
Zone I: Zone of fatty degeneration of odontoblast process
Zone 2: Zone of dentinal sclerosis characterized by deposition of cal- cium salts in dentinal tubules
Zone 3: Zone of decalcification of dentin, a narrow zone, preceding bacterial invasion
Zone 4: Zone of bacterial invasion of decalcified but intact dentin Zone 5: Zone of decomposed dentin
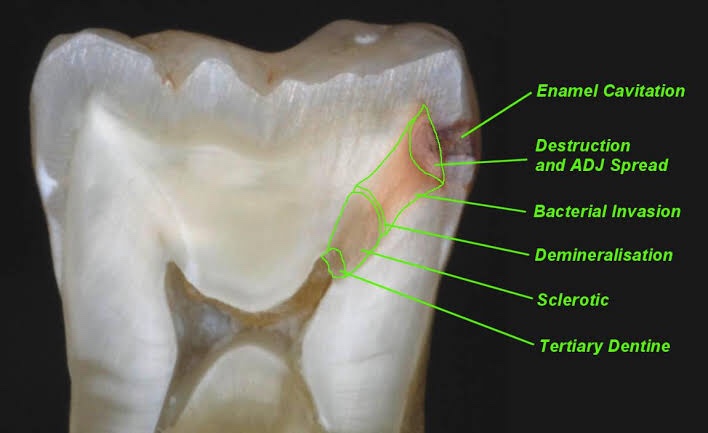
Early dentinal caries
Fatty degeneration of odontob/ast process
>Disposition of fat globules – precedes early sclerotic changes >Special stains – Sudan red
>Significance-
1.Fat contributes to impermeability
2.Predisposing factor for dental sclerosis
Sclerotic dentin
>Reaction of vital pulp – calcification of dentinal tubules (DT)
>Seals off DT from further penetration of microorganisms
>Minimal in rapidly advancing caries
>Prominent in slow caries
>Sclerotic dentin – appear white in transmitted light
Decalcification of dentinal tubules
>Above dentinal sclerosis – zone of decalcification
>Occurs in advance of bacterial invasion of DT
>Pioneer bacteria
>The initial decalcification – only the walls of DT
>Study of tubules- pure form of microorganisms
Zone of microbial invasion
>Proteolytic organisms – predominantly in deeper layers Acidogenic microorganisms – more in early caries
>Supporting the hypothesis that initiation and progression are two distinct processes and must be differentiated
Advanced dentinal caries
>Decalcification of the walls of DT – confluence
>Thickening of sheath of Neumann – along its course • Increase in the diameter of DT – microorganisms
>Focal coalescence of adjacent tubules and ovoid area of destruction- liquefaction foci
>Acidogenic organisms – initial decalcification
>Proteolytic organisms – matrix destruction
>Multiple areas of destruction>Necrotic mass of dentin (leathery consistency)
>Formation of transverse cleftsExtend at right angles to DT and parallel contour line
>Peeling away of carious dentin
REFERENCE- Shafers textbook of oral pathology 8th edition
