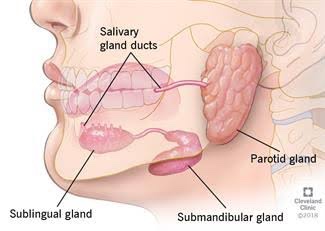
• Swellings at the angle of Mandible include: ✍🏻👇🏻
🔅Congenital disease
• Branchial Cleft Cyst
🔅Neoplasm
(i) Benign
- Hemangioma
- Lymphangioma, Cystic hygroma
- Pleomorphic adenoma (mixed tumor)
- Warthin tumor
- Neurofibroma
- Angiolipoma
- Adenoma
- Hamartoma
- Lipoma
- Oncocytoma
(ii) Malignant
- Mucoepidermoid carcinoma
- Squamous cell carcinoma
- Adenoid cystic carcinoma
- Acinic cell carcinoma
- Adenocarcinoma
- Rhabdomyosarcoma
- Lymphoma, leukemia
- Metastatic adenopathy
🔅Inflammation/Infection
- Parotitis
- Parotid Abscess
- Tuberculosis
- Sarcoidosis
- Sjögren disease
- HIV
Detailed View🔍
1) Branchial Cleft Cyst:

- Failure of involution of clefts and pouches lead to cysts, fistulas or sinus tracts.
- Its a painless fluctuant swelling
- First branchial cleft cysts are rare usually located at parotid gland or periparotid region.
- Second branchial cleft cyst – Type II are the most common
- Typically, second branchial cleft cysts present as a rounded swelling just below the angle of mandible, anterior to the sternocleidomastoid

2) Hemangiomas:
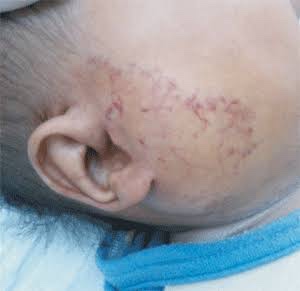
3) Lymphangiomas

4) Pleomorphic Adenoma:

5) Warthin Tumor:
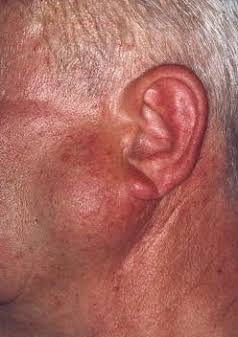
6) Parotitis & Parotid Abscess:
- Most common in children
- Mumps is the most common viral cause of parotitis
- The condition manifests tender swelling at the angle of Mandible
- Sialadenitis is most commonly due to bacterial infections caused by Staphylococcus aureus.
- Premature neonates and immunosuppressed individuals are affected.
• Swellings in the floor of Mouth: 👇🏻✍🏻
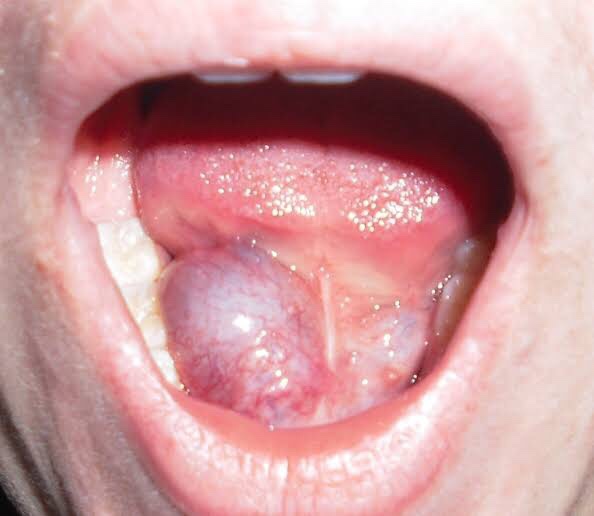
- Ranula – a type of mucocele found on the floor of the mouth. Present as a swelling of connective tissue consisting of collected Mucin from a ruptured salivary gland by local trauma.
- Swellings in the floor of the mouth are more likely to arise from structures above the Mylohyoid muscle. The commonest swellings in the floor of the mouth are denture induced hyperplasia & salivary calculus.
- Swellings in the floor of the mouth may inhibit swallowing & speech.
- Mandibular tori produce bony hard swelling lingual to the lower premolars.

Differential diagnosis of swellings of the floor of the mouth or neck (Jham et al., 2007): https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Differential-diagnosis-of-swellings-of-the-floor-of-the-mouth-or-neck-Jham-et-al-2007_tbl1_287206404
• Swellings on the Palate: 👇🏻✍🏻

- Torus palatinus is an intrinsic bone lesion whereas a dental abscess pointing on the palate (usually from the palatal roots of the 1st & 2nd maxillary molars or from upper lateral incisors) is extrinsic.
- Salivary neoplasms
- Invasive carcinoma from the maxillary sinus may produce a palatal swelling.
- Kaposi’s sarcoma, typical of HIV/AIDS may also present as lump on palate.
- Paget’s disease.
Differential diagnosis of palatal swellings: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Differential-diagnosis-of-palatal-swellings_tbl1_221967546
Dentowesome|@drmehnaz🖊
Image source: Google.com