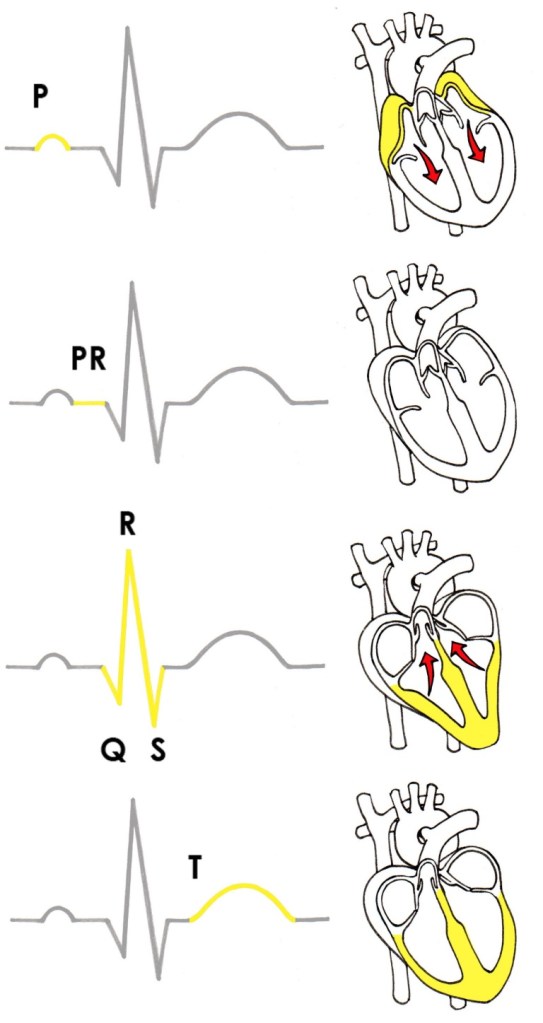
P Wave
•Positive wave
• Shape is up rounded deflection
• Cause: Depolarisation of atrial musculature.
• Duration: 0.1 sec
• Intensity: 0.1-0.12 mV
• Represents functional activity of atria.
Clinical Aspects:
1 Mitral stenosis: left atrium is hypertrophied and P wave is larger and prolonged.
2 Tricuspid stenosis: Right atrium is hypertrophied and P wave is taller but there is no change (normal) duration.
3 Atrial fibrillation: P wave disappears and is replaced by fine irregular oscillations.
4 Ectopic Pacemaker: (reverse) The impulses are sent from AV node to SA node.
QRS COMPLEX
• Q wave is often absent.
• Cause: Ventricular Depolarisation.
• Duration: 0.08 sec ( less than P wave)
• Intensity: 0.1 mV to 0.2 mV ( amplitude is more)
• R wave is 1 mV
• S wave is 0.4 mV
• Total Intensity is 1.5 mV to 1.6 mV
Clinical Aspects
1 Deep Q wave: more than 0.2 mV. This is seen Myocardial Infarction.
2 Tall R wave: more than 0.1 mV. This is seen in ventricular hypertrophy.
3 Low Voltage QRS Complex: This is related to hormones and pericardial fluid. Hypothyroidism and Pericardial fluid around the heart.
4 QRS COMPLEX: Prolonged in bundle branch block.
T wave
• Cause: Ventricular Repolarization.
• It’s positive wave because the direction of Ventricular repolarization is opposite to depolarization.
• Duration: 0.27
• Intensity: 0.3 mV
Clinical Aspects
1 Flattened T wave: old age.
2 Height increases: during exercise.
3 Inverted T wave: this is seen in myocardial infarction.
4 Tall and peaked T wave: Hyperkalaemia.
U wave
• Positive round wave
• Repolarization of papillary muscled
• Duration: 0.08 sec
• Intensity: 0.2 mV
• Rarely seen
• Prominent in hypokalaemia.
P R interval
• Onset of P wave to onset of QRS complex (PQ interval)
• Represents AV conduction time.
• Duration: 0.12 to 0.21 sec
Clinical Aspects
1 Prolonged PR interval: AV conduction block.
J Point
• The meeting point of QRS complex with ST segment.
• It represents the end of Depolarisation and beginning of repolarization.
• At this point, no current flows around heart.
– Written by Anisha Valli
