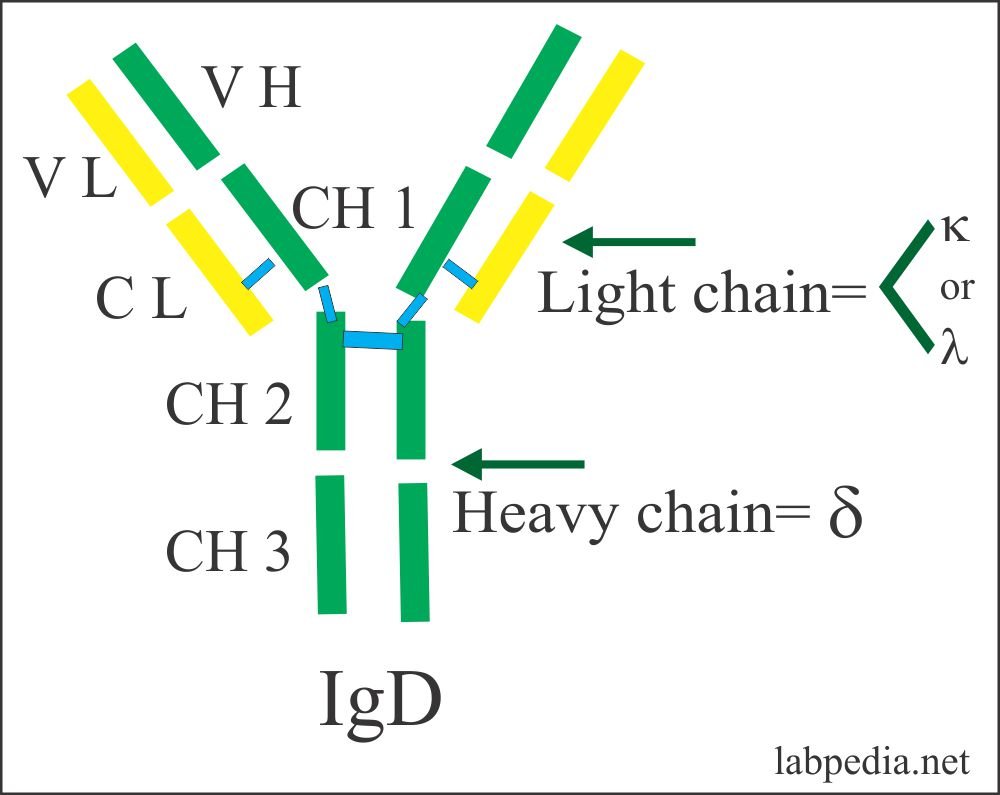
1. Immunoglobulin D( IgD)
(i) IgD resembles IgG structurally.
(ii) IgD is present in a concentration of 3 mg per 100 ml in serum. It is mostly intravascular in distribution.
(iii) Molecular weight is 180000 (7S monomer).
(iv) Half life is about three days.
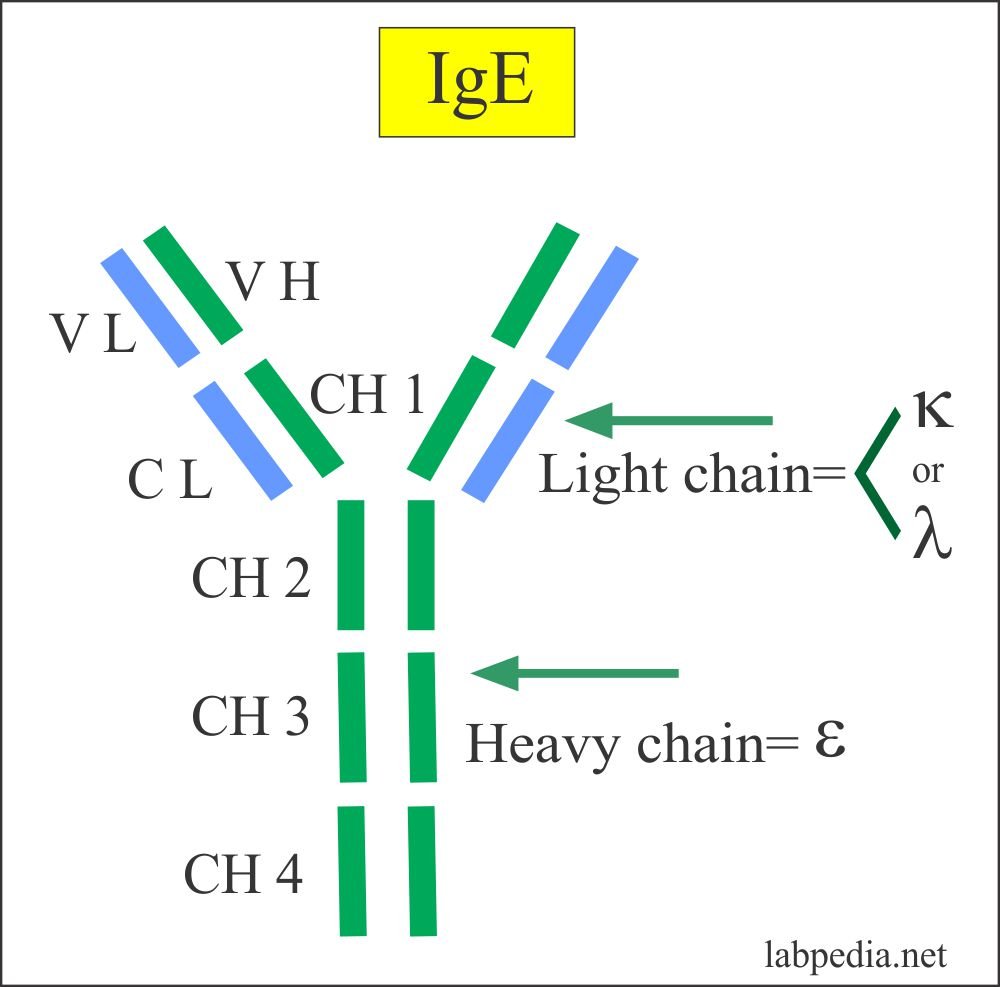
2. Immunoglobulin E (IgE)
(i) IgE is mainly produced in the linings of respiratory and intestinal tracts. It is mostly distributed extravascularly.
(ii) It is also referred to as reagins.
(iii) Molecular weight is 190000 (8 S molecule).
(iv) Half life is 2-3 days.
(v) It resembles IgG in structure.
(vi) It is heat labile whereas other immuno-globulins are heat stable.
(vii) It has affinity for surface of tissue cells, particularly mast cells of the same species (homocytotropism).
(viii) IgE mediates type I hypersensitivity (atopic) reaction. This is responsible for asthma, hay fever and eczema.
(ix) It cannot cross the placental barrier.
(x) IgE is responsible for anaphylactic type of reaction.
Source- textbook of microbiology for dental students c p baveja and Google images
