By Dr Musaddika Shaikh Dentowesome @drmusaddikashaikh
Defination :-
Arrest or prevention of bleeding by physiological process is called hemostasis
Factors :-
- F1. Fibrinogen
- F2. Prothombin
- F3. Thromboplastin
- F4. Calcium
- F5. Labile
- F6. Not known
- F7. Stable
- F8. Antihaemophillic
- F9. Christmas
- F10. Stuart
- F11. Plasma thrombin antecedent
- F12. Hegman
- F13. Fibrin stabilizing
Mechanism :-
Injury vessel walls – Formation of clot – Seal off damage blood vessel – Prevent blood loss
Series of event :-
Constriction of blood of blood vessel – Temporary haemostatic plug by platelet – haemostasis
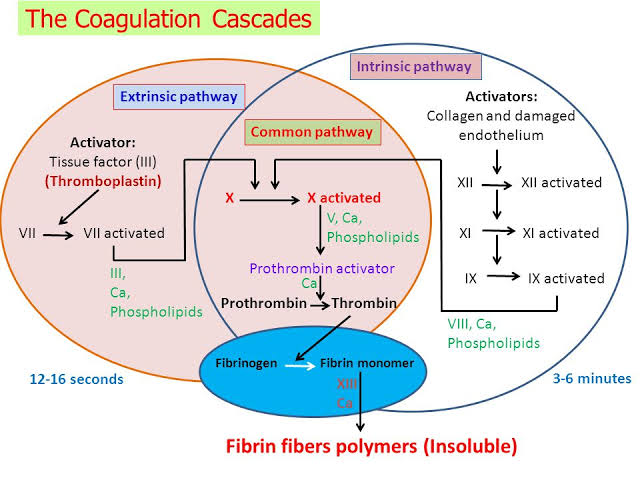
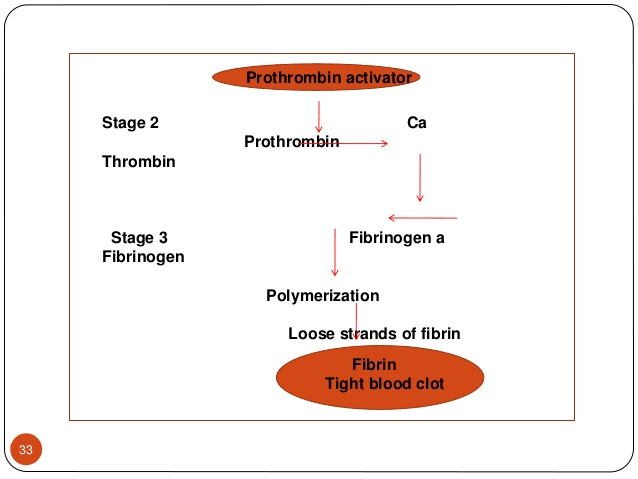
Factors responsible for coagulation :-
- Fibrin formation :- by soluble plasma fibrinogen due to f3,f4,f6
- Thrombin formation :- inactive prothrombin into thrombin by prothrombin activator
- Prothrombin activator :- by extrinsic and intrinsic factor
- Clot retraction :- conversion of prothrombin to thrombin within 15-30min
- Role of Calcium :- it act as catalyst in cascade reaction
Why does not blood clot in circulation? Smoothness of endothelial line prevents adhesion. Negatively charged particles repells cloting factor. Natural anticoagulant eg :- heparin in circulation
Reference :- Book Human physiology for bds A.K Jain Google website slide player
