A cyst was removed along with an unerupted third molar tooth. The pathologist reported a fibrous capsule that was myxoid in places and that was lined by a thin layer of squamous and cuboidal epithelium. The cyst originated from the amelocemental junction.
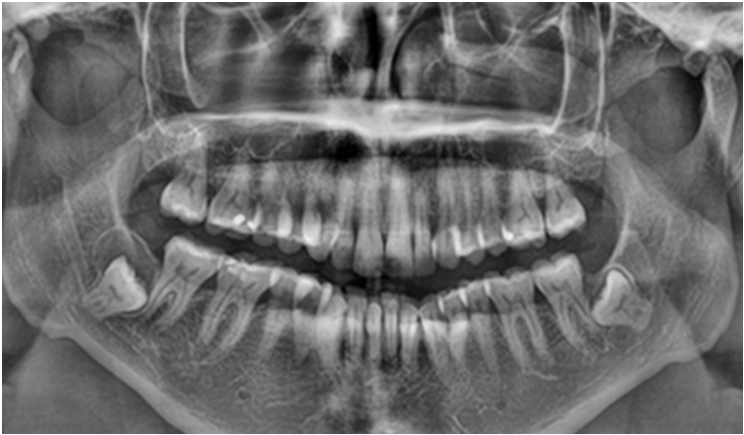
As a dental student, it’s important to have a good understanding of dentigerous cysts. Dentigerous cysts are a type of cyst that form around unerupted or impacted teeth. They develop from a structure called the dental follicle, which surrounds the tooth germ or the developing tooth.
When a tooth fails to erupt properly, sometimes a cyst can form around it. This cyst is called a dentigerous cyst. It is characterized by a fibrous capsule, which is like a protective layer, and it is lined by stratified squamous epithelium, which is a type of tissue that forms the outer layer of the cyst.
Histologically, dentigerous cysts may show various features such as the thickness of the epithelial lining or the presence of inflammation or keratinization. However, these features are not unique to dentigerous cysts and can also be seen in other types of cysts.
In terms of diagnosis, clinical features are important. Dentigerous cysts are usually discovered during routine dental exams or through radiographic evaluations. One of the key clinical features is that the cyst originates from the amelocemental junction, which is the junction between the enamel (the hard outer layer of the tooth) and the cementum (the specialized tissue covering the root of the tooth).
On an X-ray, the dentigerous cyst appears as a well-defined radiolucent area around the crown of the impacted tooth. It’s important to note that dentigerous cysts often don’t cause any symptoms and are found incidentally. However, if they grow in size or become infected, they can lead to swelling, pain, or displacement of nearby teeth.
Treatment for dentigerous cysts usually involves surgical removal or marsupialization, which is a procedure that creates a surgical opening to allow drainage and shrinkage of the cyst. This is done to prevent complications and facilitate the eruption of the impacted tooth.
Overall, understanding the clinical and histological features of dentigerous cysts is crucial for diagnosing and managing these conditions effectively as a dental student.
