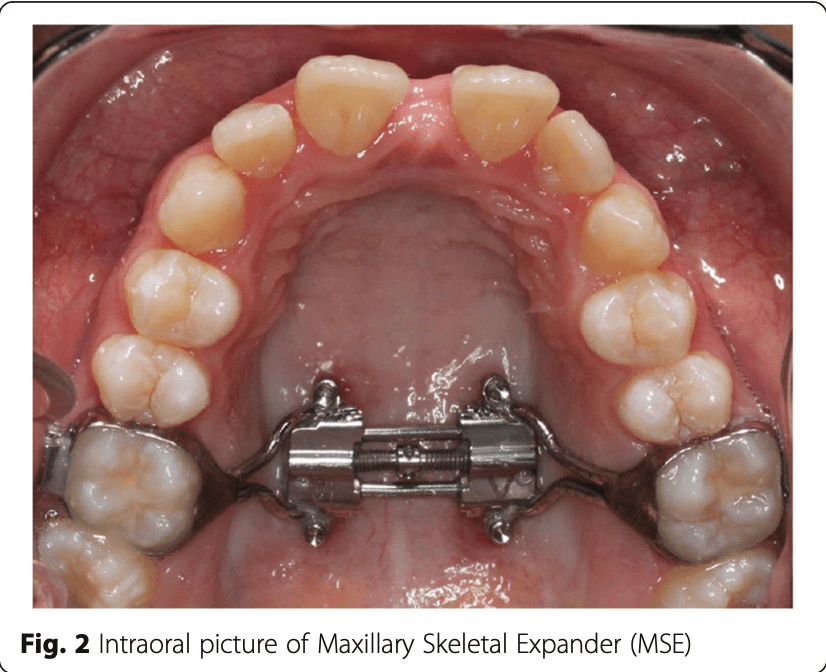
✅ Clinical Device
Maxillary Skeletal Expander (MSE)
- Type: Micro-implant-supported expander (MARPE)
- Anchorage: 4 bicortical miniscrews (palatal + nasal cortex)
- Placement: Posterior palate
- Expansion rate:
- 2 turns/day until diastema
- Then 1 turn/day
- Retention: ≥ 3 months post-expansion
📈 CBCT-Based Findings
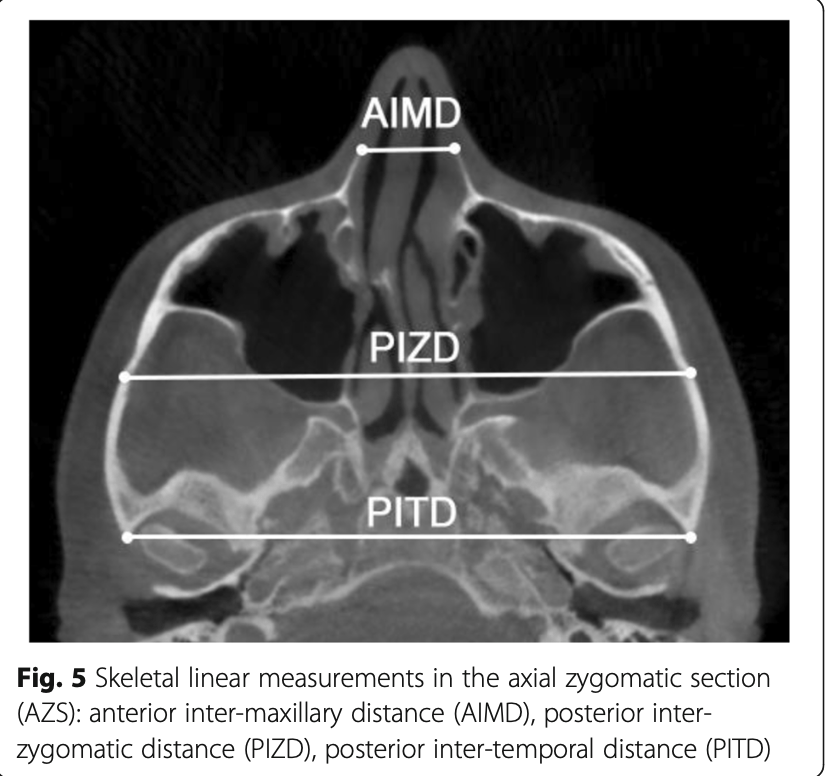
Linear Skeletal Changes
| Parameter | Mean Increase |
|---|---|
| Anterior Inter-Maxillary Distance (AIMD) | +2.76 mm |
| Posterior Inter-Zygomatic Distance (PIZD) | +2.40 mm |
| Posterior Inter-Temporal Distance (PITD) | Negligible |
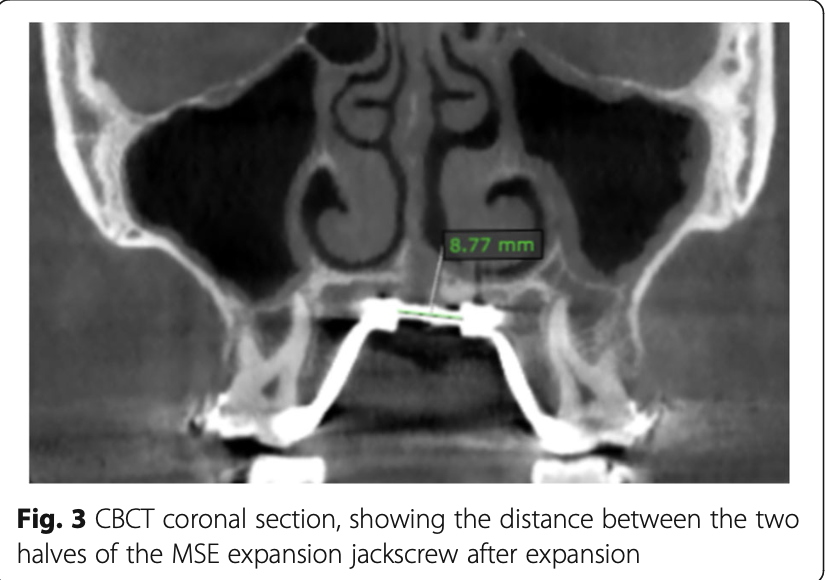
Angular Changes
| Parameter | Mean Increase |
|---|---|
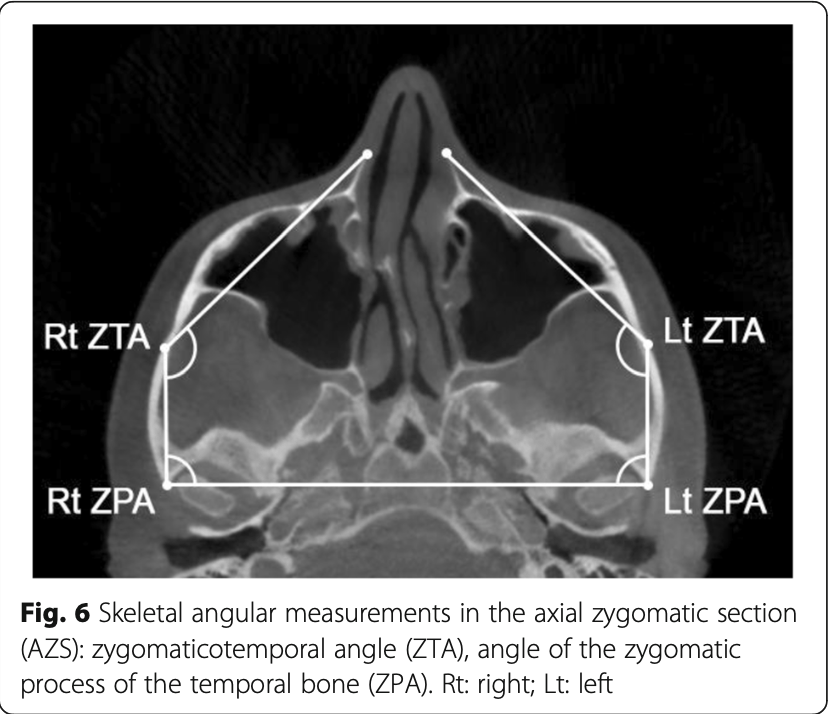
| Zygomatic Process Angle (ZPA) | Right: +1.7° Left: +2.1° |
| Zygomaticotemporal Angle (ZTA) | Negligible |
📌 Key Biomechanical Concepts
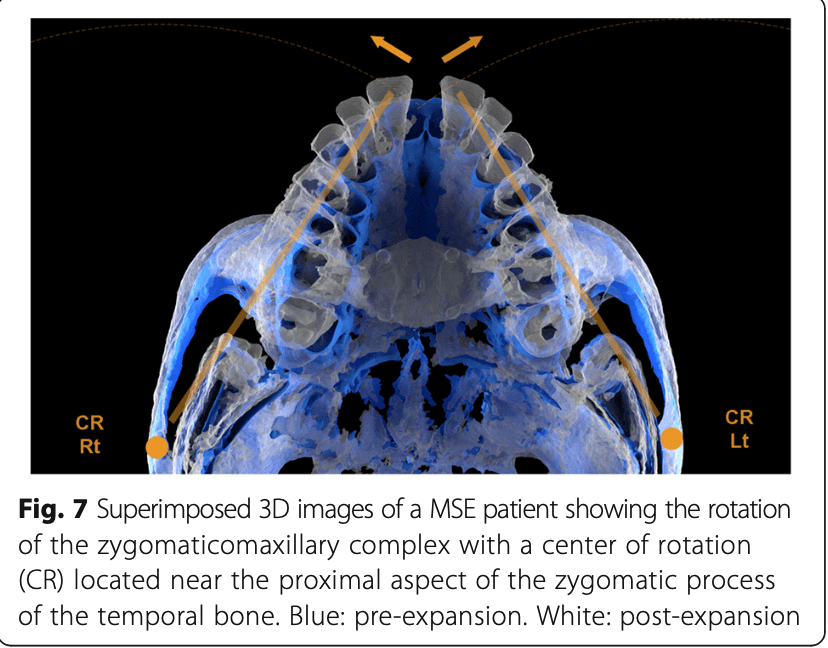
- Rotation Center:
Near the proximal zygomatic process of temporal bone
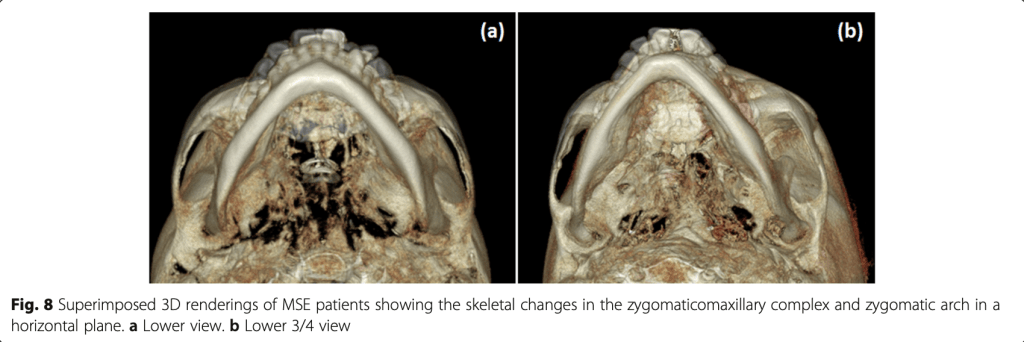
(more posterior/lateral than in tooth-borne expanders) - Movement Pattern:
Lateral + Forward movement of maxilla + zygomaticomaxillary complex - Bone Bending:
Occurs at zygomatic process of temporal bone (adaptive mechanism)
🔬 Clinical Implications
- Achieves parallel midpalatal suture opening
- Disarticulates pterygopalatine suture
- Minimal buccal tipping of molars
- Suitable for late adolescent to adult patients (13.9–26.2 yrs in study)
🧠 Quick Notes
- Use CBCT before & after expansion to analyze changes
- Avoid brackets/appliances until post-expansion imaging complete
- Monitor miniscrew engagement in both cortices on initial scan
📍 Source: Cantarella et al., Progress in Orthodontics, 2018
🧪 IRB Approved Study | UCLA Orthodontic Clinic
🔍 DOI: 10.1186/s40510-018-0240-2
SPOTIFY LINK: https://open.spotify.com/episode/4T9qeiRFJ99mZ3gdHnOA4c?si=OuVPNWyKRsmoJjtXUrhyRA
