By Dr Musaddika Shaikh Dentowesome @drmusaddikashaikh
Haemoglobin :- It is protein found in red blood cells that carries oxygen in blood and gives blood red colour
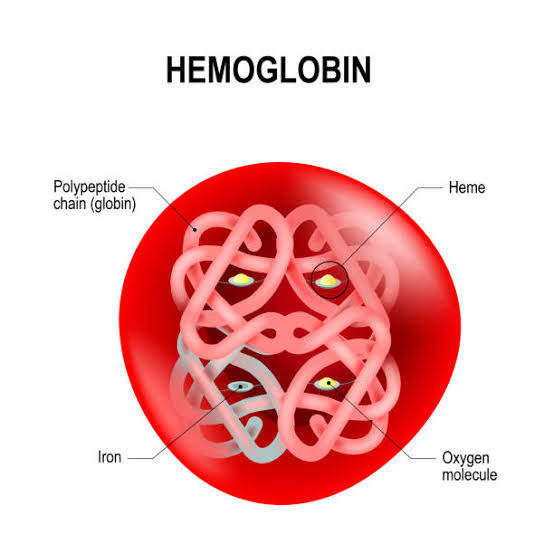
Structure :-
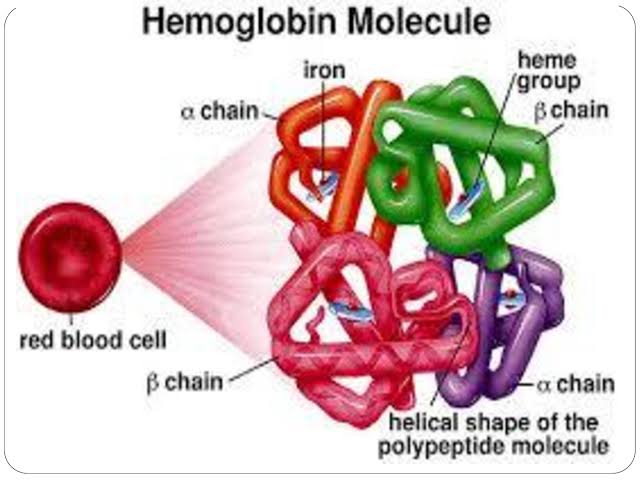
- Heame is porphin called iron protoporphyrine 9th
- Iron is ferrous form which combine with oxygen
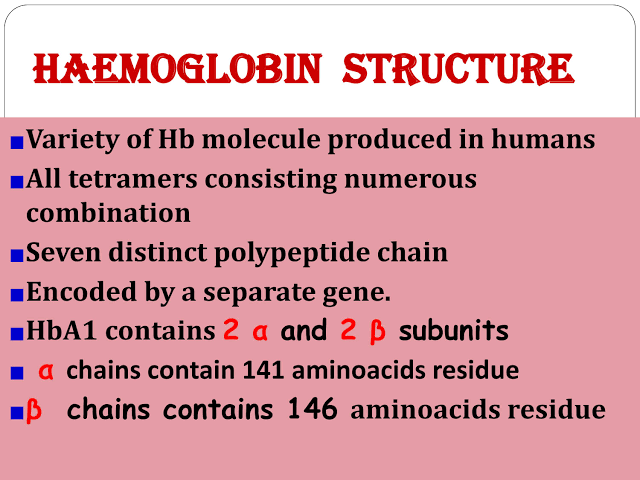
- Globin :- It is protein 4 polypeptide chain of alpha and beta which contains Mb amino acid each polypeptide attach are heam group
- Hemoglobin react with oxygen in 0.01 sec
- Molecular weight of hemoglobin 64,458 g/mol
- Oxyheamoglobin :- hemoglobin affinity for oxygen by Ph, temperature, concentration
- Carbaamino-heamoglobin :- carbon dioxide react with heamoglobin to form carbaamino-heamoglobin
- De-oxegenated heamoglobin :- oxygen removed from heamoglobin
- Carboxy-heamoglobin :- carba+monooxide reacts with heamoglobin
- Metheamoglobin :- reduced or oxygenated heamoglobin exposed to drugs is oxidised ferrous to ferric acid metheamoglobin
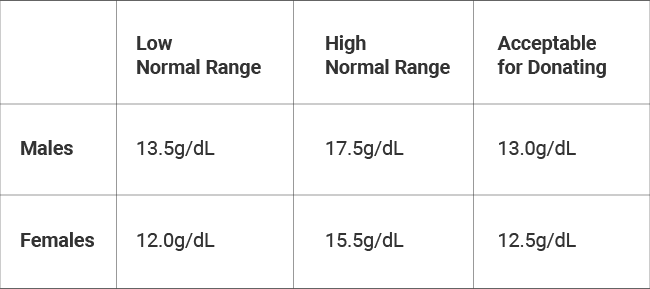
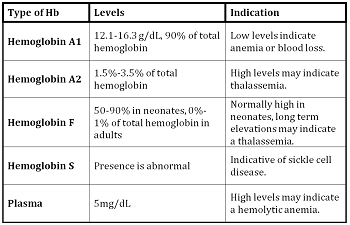
Normal values of heamoglobin :-
Types :-
Synthesis :-
- Role of protein :- Low protein reduces heamoglobin
- Role of minerals :- It helps in formation of heame
- Role of Cu :- It promotes absorption, mobilization and utilisation of iron
- Role of cobalt :- It enhances absorption in GI tract
- Role of vitamin :- Vit C,Vit B12,folic acid helps in synthesis of nucleic acid
Functions :-
- Transport of oxygen from lungs to tissues
- Transport of carbon dioxide from tissues to lungs
- Act as acid balance buffer
- It gives red colour to blood
- Genetic resistance to malaria etc
- Source of physiological active catabolites
Reference :- Book Human physiology for bds A.K Jain Google website study.com,learnpick.in, redcrossblood.org
