Written by : Dr. Urusa I Inamdar
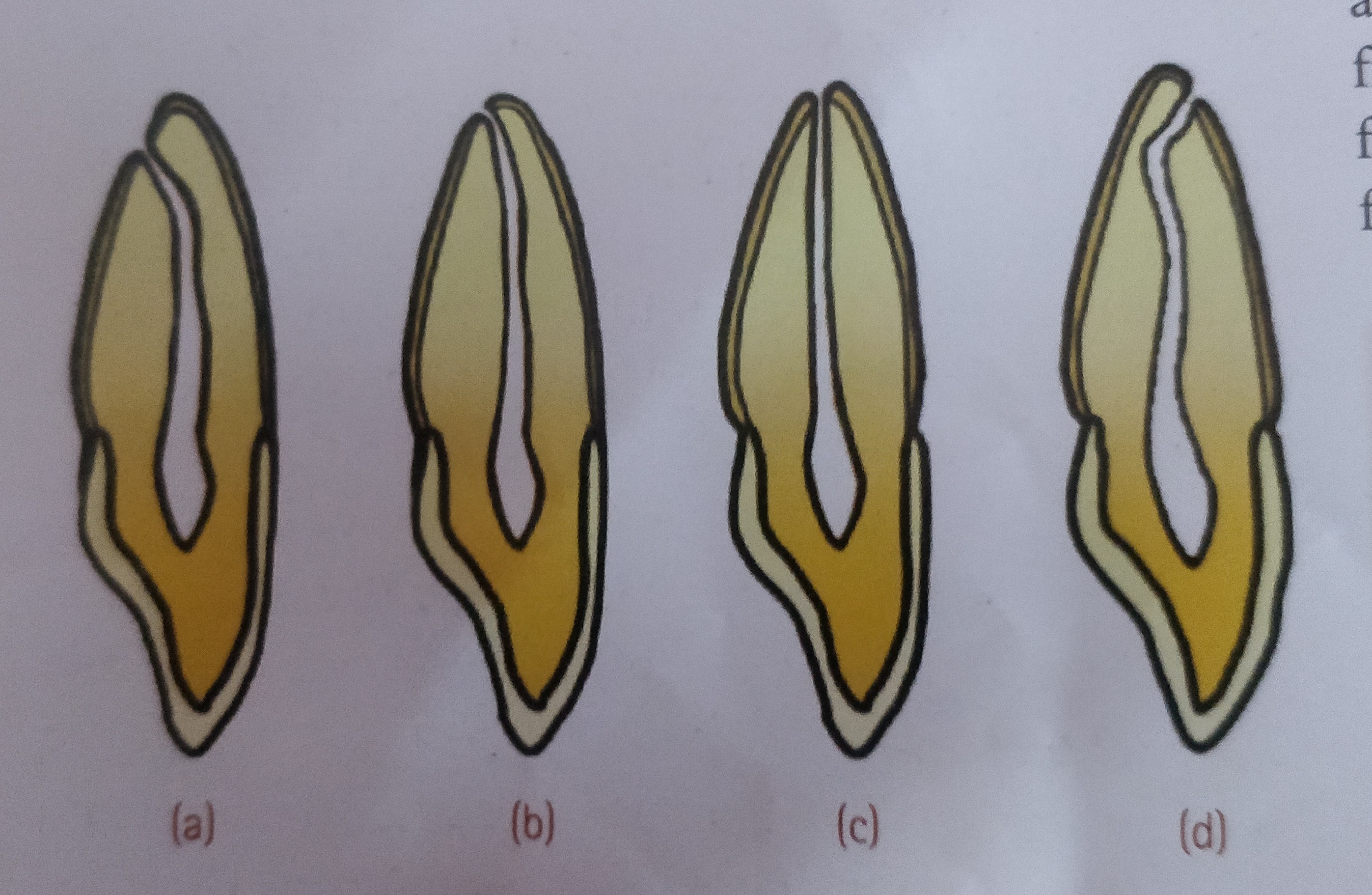
ISTHMUS:
Ribbon shaped or thin connecting structure between two root canals.
Kim et al. have classified the isthmus into following categories:
- Type I : Faint communication between two canals.
- Type II : Complete isthmus with a definite connection between two canals.
- Type III : A complete but very short isthmus between two canals.
- Type IV : Complete or incomplete isthmus between three or more canals.
- Type V : Two or three canal openings without visible connections.

Apical Foramen:
In young , incompletely developed teeth , the apical foramen is funnel shaped , with the wider portion extending outward . The mouth of the funnel is filled with periodontal tissue , which is later replaced by dentin and cementum.
As the root develops , the apical foramen becomes narrower .
It is not necessary to shape , clean , or fill root canals to their anatomic apices , but rather to the cementodentinal junction , which usually lies within the canal just short of the apex .
The apical foramen is not always the most constricted portion of the root canal. Constrictions can and do occur before the extremity of the root ks reached. Apical constrictions are found 0.5-1.0 mm away from the root apex.
The apical foramen is not always located in the centre of the root apex . It may exit on the mesial , distal , labial or lingual surface of the root , usually slightly eccentrically.
In few cases , the apical foramen has been found as much as 2-3 mm away from the anatomic apex.
The root canal obturation should end approximately 0.5-1.0 mm short of the anatomic root apex .
Lateral canals and Accessory foramina:
The periodontal vessels curve around the root apex of a developing tooth and often become entrapped in Hertwig’s epithelial root sheath , resulting in the formation of lateral canals and accesory foramina during calcification .This phenomenon frequently occurs in the apical third of the root .
Lateral canals may also occur in the area of bifurcation or trifurcation of multirooted teeth.
With increasing age , the accesory foramina diminish in number because of calcification of their contained soft tissue.
Reference:
- Dental notes
- Grossman’s Endodontic Practice
