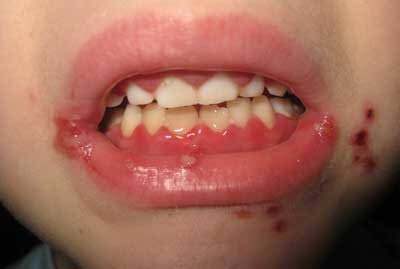
Oral disease transmitted by droplet spread/contact with the lesion.
🔹 Clinical Features:
• Incidence – Children & young adults. <6 months of age: Rare (Due to presence of circulating Ab. in the infant derived from the mother)
• Clinical Manifestations:
- Fever
- Irritability
- Headache
- Pain upon swallowing
- Regional lymphadenopathy
➡️ Within a few days mouth becomes painful with gingiva being inflamed, edematous & erythmatous.
➡️ Involvement of lips, tongue, buccal mucosa, palate, pharynx & tonsils.
Yellowish fluid-filled vesicles develop
⬇️
Rupture
⬇️
Shallow, ragged, extremely painful ulcers (grey membrane, erythmatous halo)
➡️ Ulcers heal within 7-14 days with No scar formation
➡️ Isolation of HSV-1 from these lesions after onset: (2 – 6 days)
➡️ Trigeminal for HSV-1 (Virus remain latent until reactivated in the ganglia)
➡️ Viral DNA to Host DNA – lifelong infection
➡️ Incubation Period: 2-20 days
🔹 Histological Features:
- Herpetic vesicle is an intraepithelial blister filled with fluid.
- The infected cells are swollen with pale cytoplasm & large vesicular Nuclei (Ballooning degeneration)
- Lipschutz bodies: Intranuclear inclusion bodies. Eosinophilic, Ovoid, homogenous structure within the nucleus. They displace the nucleolus & nuclear cytoplasm peripherally ➡️ Peri-inclusion halo.
- Giant cells seen
- Connective tissue shows inflammatory cells
- Vesicles rupture – exudates of fibrin, PMN, degenerative cells
- Healing – peripheral epithelial proliferation
🔹 Treatment:
➡️ While most children will be asymptomatic, diagnosis of children with symptoms is made based on clinical presentation of erythematous gingiva, mucosal hemorrhages, and clusters of small erupted vesicles throughout the mouth.
➡️ The condition is highly contagious and complications range from indolent cold sores to dehydration and even life-threatening encephalitis.
➡️ Symptomatic relief primarily involves pain management and oral fluids to prevent dehydration until the viral infection subsides.
➡️ Acyclovir is a well established antiviral drug used effectively for the treatment of herpes simplex infections, chickenpox (shortened fever time), and shingles. It is also used frequently for children with immunodeficiency.
➡️ The current recommended dose of oral acyclovir is 40 to 80 mg/kg a day, divided in 3 or 4 doses, for 7 days. Caregivers should be aware of potential adverse effects of acyclovir such as headache, malaise, and vomiting.
Dr. Mehnaz Memon🖊
References: Shafers Textbook Of Oral Pathology 7Ed, Internet
