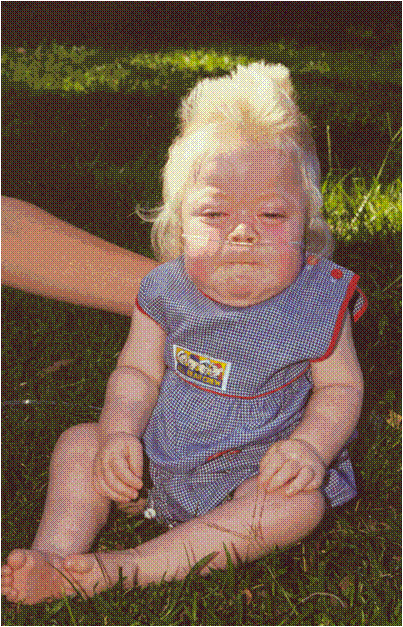
Features of Mucopolysaccharidosis Syndrome-HURLER’S SYNDROME(MPS I H, Gargoylism):
- Type- I-H
- Eponym-Hurler
- Inheritance-Autosomal Ressesive
- Enzyme Deficiency- α-L-Iduronidase
- Stored Substrate- HS- heparan sulfate and DS-dermatan sulfate
- Clinical Features – Appears in infancy; cloudy corneas, growth retardation, reduced intelligence, coronary artery disease; rarely live 10 years.
-
Chromosomal abnormality on chromosome arm 4p16.3
-
Characterized by increased levels of MPS in urine.
Clinical features:-
- Becomes apparent in first 2 years of life, life expectancy of 6-10 yrs.
- Head appears large; facial features quite typical.
- Prominent forehead
- Broad saddle nose & wide nostrils
- Puffy eyelids with coarse bushy eyebrows
- Hypertelorism
- Thick lips
- Large tongue with open mouth
- Nasal congestion & noisy breathing.
- Progressive corneal clouding classic manifestation.
- Hepatosplenomegaly, results in protrudent abdomen
- Short neck & spinal abnormalities typical.
- Flexion contractures result in “claw hand”.
- Dwarfed, mentally retarded individuals.
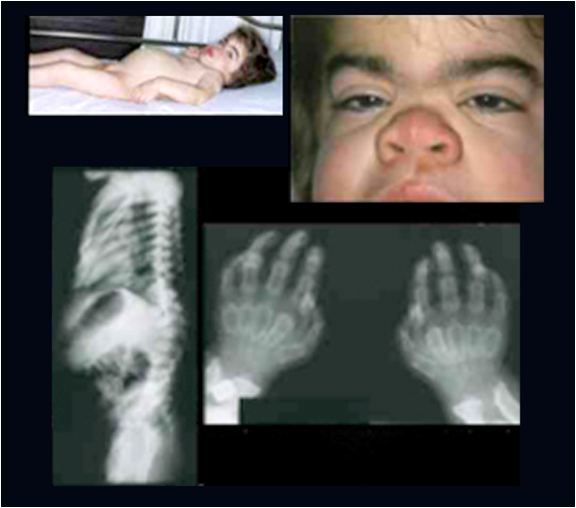
Histologic features:-
- Excessive accumulation of intracellular mucopolysaccarides in many tissues & organs.
- Accumulation of dermatan & heparan sulfate in cells of mononuclear – phogocyte system, fibroblasts & endothelial cells.
- Affected cells are swollen, have clear cytoplasm resulting from accumulation of PAS +ve material in engorged, vacuolated lysosomes.
- Involved fibroblasts assume appearance of ‘clear’ or ‘gargoyle’ cells.
- ‘Hurler cells’ relatively large with metachromatically staining cytoplasm with crescent shaped nuclei.
- Cells not identified with normal H/E stain but with toluidine blue or Alcian blue/ aldehyde fuchsin stains.
- Should be differentiated from mast cells.
Oral Manifestations:-

- Shortening and broadening of the mandible with prominent gonions.
- Localized areas of bone destruction in the jaws.
- Teeth may be small and widely spaced.
- Gingival hyperplasia has been repeatedly described in
patients with Hurler syndrome. - the tongue is also characteristically enlarged.
Laboratory findings:-
- Elevated levels of mucopolysaccharides in urine.
- Metachromatic granules or ‘Reily bodies’ often demonstrated in cytoplasm of circulating lymphocytes.
Treatment:-
- Because of multisystemic involvement in patients with mucopolysaccharidosis type I (MPS I), treatment is multidisciplinary and encompasses both the curative and palliative elements.
-
Corrective surgery may be necessary for patients with mucopolysaccharidosis type I (MPS I) who have joint contractures or foot and hand deformities.
-
Corneal transplants may be required if vision problems become severe.
-
Given the numerous mutations at this genetic locus, identification of which allele or alleles are involved requires referral to medical geneticists for diagnosis and genetic counseling.
References :-
1.SHAFERS’s 8th edition
2.NEVIELLE’S 3rd edition