- Length- 12cm
- Width- 3.5cm in the upper portion and the lower portion of the pharynx is the narrowest portion of the GIT after the appendix.

Boundaries-
- Superiorly- Base of the Skull
- Inferiorly- Oesophagus
- Posteriorly- Pre vertebral fascia
- Anteriorly- Nasal cavity, Oral cavity, Larynx
- Laterally- Medial pterygoid plate, Pterygomandibular raphe, Mandible, Tongue, Larynx, Thyroid and Cricoid cartilages, Middle ear cavity, Styloid process, CCA, ICA, ECA.
The pharynx is divided into 3 parts-
1.) Nasopharynx
- Passage of air.
- Located behind the nose.
- Extends from the base of the skull to the soft palate.
- Lines by ciliated columnar epithelium.
- Supplied by pharyngeal branch of pterygopalatine ganglion.
2.) Oropharynx
- Passage of food and air.
- Extends from the soft palate to the epiglottis.
- Lined by stratified squamous non keratinised epithelium.
- Supplied by IX and X cranial nerves.
3.) Laryngopharynx
- Passage of food.
- Extends from the epiglottis to the cricoid cartilage.
- Lined by stratified squamous non keratinised epithelium.
- Supplied by the IX and X cranial nerves.

Muscles of the pharynx-
1.) Longitudinal Muscles
- Stylopharyngeus
- Palatopharyngeus – Makes the Passavant’s ridge
- Salpingopharyngeus
2.) Circular Muscles
- Superior constrictor
- Middle constrictor
- Inferior constrictor

The space between the base of the skull and the superior constrictor is called as the pharyngobasilar fascia or the SINUS OF MORGAGNI.

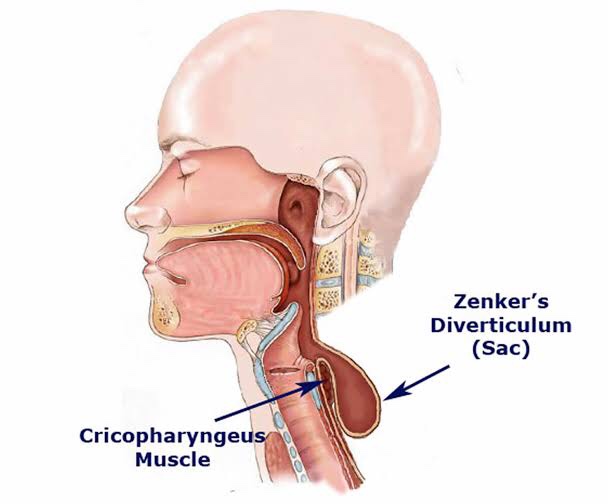
Killian’s dehiscence-
The inferior constrictor muscle splits into two- the stylopharyngeus and the cricopharyngeus.
The potential space between these two is called as the Killian’s dehiscence.

Incoordination in the area will lead to – ZENKER’S DIVERTICULUM.