
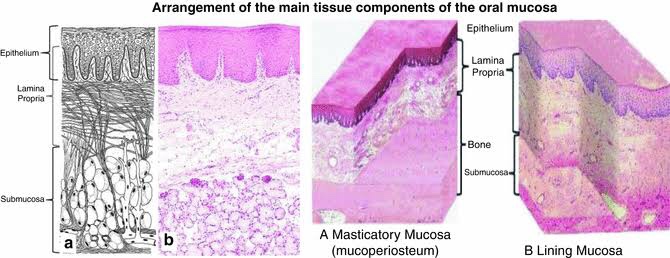
🔹Classification:
3 major types:
- Masticatory Mucosa (Gingiva & hard palate)
- Lining or reflecting Mucosa (Lip, Cheek, floor of mouth)
- Specialized Mucosa (Dorsum of tongue, taste buds)
🔹Functions:
- Defence: Oral Mucosa is impermeable to bacterial toxins. Also secretes antibodies.
- Lubrication: Secretion of salivary glands keep the oral cavity moist which helps in speech and mastication.
- Sensory: Sensitive to touch, pressure, pain & temperature.
- Protection: Protects deeper tissues from mechanical forces resulting from mastication & from abrasive nature of food stuff.
🔹Keratinized Epithelium:
➡️ Contains 4 layers starting from the bottom:
▪️Stratum Basale:
- Single layer of cuboidal cells
- They synthesize DNA & undergo Mitosis
▪️Stratum Spinosum:
- Layer is irregularly polyhedral & larger than basal cells
▪️Stratum Granulosum:
- Layer contains flatter & wider cells
- Larger than spinous cells
▪️Stratum Corneum:
- Made up of keratinized squamous which are larger & flatter than granular cells
🔹Keratinized Areas:
- Masticatory Mucosa
- Vermilion border of lip
🔹Non-Keratinized Areas:
- Lining Mucosa
- Specialized Mucosa
References: Orban’s Oral Histology
Dentowesome 2020 @dr.mehnaz
