Definitions
Cooperative binding
- Describes unique interactions between heme groups in hemoglobin
- Small movement of heme group propagates through hemoglobin’s 3D structure
HEMOGLOBIN STRUCTURE
R-form (relaxed)
- Alpha-alpha interactions: weak ionic and H-bonds form salt bridges
- Beta-beta interactions: no interactions; move apart upon oxygenation
- Alpha-beta dimers: strong hydrophobic interactions within each dimer
T-form (tense)
- 3D structure changes between oxygenated and deoxygenated states
HEME SITE
T-form (tense)
- Heme site: when O2 leaves, iron center moves out of porphyrin plane & proximal histidine moves away from iron center
- Small movement in heme group makes O2 binding unfavorable
SALT BRIDGES
- Salt bridges break and reform upon oxygen binding –> peptide wiggle-room
- Alpha chain salt bridges:
– Alpha1: arginine carboxy terminus (-) and arginine side group (+)
– Alpha2: lysine (+) and aspartate (-) - Salt bridges regulate cooperativity: iron centers move into porphyrin planes
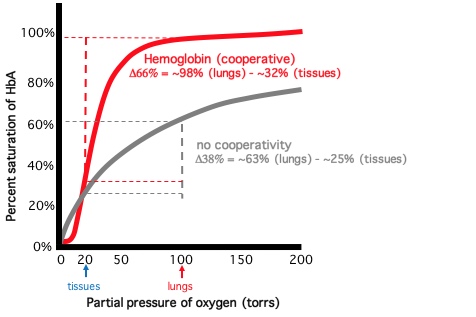
DISSOCIATION CURVE
- % oxygen saturation vs. oxygen partial pressure (torr)
- Cooperative binding produces sigmoidal binding curve
- After hemoglobin reaches 50% saturation: saturation increases rapidly (steepest point of curve)
- Hemoglobin O2 affinity rapidly increases at half saturation
